Encoded Archival Description Tag Library Version EAD3
Prepared and maintained by the Technical Subcommittee for Encoded Archival Description of the Society of American Archivists

Table of Contents
abbr actuate align althead altrender approximate arcrole audience base calendar certainty char charoff colname colnum cols colsep colwidth containerid coordinatesystem countrycode countryencoding coverage daotype datechar dateencoding dsctype encodinganalog entityref era expan frame href id identifier instanceurl label lang langcode langencoding lastdatetimeverified level linkrole linktitle listtype localtype mark morerows nameend namest normal notafter notbefore numeration otherdaotype otherdsctype otherlevel otherphysdescstructuredtype otherrelationtype parallel parent pgwide physdescstructuredtype relatedencoding relationtype relator render repositorycode repositoryencoding rowsep rules script scriptcode scriptencoding show source standarddate standarddatetime target transliteration unit unitdatetype valign value xpointer
abbr abstract accessrestrict accruals acqinfo address addressline agencycode agencyname agent agenttype altformavail appraisal archdesc archref arrangement author bibliography bibref bioghist blockquote c c01 c02 c03 c04 c05 c06 c07 c08 c09 c10 c11 c12 chronitem chronitemset chronlist citation colspec container control controlaccess controlnote conventiondeclaration corpname custodhist dao daoset date daterange dateset datesingle defitem descriptivenote did didnote dimensions dsc ead edition editionstmt emph entry event eventdatetime eventdescription eventtype expan famname filedesc fileplan footnote foreign fromdate function genreform geogname geographiccoordinates head head01 head02 head03 index indexentry item label langmaterial language languagedeclaration languageset lb legalstatus list listhead localcontrol localtypedeclaration maintenanceagency maintenanceevent maintenancehistory maintenancestatus materialspec name namegrp notestmt num objectxmlwrap occupation odd originalsloc origination otheragencycode otherfindaid otherrecordid p part persname physdesc physdescset physdescstructured physfacet physloc phystech prefercite processinfo ptr ptrgrp publicationstatus publicationstmt publisher quantity quote recordid ref relatedmaterial relation relationentry relations repository representation row scopecontent script separatedmaterial seriesstmt source sourceentry sources sponsor subject subtitle table tbody term tgroup thead title titleproper titlestmt todate unitdate unitdatestructured unitid unittitle unittype userestrict
Encoded Archival Description Tag Library, Version EAD3 [toc]
This tag library represents version EAD3 of the Encoded Archival Description
schemas, released in August 2015. It supersedes the Version 2002 tag library
published in 2002.
The SAA Technical Subcommittee for Encoded Archival Description, in partnership
with the SAA Schema Development Team, is responsible for updating and editing the
EAD schemas and tag library.
The Network Development and MARC Standards Office of the Library of Congress
serves as the host for online EAD documentation, including storage and delivery of
electronic files and maintenance of the EAD web site, located at http://www.loc.gov/ead/.
Available from:
Society of American Archivists
17 North State Street, Suite 1425
Chicago, IL 60602-3315
USA
312-606-0722
Fax: 312-606-0728
[email protected]
www.archivists.org
Society of American Archivists
17 North State Street, Suite 1425
Chicago, IL 60602-3315
USA
312-606-0722
Fax: 312-606-0728
[email protected]
www.archivists.org
© The Society of American Archivists, 2015.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
License (CC BY 4.0). See http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Some rights reserved. No
part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical or photocopying,
recording, or otherwise without attribution.
ISBN 1-931666-89-X
Preface [toc]
Encoded Archival Description (EAD) is the international metadata transmission
standard for hierarchical descriptions of archival records. Developed by the EAD
Working Group of the Society of American Archivists and first published in 1998,
EAD is an Extensible Markup Language (XML) format used by archivists around the
globe. A second version with greater international alignment, EAD 2002, was
released as a DTD in 2002 and in 2007 as Relax NG and W3C schemas. The development
of EAD made it possible to create electronic finding aids within a specifically
archival data structure compliant with General International Standard Archival
Description (ISAD(G)). This innovation was a crucial impetus behind the swift
migration of archival description to the internet, the acceptance of national
archival descriptive content standards like Describing Archives: A Content
Standard (DACS), and the emergence of a professional consensus that archival
description existed to be shared widely and shared well.
This new version of Encoded Archival Description – EAD3 – exists thanks to the
efforts and support of many people, but it exists because of the many archivists
and repositories around the world that saw the utility of EAD, used it in diverse
and inspiring ways, and continue to recognize many ways in which it might work
better.
In the years between the release of EAD 2002 and 2010, when the revision process
that led to EAD3 began, the technological landscape surrounding archival
description evolved enormously. Collection management systems, such as the
Archivists’ Toolkit, Archon, and ICA-AtoM, offered the robust advantages of
modelling descriptive information in relational databases, but exposed the
difficulty of adapting the EAD document model in data-centric applications. Linked
Open Data emerged as a viable methodology for creating a semantically meaningful
Web, for which EAD was poorly prepared. New and closely related metadata
transmission standards were developed, most notably Encoded Archival Context –
Corporate bodies, Persons, and Families (EAC-CPF), opening new frontiers in
archival metadata. Finally, over a decade of working with EAD gave archivists a
general sense that it was too complex, too forgiving, and too flexible for its own
good.
In 2010, following an update to its by-laws concerning standards maintenance, the
SAA Standards Committee charged a new Technical Subcommittee for Encoded Archival
Description (TS-EAD) to oversee the maintenance of the standard. Recognizing that
EAD needed an update, its charge instructed TS-EAD to complete a revision of the
standard within five years.
TS-EAD completed the revision of EAD with the help of the SAA Schema Development
Team and with many contributions, large and small, from the international EAD
community. EAD3 is the result of four public comment periods, countless feedback,
three working meetings, numerous conference calls, regular presentations to the
EAD Roundtable, and lots of careful analysis, spirited discussion, and hard-won
compromise. Notable milestones in the revision process include the initial comment
period, which shaped our early agenda; a three-day TS-EAD working meeting at Yale
University’s Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, which established a clear
direction; and the alpha, beta, and gamma schema releases, which gave the EAD
community concrete examples to test and critique.
Early in the revision process TS-EAD published four points of emphasis to guide us
as we weighed the benefits of changes to EAD.
Achieving greater conceptual and semantic consistency in the use of
EAD.
Exploring mechanisms whereby EAD-encoded information might more seamlessly and effectively connect with, exchange, or incorporate data maintained according to other protocols.
Improving the functionality of EAD for representing descriptive information created in international and particularly in multilingual environments.
Being mindful that a new version will affect current users.
Exploring mechanisms whereby EAD-encoded information might more seamlessly and effectively connect with, exchange, or incorporate data maintained according to other protocols.
Improving the functionality of EAD for representing descriptive information created in international and particularly in multilingual environments.
Being mindful that a new version will affect current users.
All of the changes made in EAD3 can be seen in the context of these four points.
Throughout the revision process, the most difficult decisions concerned proposals
that highlighted tensions between them, especially between making EAD more
consistent and aligned to other standards and mitigating impact on current
users.
TS-EAD’s decision-making process focused on detailed analysis and
consensus-building within the committee. As we received proposals from the
community or fellow committee members, individuals or small groups did additional
work to better understand the request, clarify the specific impact on the schema,
and make recommendations to the committee. Many issues were revisited multiple
times as we collectively came to understand better our goals and their impact.
Although healthy differences of opinion persisted throughout the revision process,
ultimately only one issue had to be decided by an executive decision by the
co-chairs. In the alpha schema element and attribute names were converted to camel
case, as is the convention in EAC-CPF. This met our goals of conceptual
consistency and interoperability with EAC-CPF, but we received strong feedback
from the community arguing against the change. Entrenched and opposing opinions –
all with strong justifications from our points of emphasis – remained within
TS-EAD; ultimately the co-chairs decided to honor precedent and sensitivity to the
impact on users and opted to remove camel case.
Of the changes made in EAD3, the most extensive departure from EAD 2002 is the
replacement of <eadheader> with <control>. Borrowed from EAC-CPF
with some enhancements, <control> offers a better model for representing
information about finding aids, including its identifiers, status, languages,
conventions, maintenance history, and sources. One notable change to
<control> as modelled in EAC-CPF is the inclusion of <filedesc>
from <eadheader>. As an aggregation of descriptions of all the material in
an archival collection, finding aids have bibliographic attributes, such as a
title or a publication statement captured in <filedesc>, that are not
necessary when documenting authority records.
The elements available within <did> (Descriptive Identification) were
extensively updated in order to better support the exchange of key descriptive
data between EAD3 and other systems. Some <did> elements, including
<origination>, <repository>, and <langmaterial>, were
modified to remove mixed content and other ambiguities. The existing
<unitdate> and <physdesc> elements were felt to be too lax to
constrain and still provide a forward migration path, so new
<unitdatestructured> and <physdescstructured> elements were
added. These "structured" elements provide nuanced data models for capturing
temporal and physical description, while the original elements remain in modified
form as unstructured alternatives and to allow for forward migration from EAD
2002. Whereas these new elements provided additional structure, the
<daogrp> element, which allowed the creation of extended links to
digital archival objects, was simplified to <daoset>, which binds two or
more simple <dao> elements.
The access point elements available within <controlaccess>, e.g.
<persname>, <subject>, <genreform>, etc., were modified in
several ways. Each must now contain one or more <part> elements so that
multi-part terms may be accurately represented in EAD, allowing, for example, the
separate capture of an individual’s surname, forename, and life dates, etc. They
also now share a common set of attributes to improve interoperability with
external vocabularies: @identifier, for the code or URI associated with
a term, @source, for identifying the originating vocabulary, and
@rules, for recording how terms are formulated. The <geogname>
element now has an optional child <geographiccoordinates> for encoding
longitude, latitude, and altitude information.
Support for multilingual description was addressed by adding @lang and
@script attributes to all non-empty elements in EAD3, making it
possible to explicitly state what language or script is used therein.
Additionally, some elements were modified to allow them to repeat where previously
they did not, thus enabling the inclusion of the same data in multiple
languages.
Early in the revision process there were multiple requests to simplify EAD, and
one suggested measure was reducing the number of elements. However, TS-EAD decided
that consistency and semantic clarity was a better measure of simplicity, not the
number of elements in the schema. The <note> element is a useful case
study. In EAD 2002 <note> was available in 8 distinct contexts, each
representing a subtly different usage; in EAD3 the <note> element has been
replaced with context-specific elements, including <didnote>,
<controlnote>, and <footnote>.
Many other changes can be categorized as supporting the drive for greater
conceptual and sematic consistency in EAD. Major descriptive elements that
previously could be contained in other descriptive elements were removed in those
contexts. For example, <arrangement> is no longer a permitted child of
<scopecontent>, <unitdate> is no longer a permitted child of
<unittitle>, and <dao> is now only available within <did>.
Block and formatting elements like <list>, <blockquote>,
<quote>, were modified or created to more closely resemble their HTML
counterparts. The <chronlist> element was updated to incorporate
<geogname> to convey the locations where events occur, more closely
aligning it with its namesake in EAC-CPF. Mixed content models were streamlined to
three progressively inclusive sets of elements allowed to intermix with text.
Attribute names were disambiguated throughout the schema: @role was
changed to @relator on access point elements and @linkrole on
linking elements, @type was renamed through the schema to
@localtype where no values are supplied by the schema, and to
@elementnametype (e.g. @listtype and @unitdatetype) where
specified values are supplied. Linking elements – of which there were many in EAD
2002 – were consolidated to a handful and limited to simple links, eliminating
overly complicated extended links. The XLink model for linking attributes was
preserved, but the XLink namespace, which had been added to the schema versions of
EAD 2002, was removed due to the onerous and needless complexity that namespaces
introduce when processing XML. Elements that existed solely to support formatting
and presentation or were otherwise deemed out of scope for archival description
were deprecated, including <frontmatter>, <descgrp>,
<runner>, <imprint>, and <bibseries>.
The feature of EAD3 that caused the most heated discussion within TS-EAD was the
inclusion of the <relations> element. Introduced in EAC-CPF and added to
EAD3 with some modifications, <relations> is available at any level of
description and contains one or more <relation> elements. A
<relation> describes – in a Linked Open Data-friendly way – the
relationship between the records being described and a corporate body, person or
family; an archival or bibliographic resource; a function; or another type of
external entity. That relationship can be an actionable link and may be qualified
by supplying relevant dates or geographic names. XML describing the related entity
may be embedded within the <objectxmlwrap> element.
TS-EAD could not reach a consensus regarding the inclusion of <relations>.
Some members felt strongly that including <relations> was essential in
order to support rich Linked Open Data applications, align with EAC-CPF, and
acknowledge draft guidelines on relationships in archival description published by
the ICA Committee on Best Practices and Standards. Others felt that it duplicated
functionality present in <controlaccess> and other existing elements, added
unnecessary complexity, and that incorporating robust support for Linked Open Data
was premature. We ultimately negotiated a compromise: <relations> would be
included in EAD3 as an "experimental" element. As an experimental element, it is
not guaranteed that <relations> will persist in the next version of EAD in
its current form. However, TS-EAD encourages its use so that the EAD community
will learn more about how the <relations> model works within archival
description. Put simply, a consensus will require more data and experience, and
including <relations> provisionally makes that possible.
The revision of EAD 1.0 to EAD 2002 established a precedent that elements to be
removed from EAD would first be deprecated – suppressed but available if necessary
– before being removed from subsequent versions. All elements deprecated in EAD
2002 were removed from EAD3. TS-EAD endeavored to honor the commitment to
deprecate removed elements, however the extent of the changes in EAD3 made
comprehensive deprecation impossible. Elements to be removed entirely from the
standard remain available in undeprecated versions of EAD3. These include
<frontmatter>, <descgrp>, <imprint>, <bibseries>,
and <runner>, as well as the @tpattern attribute. Elements that
were replaced by other elements offering commensurate functionality, or whose
availability within the standard changed are in most cases not supported in
undeprecated EAD3. Two exceptions to that rule are the full EAD 2002 versions of
<physdesc> and <unitdate> within <unittitle>, both of
which are available in undeprecated EAD3.
EAD3 replaces EAD 2002 as the current, official version of EAD. EAD 2002 was
available as a DTD, Relax NG schema, and W3C schema. Additionally, the DTD could
be edited to enable the inclusion of deprecated elements. EAD3 continues to be
available in DTD, Relax NG, and W3C versions. For repositories who choose to
continue to use deprecated elements, an undeprecated version of EAD3 is available
in DTD, Relax NG, and W3C varieties. Due to differences between DTDs and schemas,
the <objectxmlwrap> element is not available in the DTD versions of EAD3. A
Schematron schema is also available to provide further validation functionality
for EAD instances, imposing data constraints that either cannot be expressed in
DTD, Relax NG, and W3C, or were intentionally removed from the schemas by TS-EAD
due to challenges of maintaining code lists outside of our control or to allow
alternative data sources or patterns.
All code related to EAD3, including the schemas and DTDs, Schematron schema, and
migration style sheet, will be shared with a Creative Commons CC0 license, placing
them in the public domain. This tag library is published with a Creative Commons
CC BY license, allowing others to distribute, remix, tweak, and build upon it,
even commercially, as long as they credit SAA for the original tag library.
EAD3 was possible because of the generous support of the Society of American
Archivists, the Gladys Krieble Delmas Foundation, the National Endowment for the
Humanities, the Nationaal Archief of the Netherlands, the Beinecke Rare Book and
Manuscript Library, the Institute for Advanced Technology in the Humanities at the
University of Virginia, and OCLC Research. Each member of TS-EAD* made invaluable
contributions to EAD3, but two merit special mention: Terry Catapano, Schema
Development Team chair, for leading the technical development of EAD3, and Kelcy
Shepherd, for leading the revision of the Tag Library.
Mike Rush
Bill Stockting
TS-EAD Co-Chairs
*TS-EAD members during the revision process included Mike Rush, co-chair, Yale
University; Bill Stockting, co-chair, British Library (UK); Kerstin Arnold,
Bundesarchiv (Germany); Michael Fox, Minnesota Historical Society; Kris Kiesling,
University of Minnesota; Angelika Menne-Haritz, Bundesarchiv (Germany); Kelcy
Shepherd, University of Massachusetts and Amherst College; Claire Sibille,
Direction Générale des Patrimoines (France); Henny van Schie, Nationaal Archief /
Bibliotheek (Netherlands); and Brad Westbrook, University of California, San
Diego, and ArchivesSpace. Notable ex-officio contributors included Jodi
Allison-Bunnell, Orbis Cascade Alliance (EAD Roundtable); Anila Angjeli,
Bibliothèque nationale de France (TS-EAC); Hillel Arnold, Rockefeller Archives
Center (EAD Roundtable); Mark Custer, Yale University (EAD Roundtable); Merrilee
Proffitt, OCLC Research; Ruth Kitchin Tillman, Cadence Group (EAD Roundtable); and
Katherine Wisser, Simmons College (TS-EAC). Schema Development Team members
included Terry Catapano, chair, Columbia University; Karin Bredenberg, Riksarkivet
of Sweden; Florence Clavaud, National Archives of France; Michele Combs, Syracuse
University; Mark Matienzo, Yale University and DPLA; Daniel Pitti, University of
Virginia; and Salvatore Vassallo, Università degli Studi di Pavia (Italy).
Tag Library Conventions [toc]
The EAD Elements section of the Tag Library contains descriptions of 165 elements,
arranged alphabetically by element name. It presents information for each element
as shown in Figure 1.
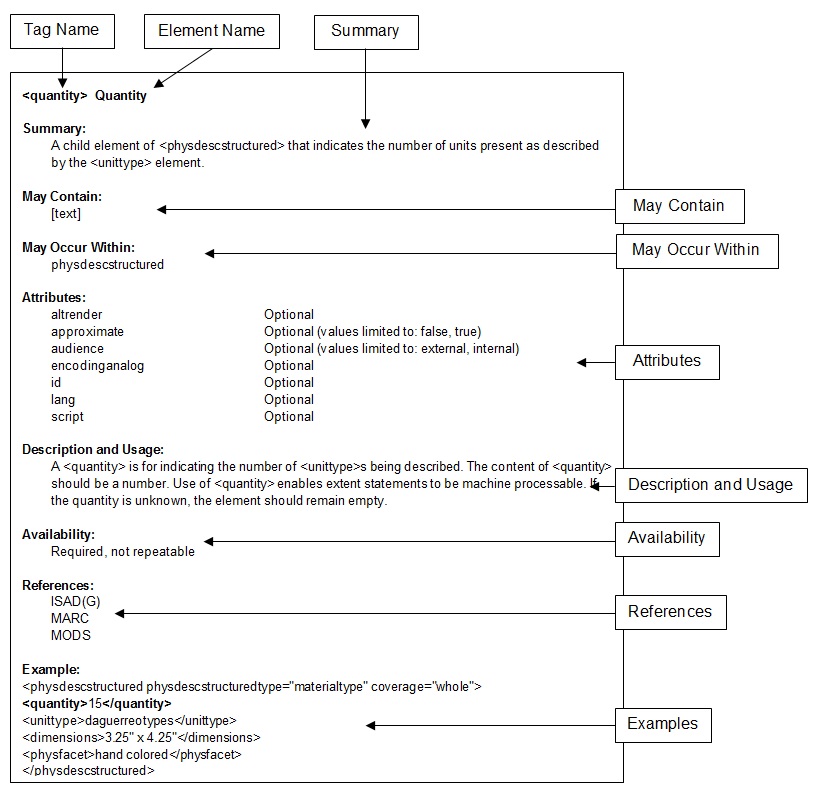
Tag Name:
Short, mnemonic form of the element name that is used in the
machine-readable encoded document. The tag name is the first word at the top of
the page. Tag names appear between angle brackets, e.g., <archdesc>,
except in the listings under "May occur within" and "May contain," and are
always in lowercase.
Element Name:
Expanded version of the tag name that more fully describes the element's
meaning. The full name of the element is usually a word or phrase that
identifies the element's purpose. In the Tag Library, the element name follows
the tag name on the page defining that element and appears with initial capital
letters, e.g., <archdesc> Archival Description.
Summary:
A brief statement that provides a concise definition of the element,
suitable for quick reference.
May Contain:
Identifies what child nodes (text or elements) may occur within the element
being defined. Elements are listed in alphabetical order by tag name. Elements
may be empty (e.g., an element which allows no child text or element nodes), or
they may contain text (listed as [text]), other elements, or a mixture of text
and other elements.Text content cannot include characters that would be
interpreted by a parser as action codes. For example, a left angle bracket has
to be represented as the character entity reference < so that it is not
misinterpreted as the start of an element name.
May Occur Within:
Identifies all of the parent elements within which the described element may
appear, listed in alphabetical order by tag name. This information conveys
information about where and how often an element is available throughout the
schema. The definitions for parent elements may provide additional information
about an element's usage.
Attributes:
Identifies all attributes that can be associated with an element. Attributes
are represented in lowercase letters in XML coding. The Tag Library uses the
convention of preceding an attribute name with an @ symbol (e.g.,
@identifier), following XPath syntax. See the EAD Attributes
section of the tag library for definitions and additional information.
Description and Usage:
This section begins with one or more paragraphs that provide a more thorough
description of the element than that found in the Summary, which may be
followed by guidance on use. The terms "parent" and "child" are used to
indicate hierarchical relationships between elements. Standard terminology is
also used to suggest the kind of element being discussed. "Wrapper element"
indicates an element that cannot contain text directly; a second, nested
element must be opened first. Wrapper elements designate sets of elements that
comprise a distinctive section of a finding aid, for example, the Descriptive
Identification <did>. "Generic element" refers to elements common to
many kinds of documents that contain information not specifically related to
archival description, e.g., <name> and <num>. "Formatting
element" indicates elements that can be used to invoke special text
presentation, such as block quotes, chronologies, and emphasis. When the schema
enforces a specific sequence of child elements, that sequence is
indicated.If useful, context-specific guidance for the usage of an
element’s attributes is given in an "Attribute usage" section. A "See also"
section may be provided to indicate additional elements that are similar,
easily confused, or otherwise related to the element being described.
Availability:
Indicates, within the context of its parent(s), whether the element is
required or optional, and whether or not it is repeatable.
References:
Identifies corresponding elements in other standards, schemas, and markup
languages: ISAD(G), MARC, MODS, and HTML. Full crosswalks for ISAD(G), MARC21,
and MODS are found in Appendix A.
Examples:
Most element descriptions include a tagged example to indicate how
attributes and elements can be used together. Many of the examples are taken
from real finding aids; others have been specially constructed for the Tag
Library. The examples illustrate any required sequences of elements, as in the
case of children within <control>, or required attributes such as
@level in <archdesc>. In other cases, the examples simply
show what is possible. Some examples have ellipses, either between or within
elements, indicating that other elements or text have been omitted. Some
elements have multiple examples—one may show very dense markup with numerous
attributes while another may illustrate a minimalist approach to the markup.
Either approach is valid in EAD, and it is up to the repository to determine
the optimal level of markup based on their specific purposes, functional
requirements, resources, or consortial guidelines.
Attributes
Introduction [toc]
Attributes are associated with most of the elements contained in EAD. Attributes
reflect named properties of an element and may take on different values, depending
on the context in which they occur. In order to set one or more attributes, an
encoder should include the name of the attribute(s) within the same angle brackets
as the start tag, together with the value(s) to which the attribute(s) is/are to
be set. That is,<[tag] [attribute]="[value]"> or<[tag] [attribute1]="[value1]" [attribute2]="[value2]">
For example:
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1937-1992</unitdate>
or
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1937/1992">1937-1992
</unitdate>
Most attributes are optional, though some are required. The attribute description
indicates whether an attribute is required. This information is also available in
the Attributes section of each element description.
The value of attributes may be constrained by the schema using specific attribute
type values. For example, id attribute is of type ID, which constrains
its value to a string beginning with an alphabetic character. An id
value must be unique within the EAD instance within which it occurs, that is, no
other tag in the entire document can have the same id value. EAD
attributes have the following data types( Capitalization of data types follows
the documentation found in the W3C Recommendation XML Schema Part 2:
Datatypes Second Edition (http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/).):
anyURI:
A Uniform Resource Identifier. This may be a Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
or a Uniform Resource Name (URN). Both relative and absolute URIs are
allowed.
ENTITY:
The name of a nonparsed entity that has been declared in the declaration
subset of the document. For example, entityref must contain the name
of an entity that has been declared in the declaration subset. Processing
software can use the reference to the nonparsed entity to display the entity in
the body of the text or in a new window.
ID:
Unique identifier. For example, most elements have an id, so that
a unique code can be established for and used to refer to that specific
element. The content of the id is of the type called "ID". Parsers
verify that the value of attributes of type "ID" are unique. The values of
id must begin with an alpha, not numeric, character, either upper
or lowercase, and may contain a . (period), : (colon), - (hyphen), or _
(underscore), but not a blank space. See also attributes of type
"IDREF."
IDREF:
ID reference value; must match an existing ID of another element in the
document. For example, the <ptr> element has a target
attribute that can only be an "IDREF," which means it has to reference a valid
ID in another element.
IDREFS:
List of ID reference values.
NMTOKEN:
A name token, which can consist of any alpha or numeric character, as well
as a . (period), : (colon), - (hyphen), or _ (underscore), but not a blank
space. A number of attributes in EAD where a character string from a code list
is to be used are of the type "NMTOKEN".
string:
The most general data type, a string can contain any sequence of
characters allowed in XML. Certain characters may have to be represented
with an entity reference, for example < for <, and & for
&.
token:
A type of string that may not contain carriage return, line feed or tab
characters, leading or trailing spaces, and any internal sequence of two or
more spaces.
The attribute value definitions in the DTD versions of EAD3 differ slightly from
those of the Relax NG and W3C Schema versions. The DTD has a limited set of
attribute types so the anyURI, token, and string data types were converted to
"CDATA" (i.e. Character Data).
When the EAD schema limits attribute values to a few choices, those values are
declared in the schema in what is known as a "closed list." For example, the
values of audience are limited to either "external" or "internal."
Other attributes are associated with semi-closed lists. Such lists include those
values believed to be the most useful in many contexts, but other values are
allowed. For example, <dsc> defines several values for dsctype,
including "otherdsctype" which may be used with otherdsctype to specify
values that are not in the semi-closed list for dsctype. The
definitions for some values in the closed and semi-closed lists appear below.
The following is a complete list of all the attributes that occur in EAD, and some
discussion of how they may be used. Further, context-specific information about
the use of certain attributes may be found in the "Attribute usage" section of the
element descriptions.
@abbr
Abbrevation [toc]
Summary:
An abbreviation for a word or phrase that is expressed in an expanded form in
the text of the current element; used for searching and indexing purposes.
Available only in <expan>.
Data Type:
token
@actuate
Actuate [toc]
Summary:
A control that defines whether a rendering application should present an
actionable link automatically (onload) or when requested by the user
(onrequest). It is used in conjunction with show to determine link
behavior.
Values:
none, onload, onrequest, other
@align
Alignment [toc]
Summary:
Horizontal position of the text within a column, indicating whether text should
be displayed flush left, flush right, centered in the column, or justified
(flush both left and right). Available in <colspec> , <entry>,
and <tgroup>.
Values:
left, right, center, justify, char
@althead
Alternative Heading [toc]
Summary:
An alternative short form of the heading element <head> that may be
used, for example, to create a running header.
Data Type:
token
@altrender
Alternative Render [toc]
Summary:
Specifies an alternative rendering for the content of the current element. May
be used if the element is to be displayed or printed differently than the
rendering established in a style sheet for other occurrences of the element,
and the values available for render are insufficient. See also
render.
Data Type:
token
@approximate
Approximate [toc]
Summary:
Indicates that the value provided is not exact. Available in
<quantity>.
Values:
false, true
@arcrole
Arc Role [toc]
Summary:
A URI that describes the nature of the source of a link as relative to the
target of the link.
Data Type:
anyURI
Example:
<relation relationtype="cpfrelation" arcrole="hasSubject">
<relationentry>Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach</relationentry>
<descriptivenote>
</relation><p>Bach's son</p>
</descriptivenote>@audience
Audience [toc]
Summary:
An attribute that helps control whether the information contained in the
element should be available to all viewers or only to repository staff.
Available for all elements except <lb> and <colspec>. The
attribute can be set to "external" in <archdesc> to allow access to all
the information about the materials being described in the finding aid, but
specific elements within <archdesc> can be set to "internal" to reserve
that information for repository access only. This feature is intended to assist
application software in restricting access to particular information by
explicitly identifying data that is potentially sensitive or may otherwise have
a limited audience. Special software capability may be needed, however, to
prevent the display or export of an element marked "internal" when a whole
finding aid is displayed in a networked environment.
Values:
external, internal
@base
Base [toc]
Summary:
Used to specify a base URI that is different than the base URI of the EAD
instance. This allows any relative URIs provided on attributes of a specific
element or its descendants to be resolved using the URI provided in that
element’s base. Available on <archdesc>, <c>,
<c01>, <c02>, <c03>, <c04>, <c05>,
<c06>, <c07>, <c08>, <c09>, <c10>,
<c11>, <c12>, <control>, <daoset>, <ead>,
<relations>, <sources>.
Data Type:
anyURI
@calendar
Calendar [toc]
Summary:
System of reckoning time, such as the Gregorian calendar or Julian calendar.
Suggested values include but are not limited to "gregorian" and "julian."
Available in <date>, <unitdate>, and
<unitdatestructured>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@certainty
Certainty [toc]
Summary:
The level of confidence for the information given in <date>,
<unitdate>, or <unitdatestructured>, e.g., approximate or
circa.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@char
Character [toc]
Summary:
Used for horizontal alignment of a single character, such as decimal alignment.
This attribute names the character on which the text will be aligned, for
example a decimal point, an asterisk, or an em-dash. Available in
<colspec> and <entry>.
Data Type:
token
@charoff
Character Offset [toc]
Summary:
Used with horizontal character alignment, such as decimal alignment. When the
align value is "char," this is the percentage of the current
column width to the left edge of the alignment character. Value is a number or
starts with a number. Available in <colspec> and <entry>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@colname
Column Name [toc]
Summary:
Name of a column in which an entry appears. Value is a character string made up
of letters and numbers with no spaces inside it. Available in <colspec>
and <entry>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@colnum
Column Number [toc]
Summary:
The number of the column, counting from 1 at the left of the table. Value is a
number. Available in <colspec>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@cols
Columns [toc]
Summary:
The number of columns in a table. Required in <tgroup>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@colsep
column Separator [toc]
Summary:
Used to indicate whether the columns in the table are to be separated by
vertical rules: "true" specifies display of a rule to the right of the column,
"false" specifies no rule is to be displayed. Available in <colspec>,
<entry>, <table>, and <tgroup>.
Values:
false, true
@colwidth
Column Width [toc]
Summary:
Width of the column measured in fixed units or relative proportions. For fixed
width, use a number followed by a unit. Possible unit values are "pt" for
point, "cm" for centimeters, "in" for inches, etc. (e.g., "2in" for 2 inches).
Proportional width can be indicated with a number and asterisk (e.g., "5*" for
five times the proportion). All integers are positive. Use values that are
appropriate to the software that governs the display of the resulting table
such as a web browser or XSL format objects processor. Available in
<colspec>.
Data Type:
token
@containerid
Container ID [toc]
Summary:
An attribute for <container> that takes as its value a locally assigned
identifier (e.g. barcode) for the container described. Unlike id,
the value of containerid need not be unique within the document, and
does not have to conform to the rules for the ID data type.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@coordinatesystem
Coordinate System [toc]
Summary:
A code for a system used to express geographic coordinates, for example WGS84,
(World Geodetic System), OSGB36 (Ordnance Survey Great Britain), or ED50
(European Datum). Required in <geographiccoordinates>.
Data Type:
token
@countrycode
Country Code [toc]
Summary:
A unique code for the country in which the materials being described are held.
Content of the attribute should be a code taken from ISO 3166-1 Codes for the
Representation of Names of Countries and their Subdivisions, column A2, or
another controlled list, as specified in the countryencoding
attribute in <control>. Available in <maintenanceagency> and
<unitid>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@countryencoding
Country Encoding [toc]
Summary:
The authoritative source or rules for values supplied in countrycode
in <maintenanceagency> and <unitid>. If the value
"othercountryencoding" is selected an alternate code list should be specified
in <conventiondeclaration>. Available only in <control>.
Values:
iso3166-1, othercountryencoding
@coverage
Coverage [toc]
Summary:
Specifies whether a statement of physical description or digital archival
object(s) relates to the entire unit being described or only a part thereof.
Required in <daoset> and <physdescstructured>, optional in
<dao>.
Values:
part, whole
@daotype
Digital Archival Object Type [toc]
Summary:
Specifies the origin of a digital archival object: born digital, derived from
non-digital records, other, or not known. Required in <dao>.
Values:
borndigital, derived, otherdaotype, unknown
@datechar
Date Characterization [toc]
Summary:
Term characterizing the nature of a date, such as dates of creation,
accumulation, or modification. Available in <unitdate> and
<unitdatestructured>.
Data Type:
token
@dateencoding
Date Encoding [toc]
Summary:
The authoritative source or rules for values provided in normal in
<date> and <unitdate>. If the value "otherdateencoding" is
selected an alternate code list should be specified in
<conventiondeclaration>.
Values:
iso8601, otherdateencoding
@dsctype
Description of Subordinate Components Type [toc]
Summary:
An optional attribute in <dsc> that indicates the approach used in
describing components within a finding aid.
Values:
analyticover, combined, in-depth, otherdsctype
@encodinganalog
Encoding Analog [toc]
Summary:
A field or element in another descriptive encoding system to which an EAD
element or attribute is comparable. Mapping elements from one system to another
enables creation of a single user interface that can index comparable
information across multiple schemas. The mapping designations may also enable a
repository to harvest selected data from a finding aid, for example, to build a
basic catalog record, or OAI-PMH compliant Dublin Core record. The
relatedencoding attribute may be used in <ead>,
<control>, or <archdesc> to identify the encoding system from
which fields are specified in encodinganalog. If
relatedencoding is not used, then include the system designation
in encodinganalog.
Data Type:
token
Examples:
<origination>
<corpname encodinganalog="MARC21 110">
</origination><part>Waters Studio</part>
</corpname><archdesc relatedencoding="MARC21">
<origination>
</archdesc><persname encodinganalog="100$a$q$d$e" source="lcnaf">
</origination><part>Waters, E. C. (Elizabeth Cat), 1870-1944,
photographer</part>
</persname>@entityref
Entity Reference [toc]
Summary:
The name of a nonparsed entity declared in the declaration subset of the
document that points to a machine-processable version of the cited reference.
Available in <dao>, <ptr>, and <ref>.
Data Type:
ENTITY
@era
Era [toc]
Summary:
Period during which years are numbered and dates reckoned, such as CE (Common
Era) or BCE (Before Common Era). Suggested values include "ce" and "bce".
Available in <date>, <unitdate>, and
<unitdatestructured>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@expan
Expansion [toc]
Summary:
The full form of an abbreviation or acronym found in an element's text; used
for indexing and searching purposes. Available only in <abbr>.
Data Type:
string
@frame
Frame [toc]
Summary:
An indication of the position of the external borders (rules) surrounding a
table when displayed. Available in <table>.
Values:
all, bottom, none, sides, top, topbot
@href
hypertext Reference [toc]
Summary:
The locator for a remote resource in a link. When linking to an external file,
href takes the form of a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). If
the value is not in the form of a URI, the locator is assumed to be within the
document that contains the linking element.
Data Type:
token
@id
ID [toc]
Summary:
An identifier that must be unique within the current document and is used to
name the element so that it can be referred to, or referenced from, somewhere
else. This facilitates building links between the element and other resources.
Do not confuse with identifier, which provides a machine-processable
identifier for an entity or concept in an external system.
Data Type:
ID
@identifier
Identifier [toc]
Summary:
On <unitid>, this is a machine-processable unique identifier for the
descriptive component in which the element appears. On access terms and other
elements whose content is drawn from an authority file, identifier
is a number, code, or string (e.g. URI) that uniquely identifies the term being
used in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge
organization system (e.g., the Library of Congress Name Authority File
identifier). In the latter case, source may be used to identify the
authority file. Available in <corpname>, <famname>,
<function>, <genreform>, <geogname>, <name>,
<occupation>, <part>, <persname>, <physfacet>,
<subject>, <term>, <title>, <unitid>,
<unittype>. Do not confuse with id, which provides a
unique ID for the element within the XML instance.
Data Type:
token
@instanceurl
Instance URL [toc]
Summary:
The URL for the EAD instance itself (as opposed to HTML or other derivatives,
which may be captured in <representation> elements). Available on
<recordid>.
Data Type:
anyURI
@label
Label [toc]
Summary:
A display label for an element. Use when a meaningful label cannot be derived
by the style sheet from the element name or when a heading element
<head> is not available. This attribute is available in all children
of <did>, as well as <language> and <script>.
Data Type:
string
@lang
Language [toc]
Summary:
Indicates the language of the content of an element. Content of the attribute
should be a code taken from ISO 639-1, ISO 639-2b, ISO 639-3, or another
controlled list, as specified in the langencoding attribute in
<control> . May be used consistently in a multi-lingual finding aid
to specify which elements are written in which language. Available on all
non-empty elements.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@langcode
Language Code [toc]
Summary:
The code for the language of the EAD instance and the language of the materials
provided as text in <language>. Content of the attribute should be a
code taken from ISO 639-1, ISO 639-2b, ISO 639-3, or another controlled list,
as specified in the langencoding attribute in <control> .
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@langencoding
Language Encoding [toc]
Summary:
Specifies which standard list of codes is used to identify the language of the
EAD instance and languages represented in the materials. The codes themselves
are specified in langcode in <language> and lang
in all non-empty elements. Available in <control>. If the value
"otherlangencoding" is selected an alternate code list should be specified in
<conventiondeclaration>.
Values:
iso639-1, iso639-2b, iso639-3, otherlangencoding
@lastdatetimeverified
Last Date and Time Verified [toc]
Summary:
Last date or last date and time the linked resource was verified. Verification
may include link resolution as well as verification of the version of the
linked object. Available in <citation>, <relation>,
<source>, and <term>.
Data Type:
Constrained to the following patterns: YYYY-MM-DD, YYYY-MM, YYYY, or
YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss [with optional timezone offset from UTC in the form of
[+|-][hh:mm], or "Z" to indicate the dateTime is UTC. No timezone implies the
dateTime is UTC.]
@level
Level [toc]
Summary:
The hierarchical level of the materials being described by the element. This
attribute is available in <archdesc>, where the highest level of
material represented in the finding aid must be declared (e.g., collection,
fonds, record group), and in <c> and <c01>-<c12>, where it
may be used to declare the level of description represented by each component
(e.g., subgroup, series, file). If none of the values in the semi-closed list
are appropriate, the value "otherlevel" may be chosen and some other value
specified in otherlevel.
Values:
class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds,
subgrp, subseries
@linkrole
Link Role [toc]
Summary:
A URI that characterizes the nature of the remote resource to which a linking
element refers.
Data Type:
anyURI
Example:
<representation href="http://drs.library.yale.edu:8083/fedora/get/beinecke:jonesss/PDF" linkrole="application/pdf">PDF version of finding aid</representation>
@linktitle
Link Title [toc]
Summary:
Information that serves as a viewable caption which explains to users the part
that a resource plays in a link. May be useful for meeting accessibility
requirements when rendering finding aids in a web browser.
Data Type:
token
@listtype
List Type [toc]
Summary:
Specifies the type of list: a definition list pairs a <label> with a
corresponding <item> containing text that describes the term; an ordered
list is a numbered or lettered list; an unordered list is one in which sequence
is not critical (e.g., a bulleted list). Available only on <list>.
Values:
deflist, ordered, unordered
@localtype
Local Type [toc]
Summary:
This optional attribute provides a means to narrow the semantics of an element,
or provide semantics for elements that are primarily structural or semantically
weak. The value of localtype may be from a local or generally used
external vocabulary. While the value of localtype may be any string,
to facilitate exchange of data, it is recommended that the value be either the
URI or the preferred label for a term defined in a formal vocabulary (e.g.,
SKOS), which is identified by an absolute URI, and is resolvable to a web
resource that describes the semantic scope and use of the value. Local
conventions or controlled vocabularies used in localtype may be
declared in <localtypedeclaration> within <control>.
Data Type:
token
@mark
Mark [toc]
Values:
For lists with a listtype value "unordered," mark may be
used to indicate the character to be used in marking each list entry. Values
are drawn from the CSS "list-style-type" property list.
Values:
disc, circle, inherit, none, square
@morerows
More Rows [toc]
Summary:
Number of additional rows in a vertical straddle. Value is a number; default
value is "0" to indicate one row only, no vertical span. Available only in
<entry>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@nameend
Name End [toc]
Summary:
Name of the rightmost column of a span. The value must be a column name, as
defined by colname on <colspec>. Available only in
<entry>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@namest
Name Start [toc]
Summary:
Name of leftmost column of a span. The value must be a column name, as defined
by colname on <colspec>. The extent of a horizontal span is
determined by naming the first column (namest) and the last column (nameend) in
the span. Available in <entry> only.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@normal
Normal [toc]
Summary:
A standardized form of the content of an element that is in uncontrolled or
natural language. A standardized form, usually from a controlled vocabulary
list, of the content of the following elements can be provided to facilitate
retrieval: <corpname>, <famname>, <function>,
<genreform>, <geogname>, <name>, <occupation>,
<persname>, <subject>, and <title>.In
<unittitle>, normal may be used to provide a sorting form
of a unit title with initial articles.
Summary:
In <date> and <unitdate>, it is recommended that
normal follows ISO 8601 Representation of Dates and Times or
other standard date format. An alternate date normalization pattern may be
specified by selecting "otherdateencoding" as the value for
dateencoding in <control> and specifying the alternate
date encoding pattern in <conventiondeclaration>.
Data Type:
token
@notafter
Not After [toc]
Summary:
A standard numerical form of an approximate date for which a latest possible
date is known. Available in <datesingle>, <fromdate>, and
<todate>. It is recommened that notafter values follow ISO
8601 or another standard date format as specified in
dateencoding.
Data Type:
token
@notbefore
Not Before [toc]
Summary:
A standard numerical form of an approximate date for which an earliest possible
date is known. Available in <datesingle>, <fromdate>, and
<todate>. It is recommened that notbefore values follow
ISO 8601 or another standard date format as specified in
dateencoding.
Data Type:
token
@numeration
Numeration [toc]
Summary:
For lists with a listtype value of "ordered," numeration
specifies the type of numeration.
Values:
armenian, decimal, decimal-leading-zero, georgian, inherit, lower-alpha,
lower-greek, lower-latin, lower-roman, upper-alpha, upper-latin,
upper-roman
@otherdaotype
Other Digital Archival Object Type [toc]
Summary:
The type of digital archival object captured in <dao>, when
daotype is set to "otherdaotype."
Data Type:
token
@otherdsctype
Other Description of Subordinate Components Type [toc]
Summary:
The type of <dsc>, when dsctype is set to "otherdsctype."
Data Type:
token
@otherlevel
Other Level [toc]
Summary:
The hierarchical level of the materials described in <archdesc>,
<c>, and <c01>-<c12> when level is set to
"otherlevel."
Data Type:
token
@otherphysdescstructuredtype
Other Structured Physical Description Type [toc]
Summary:
The type of physical description provided in <physdescstructured>, when
physdescstructuredtype is set to
"otherphysdescstructuredtype."
Data Type:
token
@otherrelationtype
Other Relation Type [toc]
Summary:
The type of relation provided in <relation>, when
relationtype is set to "otherrelationtype."
Data Type:
token
@parallel
Parallel [toc]
Summary:
Specifies if the statements of physical description in a <physdescset>
are parallel to one another or not (that is, they are alternate descriptions of
the same set of material). Optional in <physdescset>.
Values:
part, whole
@parent
Parent [toc]
Summary:
On <container>, the values of the id attributes of one or more other
<container>s that hold the container item being described in the
current element. For a folder this might point to the <container> that
describes the box in which that folder is housed. On <physloc>, the
values of the id attributes of one or more other <physloc>s that
represent a larger physical location. For a shelf, this might point to the
<physloc> that describes the range in which the shelf is found.
Available in <container> and <physloc>.
Data Type:
IDREFS
@pgwide
Page Wide [toc]
Summary:
Indicates whether a table runs the width of the page or the width of the text
column. The value "true" indicates the width of the page; "false" indicates the
text column only.
Values:
false, true
@physdescstructuredtype
Structured Physical Description Type [toc]
Summary:
A required attribute of <physdescstructured> that specifies the nature
of the statement being provided. "Carrier" refers to the number of containers;
"materialtype" indicates the type and/or number of the material types;
"spaceoccupied" denotes the two- or three-dimensional volume of the materials.
If none of these values are appropriate, the value
"otherphysdescstructuredtype" may be chosen and some other value specified in
otherphysdescstructuredtype.
Values:
carrier, materialtype, otherphysdescstructuredtype, spaceoccupied
Related Encoding [toc]
Summary:
A descriptive encoding system, such as MARC21, ISAD(G), or Dublin Core, to
which certain EAD elements can be mapped using encodinganalog.
Available in <ead>, <control>, and <archdesc>;
<control> and <archdesc> may be mapped to different encoding
systems, for example <control> mapped to Dublin Core and
<archdesc> mapped to MARC21 or ISAD(G) instead.
Data Type:
token
@relationtype
Relation Type [toc]
Summary:
A required attribute of <relation> used to indicate the type of entity
that is related to the materials being described.
Values:
cpfrelation, resourcerelation, functionrelation, otherrelationtype
@relator
Relator [toc]
Summary:
A contextual role or relationship that a controlled access term has with the
materials described. For example, <persname> may have a
relator value of "creator" or "photographer." EAD does not supply
a controlled list of values for this attribute, but use of some other
controlled vocabulary (e.g., MARC relator codes), is encouraged.
Data Type:
token
@render
Render [toc]
Summary:
Controls the formatting of the content of an element for display and print
purposes. Available in <emph>, <foreign>, <title>, and
<titleproper>. See also altrender.
Values:
altrender, bold, bolddoublequote, bolditalic, boldsinglequote, boldsmcaps,
boldunderline, doublequote, italic, nonproport, singlequote, smcaps, sub,
super, underline
@repositorycode
Repository Code [toc]
Summary:
A code in <unitid> that uniquely identifies the repository responsible
for intellectual control of the materials being described. The code should be
taken from ISO/DIS 15511 Information and documentation—International Standard
Identifier for Libraries and Related Organizations (ISIL), or another code as
specified in repositoryencoding in <control>.
Data Type:
token
@repositoryencoding
Repository Encoding [toc]
Summary:
The authoritative source or rules for values supplied in <agencycode>
and repositorycode in <unitid>. If the value
"otherrepositoryencoding" is selected an alternate code list should be
specified in <conventiondeclaration>. Available only in
<control>.
Values:
iso15511, otherrepositoryencoding
@rowsep
Row Separator [toc]
Summary:
Specifies whether the rows in a table are to be separated by horizontal lines.
A value of "false" indicates that no line is displayed, and "true" indicates
that a line should be displayed below the row.
Values:
false, true
@rules
Rules [toc]
Summary:
Name of the descriptive rules or conventions that govern the formulation of the
content of the element. Available in <corpname>, <famname>,
<function>, <genreform>, <geogname>, <name>,
<occupation>, <part>, <persname>, <physfacet>,
<subject>, <term>, <title>, <unitid>,
<unittype>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@script
Script [toc]
Summary:
Indicates the writing script of the content of an element (e.g., Cyrillic,
Katakana). Content should be taken from ISO 15924 Codes for the Representation
of Names of Scripts, or another controlled list, as specified in the
scriptencoding attribute in <control>. May be used
consistently in a multi-lingual finding aid to specify which elements are
written in which script. Available on all non-empty elements.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@scriptcode
Script Code [toc]
Summary:
The code for the writing script used with a given language. Content should be
taken from ISO 15924 Codse for the Representation of Names of Scripts, or
another controlled list, as specified in the scriptencoding
attribute in <control>. Available in <script>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@scriptencoding
Script Encoding [toc]
Summary:
The authoritative source or rules for values supplied in script and
scriptcode. If the value "otherscriptencoding" is selected an
alternate code list should be specified in <conventiondeclaration>.
Available only in <control>.
Values:
iso15924, otherscriptencoding
@show
Show [toc]
Summary:
A control that defines whether a remote resource that is the target of a link
appears in a new window, replaces the local resource that initiated the link,
appears at the point of the link (embed), initiates some other action, or
causes no target resource to display. It is used in conjunction with
actuate to determine link behavior.
Values:
new, replace, embed, other, none
@source
Source [toc]
Summary:
The controlled vocabulary that is the source of the term contained in the
element. Available in <corpname>, <famname>, <function>,
<genreform>, <geogname>, <name>, <occupation>,
<part>, <persname>, <physfacet>, <subject>,
<term>, <title>, <unitid>, and <unittype>.
Data Type:
token
@standarddate
Standard Date [toc]
Summary:
The standardized form of date expressed in <datesingle>,
<fromdate>, or <todate>. It is recommened that
standarddate values follow ISO 8601, for example, 2011-07-22,
1963, or 1912-11, or another standard date format as specified in
dateencoding.
Data Type:
token
@standarddatetime
Standard Date Time [toc]
Summary:
An ISO 8601-compliant form of the date or date and time of a specific
maintenance event expressed in <eventdatetime>. For example, 2009-12-31,
2009, 2009-12, 2009-12-31T23:59:59. Available only in
<eventdatetime>.
Data Type:
Constrained to the following patterns: YYYY-MM-DD, YYYY-MM, YYYY, or
YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss [with optional timezone offset from UTC in the form of
[+|-][hh:mm], or "Z" to indicate the dateTime is UTC. No timezone implies the
dateTime is UTC.]
@target
Target [toc]
Summary:
A pointer to the ID of another element. Used to create internal links within an
XML instance. Available in <ptr> and <ref>.
Data Type:
IDREF
@transliteration
Transliteration [toc]
Summary:
A value designating the transliteration scheme used in converting one script
into another script. For example, the ISO 15919 Transliteration of Devanagari
and related Indic scripts into Latin characters.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
@unit
Unit [toc]
Summary:
The type of measurement used to calculate the value provided in
<dimensions>.
Data Type:
token
@unitdatetype
Unit Date Type [toc]
Summary:
Identifies the type of date expressed in <unitdate> or
<unitdatestructured>.
Values:
bulk, inclusive
@valign
Vertical Alignement [toc]
Summary:
Vertical positioning of the text within a table cell.
Values:
top, middle, bottom
@value
Value [toc]
Summary:
General attribute, required in a number of children of <control>, that
provides controlled terminology related to the management of an EAD instance.
The terms available for value are defined in closed lists that vary
by element as follows:
Values:
Values in <eventtype>: created, revised, deleted, cancelled, derived,
updated, unknown
Values:
Values in <agenttype>: human, machine, unknown
Values:
Values in <publicationstatus>: inprocess, approved, published
Values:
Values in <maintenancestatus>: revised, deleted, new, deletedsplit,
deletedmerged, deletedreplaced, cancelled, derived
@xpointer
XPOINTER [toc]
Summary:
The locator for a remote resource in a simple or locator link. Takes the form
of a Uniform Resource Identifier plus a reference, formulated in XPOINTER
syntax, to a sub-resource of the remote resource. XPOINTER enables linking to
specific sections of a document that are relative, i.e., based on their
position in the document or their content, rather than by reference to a
specific identifier such as an ID.
Data Type:
token
Elements
<abbr>
Abbreviation [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding the shortened form of a word or phrase.
Description and Usage:
Used to record the abbreviated form of a word or phrase, for example, an
acronym.
Use <abbr> within <conventiondeclaration> to identify the code
for a thesaurus, controlled vocabulary, or another standard used in creating
the EAD description. To improve interoperability, it is recommended that the
value be selected from an authorized list of codes such as the MARC Description
Convention Source Codes
(http://www.loc.gov/standards/sourcelist/descriptive-conventions.html).
In other elements, use <abbr> with expan to encode
abbreviations as they occur within the description, if you wish to use an
abbreviation while also providing its fuller form.
Attribute usage:
Use @expan to provide the full form of the abbreviation,
which may be given for indexing or searching purposes.
See also:
The related element <expan> with @abbr, which can be
used to encode the full form of a name while providing the abbreviation
in an attribute for indexing or searching purposes.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
abstract, addressline, archref, author, bibref, citation, container, conventiondeclaration, date, datesingle, didnote, dimensions, edition, emph, entry, event, fromdate, head, head01, head02, head03, item, label, localtypedeclaration, materialspec, num, p, part, physdesc, physfacet, physloc, publisher, quote, ref, sponsor, subtitle, titleproper, todate, unitdate, unitid, unittitle
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <conventiondeclaration>: Optional, not repeatable
Within other elements: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<conventiondeclaration>
<abbr> ISAD(G) </abbr>
<citation>ISAD(G): General International Standard Archival Description,
second edition, Ottawa 2000</citation>
</conventiondeclaration><didnote>File also contains materials from the
<abbr expan="American Civil Liberties Union"> ACLU
</abbr>
</didnote><c02>
<did>
</c02><unittitle>
[. . .] </did><abbr expan="United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization"> UNESCO </abbr>
</unittitle><abstract>
Abstract [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that provides a brief characterization of the
materials being described.
Description and Usage:
An <abstract> is used primarily to encode biographical or historical
information about the creator and an abridged statement about the scope,
content, arrangement, or other descriptive details about the archival unit or
one of its components.
Within archdesc/did, <abstract> is derived from the longer descriptions
found in <bioghist> and <scopecontent>. Its purpose is to help
readers identify quickly those materials they need to explore at greater
length. Within the component (<c> or <c01>-<c12>) <did>,
<abstract> may describe unique characteristics of an individual
component.
Attribute usage:
Use of @localtype and @encodinganalog on
<abstract> may assist in transforming information for such
MARC21 equivalents as summary note (520$a) or biographical or historical
data (545$a).
Use @lang when abstracts are provided in more than one language.
Use @lang when abstracts are provided in more than one language.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, name, num, occupation, persname, quote, ptr, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
References:
MARC 520
MODS <abstract>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc level="fonds">
<did>
</archdesc><head>Descriptive Summary</head>
<unittitle label="Title">Richard Egan manuscript maps of Orange
County</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1878/1879">Circa
1878-1879</unitdate>
<unitid countrycode="US" repositorycode="cu-i" label="Collection number">MS-R72</unitid>
<origination label="Creator">
<persname rules="aacr2">
</origination><part>Egan, Richard</part>
<part>1842-1923</part>
</persname><repository label="Repository">
<corpname rules="aacr2">
</repository><part>University of California, Irvine</part>
<part>Library</part>
<part>Special Collections and Archives</part>
</corpname><abstract label="Abstract"> Four manuscript survey maps and one plat
map depicting areas of Orange County and attributed to the noted
surveyor and judge Richard Egan. One map is dated 1878 and 1879 by
Egan. The other maps are undated and unsigned but it is likely that he
drew them during these years. These maps primarily depict subdivisions
of non-rancho tracts of land occupying what is now Orange County, with
the addition of some topographical details. </abstract>
</did><c02 level="file">
<did>
</c02><unittitle>Family</unittitle>
<abstract> parents, grandparents, cousin Anne </abstract>
<unitdate normal="1956/1973">1956-1973</unitdate>
<container label="Box">104</container>
<container label="Folder(s)">6578-6579</container>
</did><accessrestrict>
Conditions Governing Access [toc]
Summary:
An element for information about conditions that affect the availability of the
materials being described.
Description and Usage:
Record in <accessrestrict> information about the availability of the
described materials, whether due to the nature of the information in the
materials being described, the physical condition of the materials, or the
location of the materials. Examples include restrictions imposed by the donor,
legal statute, repository, or other agency, as well as the need to make an
appointment with repository staff. May also indicate that the materials are not
restricted.
See also:
Do not confuse with <userestrict>, which records information about
limitations on the use of the described materials after access has been
granted.
Do not confuse with <legalstatus>, which records the statutorily-defined status of the materials being described.
Do not confuse with <legalstatus>, which records the statutorily-defined status of the materials being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.4.1
MARC 355, 506
MODS <accessCondition>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<accessrestrict>
<p>There are no access restrictions on this collection.</p>
</accessrestrict><accessrestrict>
<p>University records are public records and once fully processed are
generally open to research use. Records that contain personally
identifiable information will be closed to protect individual privacy.
The closure of university records is subject to compliance with
applicable laws.</p>
</accessrestrict><c02 level="file">
<did>
<container label="Box">104</container>
<container label="Folder(s)">6578-6579</container>
<unittitle>
<emph render="italic">Technics and Civilization (Form and
Personality)</emph>
</unittitle><unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1931/1933">1931-1933</unitdate>
</did><scopecontent>
<p>Draft fragments.</p>
</scopecontent><accessrestrict>
</c02><p>Only the photocopies (housed in Box 105) of these fragile
materials may be used.</p>
</accessrestrict><accruals>
Accruals [toc]
Summary:
An element for information about anticipated additions to the materials being
described.
Description and Usage:
Used to indicate anticipated additions to the material already held by the
repository. May indicate quantity and frequency of the accruals. The element
may also be used to indicate no additions are expected.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.3.3
MARC 584
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<accruals>
<p>No further materials are expected for this collection.</p>
</accruals><accruals>
<p>Noncurrent additions to this Record Group are transferred from the
Development Department annually at the end of the fiscal year in
June.</p>
</accruals><acqinfo>
Acquisition Information [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding the immediate source of acquisition of the materials
being described.
Description and Usage:
Use <acqinfo> to identify the source of the materials being described
and the circumstances under which they were received, including donations,
transfers, purchases, and deposits.
See also:
Note that the accession number may be encoded in <unitid> within
<did>.
<separatedmaterial> should be used for indicating items acquired as part of a collection and then subsequently removed from the collection.
Do not confuse with <custodhist>, which should be used for information about the chain of ownership before the materials reached the repository.
<separatedmaterial> should be used for indicating items acquired as part of a collection and then subsequently removed from the collection.
Do not confuse with <custodhist>, which should be used for information about the chain of ownership before the materials reached the repository.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.2.4
MARC 541
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<acqinfo>
<chronlist>
</acqinfo><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle>1945</datesingle>
<event>Transfer from
</chronitem><corpname>
, Accession number 45.22 </event><part>National Park Service</part>
</corpname><acqinfo>
<p>Source unknown. Originally deposited in University Library,
transferred to Department of Palaeography,
</acqinfo><date normal="19580424">24
April 1958</date>
. </p><address>
Address [toc]
Summary:
An element that binds together one or more <addressline> elements that
provide contact information for a repository or publisher.
Description and Usage:
Use to record information about the place where a repository or publisher is
located and may be contacted. Examples include a postal address, electronic
mail address, and/or phone number.
Use <address> within <repository> when encoding the contact
information of the institution or agency providing intellectual access to the
materials being described. Use <address> within <publicationstmt>
when it contains the address of the publisher of the encoded archival
description.
Consider using a style sheet to store address information that occurs in many
archival descriptions, as it is easier to update the information when located
in a single, shared file.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <publicationstmt>:One of <address>, <date>,
<num>, <p>, or <publisher> is required, repeatable
Within <repository>:Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<publicationstmt>
<publisher>The British Library</publisher>
<address>
</publicationstmt><addressline>96 Euston Road</addressline>
<addressline>London</addressline>
<addressline>NW1 2DB</addressline>
<addressline>United Kingdom</addressline>
</address><publicationstmt>
<publisher>The Bancroft Library.</publisher>
<address>
</publicationstmt><addressline>University of California, Berkeley.</addressline>
<addressline>Berkeley, California 94720-6000</addressline>
<addressline>Phone: 510/642-6481</addressline>
<addressline>Fax: 510/642-7589</addressline>
<addressline>Email: [email protected]</addressline>
</address><repository>
<corpname>
<part>University of California, Irvine. Library. Special Collections
and Archives.</part>
</corpname><address>
</repository><addressline>Irvine, California 92623-9557</addressline>
</address><addressline>
Address Line [toc]
Summary:
A generic element for recording one line of an address, whether postal or
other.
Description and Usage:
<addressline> may be repeated as many times as necessary to enter all
parts of an address.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype, if local use requires specification of the type
of information contained in the line.
May contain:
May occur within:
Availability:
Required, repeatable
Example:
<publicationstmt>
<publisher>Special Collections and Archives</publisher>
<address>
<addressline>The UCI Libraries</addressline>
<addressline>P.O. Box 19557</addressline>
<addressline>University of California</addressline>
<addressline>Irvine, California 92623-9557</addressline>
<addressline>Phone: (949) 824-7227</addressline>
<addressline>Fax: (949) 824-2472</addressline>
<addressline>Email: [email protected]</addressline>
<addressline>URL:http://www.lib.uci.edu/rrsc/speccoll.html
</addressline>
</address><date>© 2000</date>
<p>The Regents of the University of California. All rights
reserved.</p>
</publicationstmt><agencycode>
Agency Code [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <maintenanceagency> that provides a code for the
institution or service responsible for the creation, maintenance, and/or
dissemination of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <agencycode> to record a code indicating the institution or service
responsible for the creation, maintenance and/or dissemination of the EAD
instance. Use of <agencycode> is recommended, as the combination of
<agencycode> and the required <recordid> provide a globally
unique identifier for the instance.
It is recommended that the code follow the format of the International Standard
Identifier for Libraries and Related Organizations (ISIL: ISO 15511): a prefix,
a dash, and an identifier. The code is alphanumeric (characters A-Z, 0-9,
solidus, hyphen-minus, and colon) with a maximum of 16 characters. If
appropriate to local or national convention, insert avalid ISIL for an
institution, whether provided by a national authority (usually the national
library) or a service (such as OCLC). If this is not the case then local
institution codes may be given with the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code as the
prefix to ensure international uniqueness in <agencycode>.
See also:
Use <agencyname> to record the name of the agency.
Use <otheragencycode> to record any alternative codes representing the agency.
<recordid>, which together with <agencycode> provides a globally unique identifier for the EAD instance.
Use <otheragencycode> to record any alternative codes representing the agency.
<recordid>, which together with <agencycode> provides a globally unique identifier for the EAD instance.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.1
MODS <recordContentSource>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<maintenanceagency>
<agencycode> AU-ANL:PEAU </agencycode>
<agencyname>National Library of Australia</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><maintenanceagency>
<agencycode> DNASA-G </agencycode>
<otheragencycode localtype="agency">GSFC</otheragencycode>
<agencyname>NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><agencyname>
Agency Name [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <maintenanceagency> that provides the name
of the institution or service responsible for the creation, maintenance, and/or
dissemination of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <agencyname> to record the name of the institution or service
responsible for the creation, maintenance, and/or dissemination of the EAD
instance. Examples include the repository name or the name of an aggregation
service.
It is recommended to use the form of the agency name that is authorized by an
appropriate national or international agency or service.
<agencyname> may be repeated in order to provide the name of the
institution or service responsible for the EAD instance in multiple languages.
If <agencyname> is repeated it is recommended to indicate the language
of each name using lang.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local use requires recording the type of
name.
See also:
Use <agencycode> to record a code for representating the agency,
which together with <recorded> provides a globally unique identifier
for the EAD instance.
Use <otheragencycode> for any alternative codes.
Use <otheragencycode> for any alternative codes.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
References:
MODS <recordContentSource>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, repeatable
Examples:
<maintenanceagency>
<agencycode> AU-ANL:PEAU </agencycode>
<agencyname> National Library of Australia </agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><maintenanceagency>
<otheragencycode localtype="archon">GB-58</otheragencycode>
<agencyname> British Library </agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><maintenanceagency>
<agencycode>DNASA-G</agencycode>
<otheragencycode localtype="agency">GSFC</otheragencycode>
<agencyname> NASA Goddard Space Flight Center </agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><agent>
Agent [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <maintenanceevent> that provides the name of
a person, institution, or system responsible for the creation, modification, or
deletion of an EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <agent> to indicate the person, institution, or system responsible
for a maintenance event. Examples include the name of the author or encoder,
the database responsible for creating the EAD instance, and the style sheet
used to update an instance to a new version of EAD.
Give the name of the agent for each maintenance event described in
<maintenanceevent>. If the agent is a person or institution encode
the value on <agenttype> as "human." Otherwise, if the agent
is a system, encode the value on <agentype> as "machine."
See also:
Use the sibling element <agenttype> to indicate the type of
agent.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
<agenttype>
Agent Type [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <maintenanceevent> that indicates the type
of agent responsible for the creation, modification, or deletion of an EAD
instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <agenttype> and the value to indicate the type of agent
responsible for the creation, modification, or deletion of an EAD instance, as
captured in <maintenanceevent>. The element should remain empty unless
text is necessary to provide a value for <agenttype> in a language other
than English.
Attribute usage:
<agenttype> requires use of @value, which must be set to
"human," "machine," or "unknown," and should correspond to the information
recorded in <agent>. For example, if the <agent> is Jane
Marshall, the value of <agenttype> should be set to "human." If the
<agent> is a database, style sheet, or other system, the value of
<agenttype> should be set to "machine." The value of
<agenttype> may also be set to "unknown" if the agent and/or type
of agent cannot be determined.
See also:
Use the sibling element <agent> to encode the agent’s name.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Required (values limited to: human, machine, unknown)
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
<altformavail>
Alternative Form Available [toc]
Summary:
An element for indicating the existence of copies of the materials being
described.
Description and Usage:
Indicates the existence of copies of the materials being described, including
the type of alternative form, significant control numbers, location, and source
for ordering if applicable. The additional formats are typically microforms,
photocopies, or digital reproductions.
See also:
Do not confuse with <originalsloc>, which encodes information
about the existence, location, and availability of originals where the unit
described consists of copies.
Do not confuse with <dao>, which may be used to encode links to digitized versions of the materials being described.
Do not confuse with <dao>, which may be used to encode links to digitized versions of the materials being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.5.2
MARC 530
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<altformavail>
<p>This collection has been microfilmed and is available on three reels
MF1993-034:1 to MF1993-034:3.</p>
<p>Researchers interested in purchasing microfilm copies should contact
the repository.</p>
</altformavail><altformavail>
<head>Alternate Form of Material</head>
<p>Microfilm copy available (
</altformavail><num localtype="microfilm reel">
M-5030/1</num>
).</p><c02 level="file">
<did>
<container localtype="reel" label="Film Storage">1</container>
<unittitle>
<title render="italic">
</unittitle><part>The Man Who Hated Children</part>
</title><unitdate normal="1972">1972</unitdate>
<physdesc>16 mm. film</physdesc>
</did><altformavail>
</c02><p>A VHS Videocassette version is available for viewing. Video tape
is located in Video Storage.</p>
</altformavail><appraisal>
Appraisal Information [toc]
Summary:
An element for documenting decisions and actions related to assessing the
archival value and disposition of the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
A statement of the rationale for decisions related to appraisal and disposition
of the materials being described. Such decisions may be based upon the records’
current administrative, legal, and fiscal use; their evidential, intrinsic, and
informational value; their arrangement and condition; and their relationship to
other records. May include information about destruction actions, sampling, and
disposition schedules.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.3.2
MARC 583
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<appraisal>
<p>The records of the Mid-Ocean Dynamics Experiment came to the
Institute Archives in two accessions in 1980 and 1982. During processing
the collection was reduced from fifteen cubic feet to four by discarding
duplicate materials, financial records, and publications not authored by
MODE participants. Forty charts and six inches of raw data presented the
primary appraisal issues. The raw data consisted of bulletins and reports
referring to float positions, moorings, isotherms, geostrophic velocity
calculations, ships' summaries, and work proposed and work carried out
during the MODE-I experiment. As this raw data was recapitulated in
weekly
<title render="underline">
, only a sampling was retained in the collection. Also
discarded were ten charts for which there were no descriptions of
indicated data points, nor were dates or test site locations
provided.</p><part>MODE Hot Line Bulletins</part>
</title><p>Six inches of materials pertaining to the POLYMODE project,
1973-1980, were added to the Institute Archives POLYMODE
collection.</p>
<p>The appraisal of this collection was carried out in consultation with
Robert Heinmiller, a research associate at Woods Hole Oceanographic
Institution during MODE.</p>
</appraisal><appraisal>
<chronlist>
</appraisal><chronitem>
<datesingle standarddate="1975">1975</datesingle>
<event>Appraisal provided by donor, $12,500.</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle standarddate="2008">2008</datesingle>
<event>Appraised for insurance purposes, $15,750.</event>
</chronitem><archdesc>
Archival Description [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <ead> that binds together all of the
archival descriptive information in an EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
An element for binding together the bulk of an EAD document instance, which
typically should include elements describing the content, context, and extent
of a body of archival materials, as well as containing administrative and
supplemental information that facilitates use of the materials. The elements
are organized in hierarchical levels that provide a descriptive overview of the
whole, optionally followed by more specific description of the component parts.
Descriptive information is inherited downward, from one hierarchical level to
the next.
The first child of <archdesc> must be the required <did> that
provides core information about the overall unit being described in the finding
aid. This may be followed by a variety of notes and controlled access elements
that describe or provide administrative information about the whole of the
materials being described. <archdesc> may also include information about
subordinate units, which are bound together within <dsc> containing one
or more levels of subordinate components. Data elements available in
<archdesc> are repeatable in components (<c> or
<c01>-<c12>) within <dsc>.
Attribute usage:
The required @level identifies the type of aggregation being
described in the EAD instance: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, or subseries. If
"otherlevel" is used as a value for @level, the
@otherlevel should be used to provide an alternative
term.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, controlaccess, custodhist, did, dsc, fileplan, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
MARC 351$c is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Required (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Example:
<archref>
Archival Reference [toc]
Summary:
An element for citing other archival materials.
Description and Usage:
<archref> is used to cite separately described archival materials of
potential interest to the researcher, such as a series described separately
from its record group or a collection that is related topically or by
provenance.
Use <archref> to cite archival materials in <bibliography>,
<otherfindaid>, <relatedmaterial>, or
<separatedmaterial>. Also, <ref> may be used within
<archref> to link to another EAD instance.
See also:
Do not confuse with <bibref>, which is used to cite published
works or other materials that are not archival in nature.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, name, num, occupation, persname, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<relatedmaterial>
<head>Related Collections</head>
<archref>
<num localtype="collection">BANC PIC 19xx.055--ffALB</num>
,
Photographs Taken During the U.S. Geological Surveys West of the 100th
Meridian, 1871-1873, by Timothy H. O'Sullivan and William Bell </archref><archref>
<num localtype="collection">BANC PIC 19xx.089--STER</num>
,
Stereoviews of the U.S. Geographical Survey Expedition West of the 100th
Meridian of 1871, by Timothy H. O'Sullivan </archref><archref>
<num localtype="collection">BANC PIC 19xx.273--PIC</num>
,
Geographical Surveys West of the 100th Meridian (U.S.). New Mexico
Photographs from the 1873 Geographical Survey West of the 100th Meridian </archref><archref>
</relatedmaterial><num localtype="collection">BANC PIC
1905.17116-.17119--STER</num>
, Western Survey Expeditions of 1871,
1872, 1873, and 1874, by Timothy H. O'Sullivan and William Bell
</archref><relatedmaterial>
<archref>
<ref actuate="onrequest" show="new" href="smith_m">Mary Smith
Papers</ref>
</archref><archref>
</relatedmaterial><ref actuate="onrequest" show="new" href="smith_j">Jeremiah Smith
Correspondence</ref>
</archref><arrangement>
Arrangement [toc]
Summary:
An element for describing the organization or filing sequence of the
records.
Description and Usage:
Use <arrangement> to record the logical or physical groupings within a
hierarchical structure and their relationships. This includes how the described
materials have been subdivided into smaller units, e.g., record groups into
series. May also indicate the filing sequence of the described materials, for
example chronological or alphabetical arrangement.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.3.4
MARC 351
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<arrangement>
<head>Arrangement of the Collection</head>
<p>The filing system for the Braman Collection has been kept
substantially in its original form. That is, original folders and their
titles have been retained. The processor devised the basic organization
scheme for the collection and, where necessary, reorganized the papers
within the various component groups.</p>
</arrangement><c01 level="series">
<did>
<unittitle>Research files</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1887/1995">1887-1995</unitdate>
<physdescstructured coverage="whole" physdescstructuredtype="spaceoccupied">
</did><quantity>3.5</quantity>
<unittype>linear ft.</unittype>
</physdescstructured><scopecontent>
<p>This series consists of newspaper clippings and research notes of
Fred Reed, pertaining to the Champlain Transportation Company, its
vessels, and the vessels' crew members. Several of the folders of
chronological clippings include subjects, such as the move of the
Ticonderoga (1954-1955) and the sale of the Champlain Transportation
Company (1966). A number of clippings under "Persons" are obituaries.
Two folders under the subseries "Notes" contain handwritten notes by
Fred Reed broadly pertaining to the history of the Champlain
Transportation Company, including a chronology, a list of crew
members, and information about the Company's vessels.</p>
</scopecontent><arrangement>
</c01><p>Organized into three subseries:
<list listtype="unordered">
</p><item>Clippings--chronological</item>
<item>Clippings--persons</item>
<item>Notes</item>
</list><p>"Clippings-persons" is arranged alphabetically by surname, and
"Notes" alphabetically by subject.</p>
</arrangement><c03 level="file">
<did>
<unittitle id="bruce.A.2.3">Letters from various correspondents to
Craufurd Bruce</unittitle>
<unitdate normal="1807/1819">1807-19</unitdate>
<unitid>MS. Eng. c. 5746</unitid>
<physdesc>126 items</physdesc>
</did><arrangement>
<p>Alphabetical, Grey - Peterkin</p>
</arrangement><scopecontent>
</c03><p>Mainly relating to Michael Bruce, with drafts of a few letters
from Craufurd Bruce.</p>
</scopecontent><author>
Author [toc]
Summary:
An optional child element of <titlestmt> that provides the name(s) of
the institution(s) or individual(s) responsible for compiling the intellectual
content of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <author> to record the name(s) of institution(s) or individual(s)
responsible for compiling the intellectual content of the finding aid, as well
as any additional information about the roles of the author(s) a repository
wants to convey to users.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local practice requires recording the type of
author.
See also:
Use <agent> within <maintenanceevent> to designate the
encoder of the finding aid.
Use <persname> or <corpname> with the relator attribute to designate the author in a Bibliographic Reference <bibref> citation.
Use <origination> to designate the compiler, collector, or creator of the materials being described.
Use <persname> or <corpname> with the relator attribute to designate the author in a Bibliographic Reference <bibref> citation.
Use <origination> to designate the compiler, collector, or creator of the materials being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<filedesc>
<titlestmt>
</filedesc><titleproper>Register of the Rhea Higbee Wakeling
Collection</titleproper>
<author> The print and machine readable finding aids for this
collection were created by the Special Collections staff, Gerald R.
Sherratt Library. </author>
</titlestmt><filedesc>
<titlestmt>
</filedesc><titleproper>Finding Aid to the William Johannsson
Correspondence</titleproper>
<author> Martin Smith, Lead Archivist; Jane Howard, ILS intern </author>
<sponsor>IMLS Grant #HC-123</sponsor>
</titlestmt><bibliography>
Bibliography [toc]
Summary:
For citing works based on the use or analysis of the materials being
described.
Description and Usage:
<bibliography> identifies works that are based on, about, or of special
value when using the materials being described, or works in which a citation to
or brief description of the materials occurs.
The works may be encoded in <bibref> or <archref>, as a
<table>, <list>, or <chronlist>, or in a series of
<p> elements.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.5.4
MARC 510, 581
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<bibliography>
<head>Bibliography</head>
<p>Sources consulted by John Kobler.</p>
<bibliography>
<head>Monographs</head>
<bibref>
<title render="italic">
San Domingo: Imprimerie royale du Cap, 1782. Nos. 30,
35.</bibref><part>Affiches americaines</part>
</title><bibref>Ardouin, Charles Nicholas Celigny.
<title render="italic">
. Port-au-Prince, 1865.</bibref><part>Essais sur l'histoire d'Haiti</part>
</title><bibref>Bastien, Remy.
<title render="italic">
,
<part>Anthologie du folklore haitien</part>
</title><title render="doublequote">
.Mexico, 1946. pp.83-91.</bibref><part>Proverbes</part>
</title><bibref>Bellegarde, Dantes.
</bibliography><title render="italic">
. Port-au-Prince, 1948.Chap. IV: pp. 47-54.</bibref><part>Dessalines a parle</part>
</title><bibliography>
</bibliography><head>Serial publications</head>
[. . .] </bibliography><bibref>
Bibliographic Reference [toc]
Summary:
An element for citing a published work.
Description and Usage:
Use <bibref> to cite a published work such as a book, article,
dissertation, motion picture, or sound recording. The work may be based on,
about, or related in some other way to the materials described.
<bibref> may contain text, controlled access elements, or formatting
elements, and may use <ptr> or <ref> to link to the published
work. Multiple <bibref> elements may be grouped into a
<bibliography>.
See also:
Do not confuse with <ref>, which provides links both internal to a
finding aid or from the finding aid to external content.
Use the more specific <archref> to cite separately described archival materials.
Use the more specific <archref> to cite separately described archival materials.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, name, num, occupation, persname, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<p>The Archibald MacLeish Papers are described in
<bibref>
</p><title render="italic">
, p. 29. </bibref><part>Library of Congress Acquisitions: Manuscript Division,
1982</part>
</title><bibliography>
<head>Sources consulted</head>
<bibref>
<emph render="italic">Affiches americaines</emph>
. San Domingo:
Imprimerie royale du Cap, 1782. Nos. 30, 35.
<num localtype="bibid">inet</num>
</bibref><bibref> Madiou, Thomas.
</bibliography><emph render="italic">Histoire
d'Haiti</emph>
. Port-au-Prince, 1987.
<num localtype="bibid">
F1921.M154 1987</num>
</bibref><bioghist>
Biography or History [toc]
Summary:
For recording biographical or historical information about the creator(s) of
the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
A concise essay or chronology that places the archival materials in context by
providing information about their creator(s). Includes significant information
about the life of an individual or family, or the administrative history of a
corporate body. Use a series of <p> elements to capture a narrative
history, and/or <chronlist> to match dates and date ranges with
associated events (and, optionally, places).
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.2.2
MARC 545
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<bioghist>
<head>Administrative History</head>
<p id="PRO123">In October 1964 the incoming Labour government created
new office of Secretary of State for Economic Affairs (combined with
First Secretary of State) and set up the Department of Economic Affairs
under the Ministers of the Crown Act 1964 to carry primary responsibility
for long term economic planning.</p>
<p>Under the Act the posts of Economic Secretary to the Treasury and
Secretary of State for Industry, Trade and Regional Development were
abolished.</p>
<p>George Brown was appointed as First Secretary of State and Secretary
of State for Economic Affairs, and as chairman of the National Economic
Development Council (NEDC).</p>
<p>Composition of DEA: most of Treasury's National Economy Group
(excluding the short term forecasting team); economic planning staff from
the National Economic Development Office (NEDO); the regional policy
divisions from the Board of Trade; a team of industrial experts.</p>
<p>DEA charged with duty of formulating, with both sides of industry, a
National Plan (published in September 1965), co-ordinating the work of
other departments in implementing policies of economic growth,
particularly in the fields of industry, the regions, and prices and
incomes.</p>
. . . </bioghist><bioghist>
<head>Chronology</head>
<chronlist>
</bioghist><chronitem>
<datesingle standarddate="1840-10-12">12 Oct 1840</datesingle>
<event>Born Helena Opid in Krakow, Poland.</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
[. . .]
<datesingle standarddate="1861">1861</datesingle>
<event>Made stage debut as Helena Modrzejewska in charity fair
production of
</chronitem><emph render="italic">The White
Camellia</emph>
, in Bochnia, Poland.</event><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle standarddate="1909-04-09">1909</datesingle>
<event>Died April 8th at her home on Bay Island. Funeral services
held at St. Vibiana's Cathedral in Los Angeles, and Modjeska was
later buried in her native Krakow.</event>
</chronitem><blockquote>
Block Quote [toc]
Summary:
A generic formatting element that designates an extended quotation.
Description and Usage:
An extended quotation or other lengthy text to be set off from the main text by
spacing or other typographic distinction, for example, by adding additional
line spaces above and below the block quote and by indenting the left margin of
the block quote.
<blockquote> is equivalent to the element <blockquote> in
HTML.
See also:
Use <quote> to identify inline quotes within a block of
text.
May contain:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<bioghist>
<head>Administrative History</head>
<p>As the size of the Yale faculty increased, Brewster's new admissions
policies caused the make up of the undergraduate body to shift. By the
early 1960s, most undergraduates had prepared at private schools, and
many were sons of Yale alumni. As with the faculty, Brewster felt that
Yale was consistently overlooking some of the best intellectual student
talent necessary to maintain the highest levels of academic excellence.
In a 1965 speech to alumni, Brewster summarized his administration's
revised recruitment policy by stating that Yale would only seek
students</p>
<blockquote>
</bioghist><p>...whose capacity for intellectual achievement is outstanding and
who also have the motivation to put their intellectual capacities to
creatively influential use, in thought, in art, in science, or in the
exercise of public or private or professional responsibility.</p>
</blockquote><c>
Summary:
An element that designates a subordinate part of the materials being
described.
Description and Usage:
As a wrapper for a set of elements, <c> provides information about the
content, context, and extent of a subordinate body of materials. It is always a
child or descendant of <dsc> and often a child and/or parent of another
<c>. Each <c> identifies a logical section, or level, of the
described materials. The physical filing separations between components need
not always coincide with the intellectual separations. For example, a
<c> that designates dramatic works might end in the same box in which
the next <c> begins with short stories. Also, not every <c>
directly corresponds to a folder or other physical entity. Some <c>
elements simply represent a logical point in a hierarchical description.
Components may be subdivided into smaller and smaller components and may
eventually reach the level of a single item. For example, the components of a
collection may be a series, components of series may be subseries, components
of subseries may be files, and components of files may be items. A component
may be either an unnumbered <c> or a numbered <c01>,
<c02>, etc. Numbered and un-numbered components cannot be mixed in an
EAD instance, and only up to twelve numbered <c>s,
(<c01>-<c12>) may be used in an EAD instance. Numbering
components may assist a finding aid encoder in accurately nesting
components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which the @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which the @level has been set to "otherlevel."
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<dsc dsctype="combined">
<c level="series">
</dsc><did>
<unitid>Series 1</unitid>
<unittitle>Correspondence</unittitle>
</did><scopecontent>[...]</scopecontent>
<c level="subseries">
<did>
<unitid>Subseries 1.1</unitid>
<unittitle>Outgoing Correspondence</unittitle>
</did><c level="file">
[. . .] </c><did>
</c><unittitle>Abbinger-Aldrich</unittitle>
</did><c level="subseries">
</c><did>
<unitid>Subseries 1.2</unitid>
<unittitle>Incoming Correspondence</unittitle>
</did><c level="file">
[. . .] </c><did>
</c><unittitle>Adams-Ayers</unittitle>
</did><c01>
Summary:
An element that designates the top or first-level subordinate part of the
materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
encoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c01>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which the @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which the @level has been set to "otherlevel."
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c02, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<dsc dsctype="combined">
<c01 level="series">
</dsc><did>
<unittitle>Topical Files</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1918/1945">1918-1945</unitdate>
</did><scopecontent>[...]</scopecontent>
<c02 level="file">
[. . .] </c01><did>
<unittitle>California Dining Club</unittitle>
</did><c03 level="file">
<did>
</c03><unittitle>Annual financial statements</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1923/1929">1923-1929</unitdate>
</did><c03 level="file">
<did>
</c03><unittitle>Membership rosters</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1918/1932">1918-1932</unitdate>
</did><c03 level="file">
<did>
</c03><unittitle>Minutes</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1925/1930">1925-1930</unitdate>
</did><c03 level="file">
</c02><did>
</c03><unittitle>Newsletters</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1919/1932">1919-1932</unitdate>
</did><c02>
Summary:
An element that designates a second-level subordinate part of the
materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c02>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which the @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which the @level has been set to "otherlevel."
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c03, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c03>
Summary:
An element that designates a third-level subordinate part of the materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c03>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c04, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c04>
Summary:
An element that designates a fourth-level subordinate part of the
materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c04>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c05, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c05>
Summary:
An element that designates a fifth-level subordinate part of the materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c05>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c06, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c06>
Summary:
An element that designates a sixth-level subordinate part of the materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c06>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c07, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: sclass, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c07>
Summary:
An element that designates a seventh-level subordinate part of the
materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c07>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c08, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c08>
Summary:
An element that designates an eighth-level subordinate part of the
materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c08>.
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c09>
Summary:
An element that designates a ninth-level subordinate part of the materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c09>.
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c10, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c10>
Summary:
An element that designates a tenth-level subordinate part of the materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c10>.
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c11, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c11>
Summary:
An element that designates an eleventh-level subordinate part of the
materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c11>.
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c12, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<c12>
Summary:
An element that designates a twelfth-level subordinate part of the
materials.
Description and Usage:
Components may be either unnumbered <c> or numbered <c01>,
<c02>,… to <c12>. The numbering indicates hierarchy within the
endcoded finding aid, not the order of the components, so <c01> in one
part of a finding aid may designate a series, while in another part of the
finding aid it may designate an item. Numbering components may also assist a
finding aid encoder in accurately nesting components. <c12> is the
lowest hierarchical level permitted when using numbered components.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a base URI other than the URI of the EAD
instance for the purpose of resolving any relative URIs contained within
<c12>.
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements categories in another data format, such as MARC.
Use @level to identify the logical type of the component, using one of these values: class, collection, file, fonds, item, otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries. Assigning @level for the highest <c> is recommended; thereafter the attribute may be used when the repository deems it useful, or when encoding protocols dictate its use.
Use @otherlevel to specify the level of a component for which @level has been set to "otherlevel."
See also:
The element definition for <c>.
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, controlaccess, custodhist, did, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, thead, userestrict
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.4 is equivalent to level
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: class, collection, file, fonds, item,
otherlevel, recordgrp, series, subfonds, subgrp, subseries)
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<chronitem>
Chronology List Item [toc]
Summary:
An element that pairs a date with one or more events and zero or more
geographic names within a chronology list <chronlist>.
Description and Usage:
An item within a chronology list, <chronitem> must contain a date, date
range, or set of dates followed by an event or set of events. An optional
<geogname> may follow the date, date range or set of dates. Use
<dateset> to record multiple dates or date ranges and
<chronitemset> to record multiple events or geographic names within a
single <chronitem>.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype, if local use requires specification of the type
of chronological item.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, repeatable
Examples:
<chronlist>
<chronitem>
<datesingle>2015</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Woodbury, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><geogname>
<part>Roseville, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Opens additional stores</event>
</chronitemset><chronitem>
<datesingle>1948</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Minneapolis, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Graduates from the University of Minnesota</event>
<event>Begins work as a receptionist for the Humphrey for Senator
Committee</event>
</chronitemset><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle>March 1957</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
<geogname>
<part encodinganalog="651" localtype="a">Biwabik,
Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Dies</event>
</chronitemset><chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part encodinganalog="651" localtype="a">Minneapolis,
Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Buried in Lakewood Cemetery</event>
</chronitemset><chronlist>
<chronitem>
<datesingle standarddate="1927">1927</datesingle>
<geogname>
<part>Berlin, Germany </part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="mgrs">33UUU9029819737
</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Designs and builds Piscator Apartment</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle standarddate="1932">1932</datesingle>
<geogname>
<part>Basel, Switzerland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="mgrs">
32TLT9469569092</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Designs and builds Wohnbedarf Furnniture Stores</event>
</chronitem><chronitemset>
Chronology Item Set [toc]
Summary:
An element for binding together zero or more <geogname> elements and one
or more <event> elements within <chronitem>.
Description and Usage:
Use <chronitemset> within <chronitem> when it is necessary to
associate multiple <event> elements or multiple <geogname>
elements. Possible combinations include multiple events, a single event
associated with multiple locations, multiple events associated with a single
location, or multiple events associated with multiple locations.
<chronitemset> may be repeated within <chronitem> when
necessary to associate multiple instances of such combinations with the date or
dates recorded within <chronitem>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<chronitem>
<datesingle>2015</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Woodbury, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><geogname>
<part>Roseville, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Opens additional stores</event>
</chronitemset><chronitem>
<datesingle>1948</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Minneapolis, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Graduates from the University of Minnesota</event>
<event>Begins work as a receptionist for the Humphrey for Senator
Committee</event>
</chronitemset><chronitem>
<datesingle>March 1957</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
<geogname>
<part encodinganalog="651" localtype="a">Biwabik,
Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Dies</event>
</chronitemset><chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part encodinganalog="651" localtype="a">Minneapolis,
Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Buried in Lakewood Cemetery</event>
</chronitemset><chronitem>
<dateset>
<datesingle standarddate="1942-03">March 1942</datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1942-05">May 1946</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1946-09">September 1946</todate>
</daterange><chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Clear Spring</part>
<part>Maryland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="UTM">18S 248556mE
4393694mN</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Enlisted in Civilian Public Service as a conscientious
objector.</event>
<event>Served at CPS Camp No. 24, subunit 4 in Clear Spring,
Maryland. Constructed fences to conserve soil, practiced specialized
tilling, and dug water diversion ditches. Fought occasional forest
fires.</event>
</chronitemset><chronlist>
Chronology List [toc]
Summary:
An element for designating the temporal sequence of significant events
associated with the entity or material described.
Description and Usage:
<chronlist> provides a structured display for a chronological sequence
of events. Each <chronlist> contains one or more <chronitem>
elements that pair one or more dates with one or more events and zero or more
geographic names.
<chronlist> most often appears in finding aids as part of
<bioghist>, but <chronlist> is also available for use in other
elements that might need to present dates and events in a multicolumn list.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype, if local use requires specification of the type
of chronology list.
See also:
Do not confuse with <list>, which is used for formatting a
non-chronological series of <item> or <defitem>
elements.
May contain:
May occur within:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, blockquote, controlaccess, controlnote, custodhist, dsc, fileplan, footnote, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, userestrict
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<chronlist>
<listhead>
<head01>Date(s)</head01>
<head02>Location(s)</head02>
<head03>Event(s)</head03>
</listhead><chronitem>
</chronlist><dateset>
<datesingle standarddate="1942-03">March 1942</datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1942-05">May 1946</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1946-09">September 1946</todate>
</daterange><chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Clear Spring</part>
<part>Maryland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="UTM">18S 248556mE
4393694mN</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Enlisted in Civilian Public Service as a conscientious
objector.</event>
<event>Served at CPS Camp No. 24, subunit 4 in Clear Spring,
Maryland. Constructed fences to conserve soil, practiced
specialized tilling, and dug water diversion ditches. Fought
occasional forest fires.</event>
</chronitemset><chronlist>
<chronitem>
<datesingle standarddate="1927">1927</datesingle>
<geogname>
<part>Berlin, Germany </part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="mgrs">33UUU9029819737
</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Designs and builds Piscator Apartment</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle standarddate="1932">1932</datesingle>
<geogname>
<part>Basel, Switzerland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="mgrs">
32TLT9469569092</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Designs and builds Wohnbedarf Furnniture Stores</event>
</chronitem><chronlist>
<chronitem>
<daterange>
<fromdate standarddate="2010">2010</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="2015">2015</todate>
</daterange><event> EAD revision </event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
<datesingle standarddate="2014-08-13">2014 August 13</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part> Washington, D.C. </part>
</geogname><event>TS-EAD Meeting</event>
<event>EAD Roundtable Meeting</event>
</chronitemset><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle standarddate="2014-10-23"> 2014 October
23</datesingle>
<event> SAA Webinar, "EAD3: What’s new?" </event>
</chronitem><citation>
Citation [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <conventiondeclaration> and
<localtypedeclaration> for identifying any rules and conventions
applied in the compilation of the description.
Description and Usage:
Use <citation> to identify any rules and conventions used in creating
the description. Examples include content standards, controlled vocabularies,
and thesauri.
Use <citation> to cite an external resource in human and/or
machine-processable form. Provide the formal title or name of the resource,
using <emph> to specify any formatting (such as italic or bold, etc.)
deemed useful.
Attribute usage:
Use @href to link to the cited resource.
See also:
Use <source> to cite a source of evidence used in describing the
archival materials.
Use <bibliography> to provide one or more citations for a published work based on, about, or related to the materials being described.
Use <bibliography> to provide one or more citations for a published work based on, about, or related to the materials being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: none, onload, onrequest, other)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (must follow pattern based on ISO 8601)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: embed, new, none, other, replace)
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<conventiondeclaration>
<abbr>ISAD(G)</abbr>
<citation> ISAD(G): General International Standard Archival Description,
second edition, Ottawa 2000 </citation>
</conventiondeclaration><conventiondeclaration>
<abbr>NCARules</abbr>
<citation> National Council on Archives, Rules for the Construction of
Personal, Place and Corporate Names, 1997 </citation>
</conventiondeclaration><localtypedeclaration>
<citation> IAMS Catloguing Guidelines Part 1: Describing Archives and
Manuscripts </citation>
</localtypedeclaration><colspec>
Table Column Specification [toc]
Summary:
An empty formatting element that specifies the position and size of a single
column in a table.
Description and Usage:
Use <colspec> to specify the position, size, and display aspects of a
column. Attributes specify the unique name of the column, its unique number
within the table, its width and rules, and the horizontal alignment of text
within the column. Note that the quantity of columns in <table> is
determined by the cols of <tgroup>, not by the number of
<colspec> elements present. The values set for <colspec>
override any values implied from <tgroup> or <thead>.
Attribute usage:
See the Attributes section of the Tag Library for information about
specific attributes.
See also:
Related elements <table> and <tgroup>.
May contain:
[empty]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: center, char, justify, left,
right)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<container>
Container [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> for indicating the container in which the
material being described is housed, e.g., box, folder.
Description and Usage:
<container> contributes to locating the described materials by
indicating the kinds of containers that physically hold the materials and
identifying any sequential numbers assigned to those containers.
<container> is used most frequently at the component level. This
storage information can help researchers understand how extensive the described
material is, especially in the absence of a specific
<physdescstructured> or <physdesc> statement at the component
level.
Consistency in the use of <container> and its attributes is essential to
enabling a style sheet to properly display the information, which often
consists of a tabular listing of archival materials and their associated boxes,
folders, etc. For example, <container localtype="Box"> is not necessarily
the same as <container localtype="box"> to a style sheet. Also keep in
mind that a style sheet may automatically display column headings based on the
localtype value. It is important to establish one method of
expressing values in localtype and be consistent within and across
your institution's finding aids.
Attribute usage:
Use @parent to indicate the container in which the current
container is housed, e.g., a box in which a folder is housed.
See also:
Use <physloc> to designate the shelves, stacks, rooms, buildings,
or other places where the containers are stored.
Use <unitid> to designate control numbers not associated with a physical container, for example, accession numbers.
Use <unitid> to designate control numbers not associated with a physical container, for example, accession numbers.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (IDREFS)
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c01 level="series">
<did>
<unittitle>...</unittitle>
</did><c02 level="file">
<did>
</c02><container localtype="box"> 3 </container>
<container localtype="folder"> 18 </container>
<unittitle>Parent-Teacher Association of
Fondsville</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1959/1972">1959-1972</unitdate>
</did><c02 level="file">
</c01><did>
</c02><container localtype="box"> 3 </container>
<container localtype="folder"> 19 </container>
<unittitle>Pasta and Politics Club</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1967/1975">1967-1975</unitdate>
</did><dsc dsctype="combined">
<c level="series">
</dsc><did>
<unittitle>Correspondence</unittitle>
</did><scopecontent>
<p>[...]</p>
</scopecontent><c level="file">
<did>
</c><container id="mss1993-043.1.1" localtype="box"> 1 </container>
<container parent="mss1993-043.1.1" localtype="folder"> 1 </container>
<unittitle>Family</unittitle>
<unitdate normal="1942/1947">1942-1947</unitdate>
</did><c level="file">
<did>
</c><container parent="mss1993-043.1.1" localtype="folder"> 2 </container>
<unittitle>General</unittitle>
<unitdate normal="194401/194408">January-August
1944</unitdate>
</did><c level="file">
</c><did>
</c><container parent="mss1993-043.1.1" localtype="folder"> 3 </container>
<unittitle>General</unittitle>
<unitdate normal="194409/194503">August 1944-March
1945</unitdate>
</did><control>
Control [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <ead> for recording bibliographic and
administrative information about an EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <control> to record any bibliographic information about an EAD
instance and administrative information necessary to manage it.
<control> can include information about the identity, creation,
maintenance, and status of the instance as well as about the languages, rules,
and authorities used in the composition of the description.
<control> must contain the following information about the EAD
instance:
A unique identifier within <recordid>. (Other associated
identifiers may be given in <otherrecordid>.)
Bibliographic information in <filedesc>, with at least a <titleproper> within <titlestmt>.
A description of the agency responsible for creation and maintenance in <maintenanceagency>.
Statements about current version status in <maintenancestatus>.
Information related to creation, maintenance, and disposition in <maintenancehistory>.
Bibliographic information in <filedesc>, with at least a <titleproper> within <titlestmt>.
A description of the agency responsible for creation and maintenance in <maintenanceagency>.
Statements about current version status in <maintenancestatus>.
Information related to creation, maintenance, and disposition in <maintenancehistory>.
Additional, optional child elements include three elements to declare
languages, rules, and conventions used in the EAD instance.
<languagedeclaration> may be used to provide information on the
language(s) and script(s) used in the description.
<conventiondeclaration> provides information on the standards,
authorities, or controlled vocabularies used in the instance.
<localtypedeclaration> declares the local conventions and controlled
vocabularies used in localtype.
The prescribed order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<recordid>
<otherrecordid>
<representation>
<filedesc>
<maintenancestatus>
<publicationstatus>
<maintenanceagency>
<languagedeclaration>
<conventiondeclaration>
<localtypedeclaration>
<localcontrol>
<maintenancehistory>
<sources>
<otherrecordid>
<representation>
<filedesc>
<maintenancestatus>
<publicationstatus>
<maintenanceagency>
<languagedeclaration>
<conventiondeclaration>
<localtypedeclaration>
<localcontrol>
<maintenancehistory>
<sources>
Many of these elements are repeatable, allowing the recording of multiple
languages and conventions, for example.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a URI (other than the base URI of the EAD
instance) to be used for resolving relative URIs within <control> or
descendant elements.
Use @countryencoding to identify the authoritative source for values supplied in @countrycode. This attribute may be set to "iso3166-1" or "othercountryencoding." If the value "othercountryencoding" is selected, further information regarding the country codes used in the instance should be supplied in <conventiondeclaration>.
Use @dateencoding to identify the rules for values provided in @normal, @standarddate, @notbefore, and @notafter in date elements. This attribute may be set to "iso8601" or "otherdateencoding." If the value "otherdateencoding" is selected, further information regarding the rules for normalized date values used in the instance should be supplied in <conventiondeclaration>.
Use @langencoding to identify the authoritative source for values supplied in @lang and @langcode. This attribute may be set to "iso639-1," "iso639-2b," "iso639-3," or "otherlangencoding." Previous versions of EAD prescribed the use of ISO 639-2b, so "iso639-2b" may be the most commonly used value. If the value "otherlangencoding" is selected, further information regarding the language codes used in the instance should be supplied in <conventiondeclaration>.
Use @countryencoding to identify the authoritative source for values supplied in @countrycode. This attribute may be set to "iso3166-1" or "othercountryencoding." If the value "othercountryencoding" is selected, further information regarding the country codes used in the instance should be supplied in <conventiondeclaration>.
Use @dateencoding to identify the rules for values provided in @normal, @standarddate, @notbefore, and @notafter in date elements. This attribute may be set to "iso8601" or "otherdateencoding." If the value "otherdateencoding" is selected, further information regarding the rules for normalized date values used in the instance should be supplied in <conventiondeclaration>.
Use @langencoding to identify the authoritative source for values supplied in @lang and @langcode. This attribute may be set to "iso639-1," "iso639-2b," "iso639-3," or "otherlangencoding." Previous versions of EAD prescribed the use of ISO 639-2b, so "iso639-2b" may be the most commonly used value. If the value "otherlangencoding" is selected, further information regarding the language codes used in the instance should be supplied in <conventiondeclaration>.
May contain:
conventiondeclaration, filedesc, languagedeclaration, localcontrol, localtypedeclaration, maintenanceagency, maintenancehistory, maintenancestatus, otherrecordid, publicationstatus, recordid, representation, sources
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: iso3166-1, othercountryencoding)
Optional (values limited to: iso8601, otherdateencoding)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: iso639-1, iso639-2b, iso639-3,
otherlangencoding)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: iso15511, otherrepositoryencoding)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: iso15924, otherscriptencoding)
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
<controlaccess>
Controlled Access Headings [toc]
Summary:
An element that binds together elements containing access headings for the
described materials.
Description and Usage:
Use <controlaccess> to bundle in a single group access points — names,
topics, places, functions, occupations, titles, and genre terms — that
represent the contexts and contents of the materials described. Although
<controlaccess> is often used within <archdesc> to provide
significant access terms for the entirety of the materials described, it may be
used at the component level to provide terms specific to a component if so
desired.
<controlaccess> helps to enable authority-controlled searching across
finding aids, particularly when its children contain terms drawn from
nationally or internationally controlled vocabularies such as the Library of
Congress Subject Headings (LCSH) or the UK Archival Thesaurus (UKAT) for
topics, the Virtual International Authority File (VIAF) for names, or GeoNames
for places.
See also:
<relations> contains one or more <relation> elements that
identify an external entity or concept, and describe the nature of the
relationship of the described materials to that entity or concept.
May contain:
blockquote, chronlist, controlaccess, corpname, famname, function, genreform, geogname, head, list, name, occupation, p, persname, subject, table, title
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<controlnote>
Control Note [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <notestmt>, used to provide a general note related to
the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <controlnote> to record general descriptive information about a
finding aid. <controlnote> is similar to the "general notes" in
traditional bibliographic descriptions. Repeat <controlnote> if it is
necessary to capture multiple but separate general statements about the finding
aid.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local practice requires recording the type of
note.
See also:
Use <descriptivenote> for general information about the materials
being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, repeatable
Examples:
<notestmt>
<controlnote localtype="bpg">
</notestmt><p>This encoded finding aid is compliant with the Yale EAD Best
Practice Guidelines, Version 1.0.</p>
</controlnote><notestmt>
<controlnote>
<p>Contact information:
</controlnote><ref show="new" actuate="onrequest" href="http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.mss/mss.contact">
http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.mss/mss.contact</ref>
</p>http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.mss/mss.contact</ref>
<controlnote>
</notestmt><p>Catalog Record:
</controlnote><ref href="http://lccn.loc.gov/mm82036905" actuate="onrequest" linktitle="MARC record for collection">http://lccn.loc.gov/mm82036905</ref>
</p><conventiondeclaration>
Convention Declaration [toc]
Summary:
An optional child element of <control>, used to bind together
<citation> with optional <abbr> and <descriptivenote>
elements that identify rules or conventions applied in compiling the
description.
Description and Usage:
A statement about any rules or conventions used in constructing the
description. Examples include content standards, controlled vocabularies, or
thesauri.
You may use <conventiondeclaration> to:
identify any rules used to formulate the content of controlled access
terms and referenced in @rules.
identify any controlled vocabularies used to populate controlled access terms and referenced in @source.
identify any related encoding schemes referenced in @relatedencoding.
specify standards used to formulate data elements or provide codes.
<conventiondeclaration> should always be included when @langencoding, @scriptencoding, @dateencoding, @countryencoding, or @repositoryencoding are set to the "other" value.
identify any controlled vocabularies used to populate controlled access terms and referenced in @source.
identify any related encoding schemes referenced in @relatedencoding.
specify standards used to formulate data elements or provide codes.
<conventiondeclaration> should always be included when @langencoding, @scriptencoding, @dateencoding, @countryencoding, or @repositoryencoding are set to the "other" value.
Each additional rule or set of rules, controlled vocabulary, or standard should
be contained in a separate <conventiondeclaration>.
It may not be necessary to include <conventiondeclaration> in such cases
where the above scenarios are addressed in local or consortial
documentation.
<abbr> may be used to identify the standard or controlled vocabulary in
a coded structure. The content of <abbr> should be the same value given
to rules, source, or relatedencoding when
referencing a given convention. Any notes relating to how these rules or
conventions have been used may be given within <descriptivenote>.
The prescribed order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<abbr>
<citation>
<descriptivenote>
<citation>
<descriptivenote>
See also:
Use <localtypedeclaration> to identify local values used in
@localtype attributes.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.7.2
MODS <descriptionStandard>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<control> [. . .]
<conventiondeclaration>
<abbr>ISAD(G)</abbr>
<citation>ISAD(G): General International Standard Archival
Description, second edition, Ottawa 2000</citation>
</conventiondeclaration><conventiondeclaration>
<abbr>NCARules</abbr>
<citation>National Council on Archives, Rules for the Construction of
Personal, Place and Corporate Names, 1997</citation>
</conventiondeclaration><conventiondeclaration>
[. . .] </control><citation>ISO 8601 - Data elements and interchange formats -
Information interchange - Representation of dates and times, 2nd ed.,
Geneva: International Standards Organization, 2000</citation>
</conventiondeclaration><control> [. . .]
<conventiondeclaration>
[. . .] </control><abbr>DACS</abbr>
<citation href="http://www2.archivists.org/standards/DACS" lastdatetimeverified="2015-07-02T16:30:21-5:00" linktitle="DACS in HTML on SAA website" actuate="onload" show="new">Describing Archives: a Content
Standard</citation>
<descriptivenote>
</conventiondeclaration><p>DACS was used as the primary description standard.</p>
</descriptivenote><corpname>
Corporate Name [toc]
Summary:
An element for identifying the name of an organization or group of people.
Description and Usage:
Identifies the name of an organization or group of people that act as an
organizational entity. Examples include names of associations, institutions,
business firms, nonprofit enterprises, governments, government agencies,
projects, programs, religious bodies, churches, conferences, athletic contests,
exhibitions, expeditions, fairs, and ships.
<corpname> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part> elements may be used to capture each component
of the corporate name, e.g.,
Part 1: Yale University
Part 2: Dept. of Astronomy
Use <corpname> within <controlaccess> for encoding corporate
names as defined by controlled vocabularies or according to appropriate rules.
You may also use <corpname> for encoding corporate names as they appear
within text.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the corporate body in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local use requires specification of the type of corporate name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the corporate name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the corporate name has to the described materials, for example, "compiler," "creator," "collector," or "subject." The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the corporate body in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local use requires specification of the type of corporate name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the corporate name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the corporate name has to the described materials, for example, "compiler," "creator," "collector," or "subject." The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, origination, p, physfacet, ref, repository, unittitle
References:
MARC 610, 611, 710, 711
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<controlaccess>
<corpname encodinganalog="610" identifier="http://viaf.org/viaf/139169065" lang="eng">
<part>Hudson's Bay Company</part>
</corpname><corpname encodinganalog="610" identifier="http://viaf.org/viaf/139169065" lang="fre">
</controlaccess><part>Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson</part>
</corpname><archdesc level="collection">
<did>
[ . . .] </archdesc><origination label="Creator">
[ . . .] </did><corpname encodinganalog="110" source="lcnaf">
</origination><part>National Association for the Advancement of Colored
People</part>
</corpname><custodhist>
Custodial History [toc]
Summary:
An element for information about the chain of ownership or custody of the
materials being described, before they reached the archives.
Description and Usage:
<custodhist> may be used to describe both physical possession and
intellectual ownership, providing details of changes of ownership and/or
custody that may be significant in terms of authority, integrity, and
interpretation.
See also:
Use <acqinfo> to record information about the immediate source of
the described materials and the circumstances under which they were received
by the repository.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.2.3
MARC 561
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<custodhist>
<p>The George Franklin Papers were maintained by the staff of the
Mayor's Office, City of Irvine, California, in the records storage
facility at City Hall from the time of Franklin's death in 1972 until
they were transferred, at his family's request, to Special Collections
and Archives, The UC Irvine Libraries, in 1988.</p>
</custodhist><custodhist>
<chronlist>
</custodhist><chronitem>
<daterange>
<fromdate standarddate="1972">1972</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1988">1988</todate>
</daterange><geogname>
<part>Irvine, California</part>
</geogname><event>Held by Mayor's office</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
<daterange>
<fromdate standarddate="1988">1988</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="2008">2008</todate>
</daterange><geogname>
<part>Irvine, California</part>
</geogname><event>Held by Special Collections and Archives, The UC Irvine
Libraries</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle standarddate="2009">2009</datesingle>
<geogname>
<part>Austin, Texas</part>
</geogname><event>Held by Harry Ransom Center</event>
</chronitem><dao>
Digital Archival Object [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> used for linking to born digital records or a
digital representation of the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
<dao> is a linking element that uses href to connect to born
digital records or digital representations of the described materials. Digital
representations may include graphic images, audio or video clips, images of
text pages, and electronic transcriptions of text. The objects can be selected
examples, or digital surrogates of all the materials in a collection, fonds, or
an individual file.
An optional <descriptivenote> may be used to provide a description of
the object being linked to, if the information in a sibling<unittitle>
is insufficient.
Attribute usage:
Use the required @daotype to specify if <dao> is born
digital ("borndigital"), was digitized by the repository from physical
holdings ("derived"), if the type is unknown, or other. If selecting
"otherdaotype," then use @otherdaotype to further specify the
type.
Use @coverage, with the possible values "whole" or "part," to indicate whether the digital archival object represents the entire set or records being described or a part of it.
Use @coverage, with the possible values "whole" or "part," to indicate whether the digital archival object represents the entire set or records being described or a part of it.
See also:
<daoset> for grouping two or more related <dao> elements.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MODS <location><url>
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: none, onload, onrequest, other)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional (values limited to: part, whole)
Required (values limited to: borndigital, derived, unknown,
otherdaotype)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c>
<did>
</c><unittitle>Quilting bee, Union Town, Md.</unittitle>
<unitdate>1930</unitdate>
<physdesc>1 photograph</physdesc>
<dao daotype="derived" actuate="onload" show="embed" href=" http://www.lib.utexas.edu/taro/utcah/00462/cah-00462.jpg "></dao>
</did><daoset label="Digital Objects" coverage="part">
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="part" actuate="onload" show="embed" linktitle="Chapter 1" localtype="thumbnail" href="http://imgs.ud.edu/archives/image/f12001_1thumb.gif"></dao>
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="part" actuate="onrequest" show="new" linktitle="Chapter 1" localtype="fullsize" href="http://imgs.ud.edu/archives/image/f12001_1.jpg"></dao>
</daoset><daoset label="Digital Objects" coverage="whole">
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="whole" actuate="onrequest" show="new" linkrole="The Pippa and Porthos (cover)" href="http://brbl-media.library.yale.edu/images/1044151_quarter.jpg"></dao>
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="whole" actuate="onrequest" show="new" linkrole="The Pippa and Porthos (title page)" href="http://brbl-media.library.yale.edu/images/1044153_quarter.jpg"></dao>
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="whole" actuate="onrequest" show="new" linkrole="The Pippa and Porthos (p.1)" href="http://brbl-media.library.yale.edu/images/1044154_quarter.jpg"></dao>
[.
. .]
<descriptivenote>
</daoset><p>Digitized pages of Barrie’s "The Pippa and Porthos."</p>
</descriptivenote><daoset>
Digital Archival Object Set [toc]
Summary:
An element for binding together two or more links to digital archival
objects.
Description and Usage:
Use <daoset> to group multiple links to born digital records or digital
representations of the materials being described. <dao> and
<daoset> allow the content of an archival collection or record group
to be incorporated into the finding aid. These digital representations include
graphic images, audio or video clips, images of text pages, and electronic
transcriptions of text. The objects can be selected examples, or digital
surrogates of all the materials in a collection, fonds, or an individual
file.
<daoset> must contain more two or more <dao> elements, which may
be followed by an optional <descriptivenote> to provide a description of
the objects being linked to.
Attribute usage:
Use @coverage to indicate whether the set is part of or the
whole of the unit being described.
Use @localtype to indicate the nature of the set of digital archival objects.
Use @localtype to indicate the nature of the set of digital archival objects.
See also:
<dao> for linking to a single digital archival object.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MODS <location><url>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: part, whole)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<daoset label="Digital Objects" coverage="part">
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="part" actuate="onload" show="embed" linktitle="Chapter 1" localtype="thumbnail" href="http://imgs.ud.edu/archives/image/f12001_1thumb.gif"></dao>
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="part" actuate="onrequest" show="new" linktitle="Chapter 1" localtype="fullsize" href="http://imgs.ud.edu/archives/image/f12001_1.jpg"></dao>
</daoset><daoset label="Digital Objects" coverage="whole">
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="whole" actuate="onrequest" show="new" linkrole="The Pippa and Porthos (cover)" href="http://brbl-media.library.yale.edu/images/1044151_quarter.jpg"></dao>
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="whole" actuate="onrequest" show="new" linkrole="The Pippa and Porthos (title page)" href="http://brbl-media.library.yale.edu/images/1044153_quarter.jpg"></dao>
<dao daotype="derived" coverage="whole" actuate="onrequest" show="new" linkrole="The Pippa and Porthos (p.1)" href="http://brbl-media.library.yale.edu/images/1044154_quarter.jpg"></dao>
[.
. .]
<descriptivenote>
</daoset><p>Digitized pages of Barrie’s "The Pippa and Porthos."</p>
</descriptivenote><date>
Date [toc]
Summary:
An element used to express a date.
Description and Usage:
Use <date> to highlight any dates that merit encoding and are not more
appropriately encoded in other, more specific date-related elements, e.g.,
<unitdate> or <unitdatestructured>.
Attribute usage:
A standard numeric form of the date (YYYY-MM-DD) can be expressed with
@normal to facilitate machine processing of dates, for example,
1948-01-01/1998-04-01 (YYYY-MM-DD/YYYY-MM-DD), or 1948/1998
(YYYY/YYYY).
Use @localtype to supply a more specific designation, for example, "life," "flourish," "depiction," "publication," or "acquisition."
Use @certainty to indicate the degree of precision in the dating, for example, "circa," "approximately," or "after."
Use @calendar to indicate the calendar from which the date stems, e.g., "gregorian".
Use @era to indicate the era in which the date occurred, e.g., "ce" for Common Era.
Use @normal to capture a standardized expression of the date or dates to facilitate machine processing.
Use @localtype to supply a more specific designation, for example, "life," "flourish," "depiction," "publication," or "acquisition."
Use @certainty to indicate the degree of precision in the dating, for example, "circa," "approximately," or "after."
Use @calendar to indicate the calendar from which the date stems, e.g., "gregorian".
Use @era to indicate the era in which the date occurred, e.g., "ce" for Common Era.
Use @normal to capture a standardized expression of the date or dates to facilitate machine processing.
See also:
Do not confuse with <unitdate> and <unitdatestructured>,
which provide the date of creation and other relevant dates of the described
materials.
Do not confuse with <daterange>, <dateset>, and <datesingle>, which are used to record dates in the creation (within <unitdatestructured>), contextual history (within <chronlist>), local control of the described materials (within <localcontrol>), or their relationships to other entities (within <relations>).
Do not confuse with <eventdatetime>, which is used for the date and time of a maintenance event in the history of the EAD instance.
Do not confuse with <daterange>, <dateset>, and <datesingle>, which are used to record dates in the creation (within <unitdatestructured>), contextual history (within <chronlist>), local control of the described materials (within <localcontrol>), or their relationships to other entities (within <relations>).
Do not confuse with <eventdatetime>, which is used for the date and time of a maintenance event in the history of the EAD instance.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<bibref>
<persname relator="author">
<part>Kinder, Dolores.</part>
</persname><title>
<part>Once Upon a Lullaby.</part>
</title><geogname>
<part>New York: </part>
</geogname><corpname relator="publsher">
<part>Wells & Sons, </part>
</corpname><date localtype="publication"> 1931 </date>
</bibref><acqinfo>
<p>This collection, number
</acqinfo><num localtype="donor">1988-015,</num>
was donated by Mrs. Dolores Franklin on
<date localtype="acquisition" normal="19880423"> April 23, 1988. </date>
</p><daterange>
Date Range [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element for binding together <fromdate> and <todate> in
order to represent a range of dates.
Description and Usage:
Use <daterange> to express a range of dates in the creation, contextual
history, or local control of the described materials, or their relationships to
other entities such as persons, families, corporate bodies, resources,
functions, events, places, and topics. <daterange> contains
<fromdate> and/or <todate>, and therefore may express a range
of dates as a starting point with no end point, a start and end point, or an
end point with no starting point. The content of the children of
<daterange> is intended to be a human-readable, natural language
expression of the date. If, however, indexing or other machine processing of
dates is desired, standarddate should be used on the children of
<daterange> to record the date in machine-processable form as
well.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype to supply a more specific characterization of
the date range.
See also:
If an event or relationship has a single date, use
<datesingle>.
Record a complex date (for example, one that includes single dates and date ranges) in <dateset>.
For the date and time of a maintenance event in the history of the EAD instance, use <eventdatetime>.
Record a complex date (for example, one that includes single dates and date ranges) in <dateset>.
For the date and time of a maintenance event in the history of the EAD instance, use <eventdatetime>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <chronitem> and <unitdatestructured>: One of
<daterange>, <dateset>, or <datesingle> is required,
not repeatable
Within <dateset>: One of <daterange> or <datesingle> is
required, repeatable
Within <localcontrol> and <relation>: Optional, not
repeatable
Examples:
<unitdatestructured calendar="gregorian" era="ce">
<dateset>
</unitdatestructured><datesingle standarddate="1963-01-22">22 January
1963</datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1971-06-01">1 June 1971</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1974-04-30">30 April 1974</todate>
</daterange><chronitem>
<daterange>
<fromdate>1819</fromdate>
<todate>1820</todate>
</daterange><event>Studies theology at Yale College</event>
</chronitem><unitdatestructured unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notafter="1962">1962</fromdate>
<todate notafter="1968">1968</todate>
</daterange><unitdatestructured certainty="circa" unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notbefore="1971" notafter="1975">around 1973</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1992">1992</todate>
</daterange><dateset>
Date Set [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element for encoding complex dates that cannot be adequately
represented in one <datesingle> or <daterange>.
Description and Usage:
<dateset> binds together single dates and date ranges, multiple single
dates, or multiple date ranges. <dateset> is used in situations where
complex date information needs to be conveyed and requires at least two child
elements. These can be a combination of <datesingle> and
<daterange>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <chronitem> and <unitdatestructured>: One of
<daterange>, <dateset>, or <datesingle> is required,
not repeatable
Within <relation>: Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<unitdatestructured calendar="gregorian" era="ce">
<dateset>
</unitdatestructured><datesingle standarddate="1963-01-22">22 January
1963</datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1971-06-01">1 June 1971</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1974-04-30">30 April 1974</todate>
</daterange><unitdatestructured>
<dateset>
</unitdatestructured><daterange>
<fromdate>1900</fromdate>
<todate>1910</todate>
</daterange><datesingle>1921 </datesingle>
</dateset><datesingle>
Single Date [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding an individual date related to the materials being
described.
Description and Usage:
<datesingle> is an element for expressing a single date in the creation,
contextual history, or local control of the described materials, or in their
relationships to other entities such as persons, families, corporate bodies,
resources, functions, events, places, and topics. <datesingle> may
contain actual or approximate dates. The content of the element is intended to
be a human-readable, natural language expression of the date. If, however,
indexing or other machine processing of dates is desired,
standarddate should be used to record the date in
machine-processable form as well.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype to supply a more specific characterization of
the date.
Use @notafter and @notbefore to capture the earliest and latest possible dates in machine-processable form in cases when the date is uncertain.
Use @standarddate to provide a machine-processable form of the date. Note that this attribute is for a single date only, while the @normal attribute available on <unitdate> can express a single date or date range.
Use @notafter and @notbefore to capture the earliest and latest possible dates in machine-processable form in cases when the date is uncertain.
Use @standarddate to provide a machine-processable form of the date. Note that this attribute is for a single date only, while the @normal attribute available on <unitdate> can express a single date or date range.
See also:
If an event or relationship has a range of dates, use
<daterange>.
Record a complex date (for example, one that includes single dates and date ranges) in <dateset>.
For the date and time of a maintenance event in the history of the EAD instance, use <eventdatetime>.
Record a complex date (for example, one that includes single dates and date ranges) in <dateset>.
For the date and time of a maintenance event in the history of the EAD instance, use <eventdatetime>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <chronitem> and <unitdatestructured>: One of
<daterange>, <dateset>, or <datesingle> is required,
not repeatable
Within <dateset>: One of <daterange> or <datesingle> is
required, repeatable
Within <localcontrol> and <relation>: Optional, not
repeatable
Examples:
<unitdatestructured calendar="gregorian" era="ce">
<dateset>
</unitdatestructured><datesingle standarddate="1963-01-22">22 January 1963 </datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1971-06-01">1 June 1971</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1974-04-30">30 April 1974</todate>
</daterange><chronitem>
<datesingle> 1793 May 24 </datesingle>
<geogname>
<part>Deerfield, Mass</part>
</geogname><event>Born</event>
</chronitem><defitem>
Definition List Item [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element for binding pairs of labels and items within a list.
Description and Usage:
An element, used within a definition list, that pairs a required <label>
and <item>. The item may be an expansion of the label, as in a list of
abbreviations. Definition lists are often displayed in two columns.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<list listtype="deflist">
<listhead>
<head01>Abbreviation</head01>
<head02>Expansion</head02>
</listhead><defitem>
<label>ALS</label>
<item>Autograph Letter Signed</item>
</defitem><defitem>
</list><label>TLS</label>
<item>Typewritten Letter Signed</item>
</defitem><descriptivenote>
Descriptive Note [toc]
Summary:
An element used to provide general descriptive information related to its
parent element.
Description and Usage:
<descriptivenote> provides additional descriptive information about the
element in which it is contained. Notes must contain one or more <p>
elements.
See also:
Do not confuse with <odd>, which is used for other descriptive
data that is not easily incorporated into other named elements within
<archdesc> and <c>.
May contain:
May occur within:
conventiondeclaration, dao, daoset, langmaterial, languagedeclaration, languageset, localtypedeclaration, maintenanceagency, physdescstructured, relation, source
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<conventiondeclaration>
<abbr>AU-CRS</abbr>
<citation>Australia’s Commonwealth Records Series (CRS)
System</citation>
<descriptivenote>
</conventiondeclaration><p>Series controlled and described under the rules of the National
Archives of Australia’s Commonwealth Records Series (CRS)
System.</p>
</descriptivenote><conventiondeclaration>
<abbr>DACS</abbr>
<citation href="http://www2.archivists.org/standards/DACS" lastdatetimeverified="2015-07-02T16:30:21-5:00" linktitle="DACS in HTML on SAA website" actuate="onload" show="new">Describing Archives: a Content
Standard</citation>
<descriptivenote>
</conventiondeclaration><p>DACS was used as the primary description standard.</p>
</descriptivenote><langmaterial>
<languageset>
<language langcode="lat">Latin</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="ang">Old English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>The majority of the documents are written in Modern English.
Roberts copies multiple passages from original manuscripts in Latin
and Old English.</p>
</descriptivenote><did>
Descriptive Identification [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element that encloses information essential for identifying the
material being described.
Description and Usage:
<did> binds together other elements that provide core information needed
for identifying the described materials. <did> occurs in
<archdesc> and <c>, <c01> - <c12>. The various
<did> child elements are intended for brief, clearly designated
statements of information, whereas following sibling elements of <did>
such as <custodhist>, <arrangement>, or <scopecontent>
allow for more detailed, narrative description.
<did> groups elements that constitute a good basic description of an
archival unit. This grouping ensures that the same data elements and structure
are available at every level of description within the EAD hierarchy. It
facilitates the retrieval or output of a coherent body of elements for resource
discovery and recognition.
The <did> in <archdesc> is sometimes called the high-level
<did>, because it covers the entirety of the materials described by
the EAD instance. Consider using the following child elements in the high-level
<did>: <origination>, <unittitle>, <unitdate> or
<unitdatestructured>, <physdesc> or
<physdescstructured>, <repository>, and <abstract>.
<unitid> and <physloc> are suggested if applicable to a
repository's practice. <did> within components can have fewer elements,
and might have only <container> or <unitid> and
<unittitle>.
May contain:
abstract, container, dao, daoset, didnote, head, langmaterial, materialspec, origination, physdescset, physdesc, physdescstructured, physloc, repository, unitdate, unitdatestructured, unitid, unittitle
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc localtype="inventory" level="subgrp">
<did>
[ . . .] </archdesc><head>Overview of the Records</head>
<repository label="Repository:">
<corpname>
</repository><part>Minnesota Historical Society</part>
</corpname><origination label="Creator:">
<corpname>
</origination><part>Minnesota.</part>
<part>Game and Fish Department</part>
</corpname><unittitle label="Title:">Game laws violation
records,</unittitle>
<unitdate label="Dates:">1908-1928</unitdate>
<abstract label="Abstract:">Records of prosecutions for and seizures
of property resulting from violation of the state's hunting and
fishing laws.</abstract>
<physdesc label="Quantity:">2.25 cu. ft. (7 v. and 1 folder in 3
boxes)</physdesc>
</did><c02 id="able-pa" level="file">
<did>
</c02><unittitle>Adult Basic and Literacy Education, Pennsylvania
(ABLE)</unittitle>
<abstract>includes "Focus on..." newsletters</abstract>
<physdescstructured coverage="whole" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity>21</quantity>
<unittype>reels</unittype>
</physdescstructured><container localtype="Box">20</container>
</did><c03>
<did>
</c03><unittitle>Class Notes, Undergraduate</unittitle>
<unitdatestructured unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notafter="1962">1962</fromdate>
<todate notafter="1968">1968</todate>
</daterange><physdesc>12 notebooks</physdesc>
<container localtype="boxes">5-6</container>
<didnote>The notebooks contain months and days, not years. Estimated
dates are based on the years Scully attended the University of
Maryland.</didnote>
</did><didnote>
Descriptive Identification Note [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that can express any kind of explanatory
information.
Description and Usage:
<didnote> can encode textual notes within <did> that are not more
appropriately encoded in the other available elements.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.6.1
MARC 500
MODS <note>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc level="collection">
<did>
</archdesc><repository label="repository" encodinganalog="852">
<corpname>
<part>Library of Congress, </part>
<part>Prints and Photographs Division,</part>
</corpname><address>
</repository><addressline>Washington, D.C. 20540</addressline>
</address><didnote> For information about Prints and Photographs Division
collections and services, see the Prints and Photographs Division's
Reading Room Home Page:
</did><ptr actuate="onrequest" href="http://lcweb.loc.gov/rr/print.htm" show="new" linkrole="text/html"></ptr>
</didnote><did>
<unittitle>Class Notes, Undergraduate</unittitle>
<unitdatestructured unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notafter="1962">1962</fromdate>
<todate notafter="1968">1968</todate>
</daterange><physdesc>12 notebooks</physdesc>
<container localtype="boxes">5-6</container>
<didnote> The notebooks contain months and days, not years. Estimated
dates are based on the years Scully attended the University of Maryland.
</didnote>
</did><dimensions>
Dimensions [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <physdescstructured> that provides information about
the size of the material being described.
Description and Usage:
<dimensions> may be used to specify the size, in two or three
dimensions, of the units identified by <unittype> within
<physdescstructured>. It usually includes numerical data. Express
measurements in any convenient unit as indicated in the unit
attribute. Multiple dimensions, for example, height-by-width, can be encoded in
a single <dimensions> or in separate <dimensions> with
distinctive localtype values.
Attribute usage:
If the kind of measurement is not clear in the text, @unit may
be used to specify this information, for example, "inches" or
"centimeters."
If desired, @localtype may be used to capture the kind of dimensions being measured, such as "height" or "circumference."
If desired, @localtype may be used to capture the kind of dimensions being measured, such as "height" or "circumference."
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity>5</quantity>
<unittype>dageurreotypes</unittype>
<physfacet>hand-tinted</physfacet>
<dimensions>6.5 x 8.5 inches</dimensions>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="whole" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity>10</quantity>
<unittype>posters</unittype>
<dimensions>
</physdescstructured><dimentions unit="inches" localtype="height">23</dimentions>
<dimentions unit="inches" localtype="width">35</dimentions>
</dimensions><dsc>
Description of Subordinate Components [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element that bundles information about the hierarchical groupings of
the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
Use <dsc> to wrap subordinate components in the archival hierarchy of
the materials being described. Although <dsc> may repeat, it is
recommended to include only a single <dsc> element. Because it is a
wrapper element and not an essential part of archival description, <dsc>
may be deprecated in future versions of EAD. Avoiding multiple <dsc>
elements within an EAD instance will make future migrations simpler.
The subordinate components can be presented in several different forms or
levels of descriptive detail, which are identified by the element's optional
dsctype. For example, "combined" is used when the narrative
description of a series is followed immediately by a listing of the contents of
that series within a single <dsc>. The dsctype value
"analyticover" identifies an overview description of series and subseries,
which might be followed by a second <dsc> with the dsctype
set to "in-depth" that provides a more detailed listing of the content of the
materials, including information about the container numbers associated with
those materials. The dsctype "otherdsctype" is for models that do
not follow any of the above-mentioned formats, in which case
otherdsctype can then be used to specify a particular
presentation model.
If <dsc> contains children other than <thead> or component
elements (<c>, <cXX>), those elements must come first, followed
by the optional <thead>, then <c> or <c01>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional (values limited to: analyticover, combined, in-depth,
otherdsctype)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<dsc dsctype="combined">
<c01 level="series">
[ . . .] </dsc><did>
<unittitle>Activities</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1965-1971</unitdate>
<physdesc>0.3 linear ft.</physdesc>
</did><scopecontent>
<p>The Activities series gives examples of the types of activities
offered at the camp. The folders contain reports, schedules, and
inventories from each activity area of the camp. These records are
predominantly from the late 1960s and early 1970s and replicate
some of the information found in the staff manuals.</p>
</scopecontent><c02 level="file">
<did>
</c02><container localtype="box">1</container>
<unittitle>General</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1970-1971</unitdate>
</did><c02 level="file">
<did>
</c02><container localtype="box">1</container>
<unittitle>Camp Crafts</unittitle>
<unitdate>1967</unitdate>
</did><c02 level="file">
<did>
</c02><container localtype="box">1</container>
<unittitle>Education Program</unittitle>
<unitdate>1967</unitdate>
</did><c02 level="file">
[ . . .] </c01><did>
</c02><container localtype="box">1</container>
<unittitle>Expressive Arts</unittitle>
<unitdate>1970</unitdate>
</did><dsc dsctype="analyticover">
<c01 level="series">
<did>
<unitid>1-429-1</unitid>
<unittitle>Forest Stand Maps by Township and Basemap </unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1958-1979</unitdate>
<physdesc>36 ft. (approx. 1700 sheets) of cartographic
records.</physdesc>
<materialspec>Scale: predominantly 4 inches to 1 mile
(1:15,840)</materialspec>
</did><scopecontent>
</c01><p>Series consists of forest stand maps. A map sheet was created
for each township of the surveyed section of the province and for
each basemap area in unsurveyed areas.</p>
[ . . .]
</scopecontent><c01 level="series">
[ . . .] </dsc><did>
<unitid>RG 1-429-2</unitid>
<unittitle>Forest Stand Map Composites</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1958-1971</unitdate>
<physdesc>ca.70 maps</physdesc>
<materialspec>Scale: 1 inch to 1 mile</materialspec>
</did><scopecontent>
</c01><p>Series consists of composite maps of the forest resource
inventory data from all the townships within a Forestry Management
Unit. The composites offer a broader view of an area than the
township/basemaps, however the forest stand statistics are quite
small and difficult to read.</p>
[ . . .] </scopecontent><dsc dsctype="in-depth">
<c01 level="series">
<did>
<unitid>Series 1</unitid>
<unittitle>Administrative Records</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1912-1956</unitdate>
</did><c02>
<did>
</c02><container id="mss92-894c-bx1" localtype="box">Box
1</container>
<container parent="mss92-894c-bx1" label="Folder" localtype="folder">7-8 </container>
<unittitle>Annual reports</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1912-16, 1922</unitdate>
</did><c02>
<did>
</c02><container parent="mss92-894c-bx1" label="Folder" localtype="folder">9 </container>
<unittitle>Board of Directors, Minutes and
correspondence</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1947-1949</unitdate>
</did><c02>
<did>
</c02><container parent="mss92-894c-bx1" label="Folder" localtype="folder">10 </container>
<unittitle>Contracts and specifications for construction of
nurses' quarters</unittitle>
<unitdate>ca. 1947</unitdate>
</did><c02>
</c01><did>
</c02><container parent="mss92-894c-bx1" label="Folder" localtype="folder">11 </container>
<unittitle>Marin County Reports</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1955-1956</unitdate>
</did><c01 level="series">
</dsc><did>
<unitid>Series 3</unitid>
<unittitle>Philip King Brown</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1910-1931, n.d.</unitdate>
</did><c02>
<did>
</c02><container parent="mss92-894c-bx1" label="Folder" localtype="folder">21 </container>
<unittitle>Correspondence</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1910-1931</unitdate>
</did><c02>
[ . . .] </c01><did>
</c02><container parent="mss92-894c-bx1" label="Folder" localtype="folder">22 </container>
<unittitle>Writings</unittitle>
<unitdate>n.d.</unitdate>
</did><ead>
Encoded Archival Description [toc]
Summary:
The required root element of an EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
<ead> wraps all other elements in an Encoded Archival Description
document or finding aid. Also referred to more specifically as an inventory or
register, a finding aid establishes physical and intellectual control over many
types of archival materials and helps researchers understand and access the
materials being described. <ead> must contain <control> followed
by <archdesc>.
Attribute usage:
The @audience value may be set to "external" to display data in
all descendant elements, unless the value is changed for a specific
element.
Use @base to specify a URI (other than the base URI of the EAD instance) to be used for resolving relative URIs within <ead> or descendant elements.
Use @base to specify a URI (other than the base URI of the EAD instance) to be used for resolving relative URIs within <ead> or descendant elements.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
<edition>
Edition [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <editionstmt> for recording the version of an EAD
instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <edition> to indicate the version of an EAD instance. Generally, a
new edition of a finding aid represents substantial additions or changes and
should supersede previous online versions.
See also:
Use <maintenanceevent> to record the date when changes have been
introduced to the EAD instance, the type of changes, and the person or
organization responsible. The child <eventdescription> optionally
allows you to provide details about the changes.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <editionstmt>, one of <edition> or <p> is required,
repeatable
<editionstmt>
Edition Statement [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <filedesc>, used to provide information about the
version of an EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <editionstmt> to indicate the version of an EAD instance, as well as
providing any related narrative information. Generally, a new edition of a
finding aid represents substantial additions or changes and should supersede
previous online versions.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
<emph>
Emphasis [toc]
Summary:
A formatting element for marking words or phrases that are emphasized or
specially formatted.
Description and Usage:
A formatting element for marking words or phrases that are emphasized for
linguistic effect or specially formatted. Use render to specify the
kind of emphasis, e.g., bold or italic, or formatting, e.g. superscript or
subscript.
When the content of an entire element should always be rendered in italics or
some other display feature, use the style sheet functions instead of
<emph>.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, addressline, archref, author, bibref, citation, container, date, datesingle, didnote, dimensions, edition, emph, entry, event, fromdate, head, head01, head02, head03, item, label, materialspec, num, p, part, physdesc, physfacet, physloc, publisher, quote, ref, sponsor, subtitle, titleproper, todate, unitdate, unitid, unittitle
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: altrender, bold, bolddoublequote,
bolditalic, boldsinglequote, boldsmcaps, boldunderline, doublequote,
italic, nonproport, singlequote, smcaps, sub, super, underline)
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<abstract label="Abstract">Papers document Donald C. Stone's work with
Ornstein and Swencionis on the
<emph render="italic">est</emph>
Outcome Project, and the development of his doctoral research, including his
various publications on the human potential movement, up to the completion
of his doctoral dissertation. </abstract><entry>
Table Entry [toc]
Summary:
A formatting element that designates the contents of a cell in a table.
Description and Usage:
In a table, a cell is the intersection of a row and a column. Attributes of
<entry> control cell spanning, alignment of the contents, and the
rules on the cell edges. The attributes can be specified for <entry> or
inherited from the nearest of the following table elements: <table>,
<tgroup>, <colspec>, <tbody>, <thead>, or
<row>.
Attribute usage:
Three attributes are used together to force horizontal alignment on a
specific character, such as a decimal point.
See also:
Related elements <colspec>, <row>, <table>,
<tbody>, <tgroup>, and <thead>.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, list, name, num, occupation, persname, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: center, char, justify, left,
right)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: bottom, middle, top)
Availability:
Required, repeatable
Example:
<table frame="none">
<tgroup cols="3">
</table><colspec colnum="1" colname="1" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<colspec colnum="2" colname="2" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<colspec colnum="3" colname="3" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<thead>
<row>
</thead><entry colname="1"> Major Family Members</entry>
<entry colname="2"> Spouses</entry>
<entry colname="3"> Children</entry>
</row><tbody>
</tgroup><row>
[. . .] </tbody><entry colname="1"> John Albemarle (1760-1806) </entry>
<entry colname="2"> Mary Frances Delaney (1769-1835) </entry>
<entry colname="3"> John Delaney Albemarle (1787-1848)
</entry>
</row><event>
Event [toc]
Summary:
An element describing a happening or occurrence recorded within a chronology
list.
Description and Usage:
Use <event> within <chronitem> to pair a description of the event
with one or more dates and an optional place. If one or more events occurred
related to the date(s) in question or if more than one place is associated with
the event, use <chronitemset> to bundle multiple <event> – or
<geogname> – elements.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, list, name, num, occupation, persname, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <chronitem>: Optional, not repeatable
Within <chronitemset>: Required, repeatable
Example:
<chronlist>
<chronitem>
<datesingle>2015</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Woodbury, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><geogname>
<part>Roseville, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Opens additional stores</event>
</chronitemset><chronitem>
<datesingle>1948</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Minneapolis, Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Graduates from the University of Minnesota</event>
<event>Begins work as a receptionist for the Humphrey for Senator
Committee</event>
</chronitemset><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle>March 1957</datesingle>
<chronitemset>
<geogname>
<part encodinganalog="651" localtype="a">Biwabik,
Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Dies</event>
</chronitemset><chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part encodinganalog="651" localtype="a">Minneapolis,
Minnesota</part>
</geogname><event>Buried in Lakewood Cemetery</event>
</chronitemset><eventdatetime>
Event Date and Time [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <maintenanceevent> that records the date and
time of a specific maintenance action for an EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
<eventdatetime> is for recording the date and time that a maintenance
event occurred. Examples of maintenance events include the creation, update,
revision, or other modification to an EAD instance. If desired, the date and
time may be captured in natural language in the element.
Attribute usage:
Use @standarddatetime to provide a machine-processable
expression of the date or date and time, formulated according to the ISO
8601 standard.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.7.3
MODS <recordCreationDate>, <recordChangeDate>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (must follow pattern based on ISO 8601)
Required, not repeatable
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Example:
<maintenancehistory>
<maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="derived"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-13T08:05:33-05:00">13
September 2015</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>EAD2002_to_EAD3.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>Conversion from EAD 2002 finding aid using XSL
transformation.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-14T10:05:23-05:00">14
September 2014</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="human"></agenttype>
<agent>Lisa Bolkonskaya</agent>
<eventdescription>Conversion from EAD 2002 revised. Conventions and
local control added..</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
</maintenancehistory><eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-16T14:23:42-05:00">16
September 2014</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="human"></agenttype>
<agent>Lisa Bolkonskaya</agent>
<eventdescription>Minor revisions. Added
sources.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><eventdescription>
Event Description [toc]
Summary:
An optional child of <maintenanceevent>, used to provide a description
of the maintenance activity.
Description and Usage:
Use <eventdescription> to record a full description of a maintenance
event. Examples of maintenance events include the creation, update, revision,
or other modification to an EAD instance.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local practice requires recording the type of
description.
See also:
Use the required <eventtype> to provide a basic categorization of
the maintenance event.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<eventtype>
Event Type [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <maintenanceevent> that provides a
controlled list of values for recording the type of maintenance activity.
Description and Usage:
Use <eventtype> to indicate the type of maintenance events that have
taken place on an EAD instance during the course of its history. In addition to
commonly occurring events such as the creation, update, or revision of an
instance, you may also record activities such as the cancellation or deletion
of an instance, as this information may be useful in shared systems.
Meanings for the required value are:
Attribute usage:
cancelled: marks an instance as not current (obsolete or rejected), but
retained for reference
created: the initial creation of the EAD instance
deleted: indication that the instance has been deleted from the system
derived: indicates that the instance was derived from another descriptive system
revised: any type of general modification to the EAD instance
unknown: when the type of event is not known
updated: when an instance has been brought up to date with significant changes to the materials being described or to the version of EAD used
created: the initial creation of the EAD instance
deleted: indication that the instance has been deleted from the system
derived: indicates that the instance was derived from another descriptive system
revised: any type of general modification to the EAD instance
unknown: when the type of event is not known
updated: when an instance has been brought up to date with significant changes to the materials being described or to the version of EAD used
See also:
Use <eventdescription> to provide a fuller description of the
maintenance event.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Required (values limited to: cancelled, created, deleted, derived,
revised, unknown, updated)
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
<expan>
Expansion [toc]
Summary:
A phrase level element for designating the full form of a word or phrase.
Description and Usage:
A phrase level element to designate the full form of a word or phrase that
often appears as an abbreviation or acronym. Use abbr to supply the
abbreviated form for indexing or searching purposes.
See also:
The related element <abbr> with @expan, which can be
used to encode the abbreviation of a name while providing the full form in
an attribute for indexing or searching purposes.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
abstract, addressline, archref, author, bibref, citation, container, date, datesingle, didnote, dimensions, edition, emph, entry, event, fromdate, head, head01, head02, head03, item, label, materialspec, num, p, part, physdesc, physfacet, physloc, publisher, quote, ref, sponsor, subtitle, titleproper, todate, unitdate, unitid, unittitle
Attributes:
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<didnote>File also contains materials from the
<expan abbr=" ACLU ">
American Civil Liberties Union </expan>
. </didnote><c02>
<did>
</c02><unittitle>
[. . .] </did><expan abbr="UNESCO"> United Nations Educational, Scientific and
Cultural Organization </expan>
</unittitle><famname>
Family Name [toc]
Summary:
An element for identifying the name of a group of people with blood relations,
or persons who form a household.
Description and Usage:
An element for identifying the name of a group of persons closely related by
blood or persons who form a household, and are related to the materials being
described. Includes single families and family groups, e.g., Patience Parker
Family and Parker Family.
<famname> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part> elements may be used to capture each component
of the family name, e.g.,
Part 1: Butts family
Part 2: 1810
Part 3: Long Beach, CA
Use <famname> within <controlaccess> for encoding family names as
defined by controlled vocabularies or according to appropriate rules. You may
also use <famname> for encoding family names as they appear within
text.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the family in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of family name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the family name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the family name has to the described materials, for example, "compiler," "creator," "collector," or "subject." The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the family in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of family name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the family name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the family name has to the described materials, for example, "compiler," "creator," "collector," or "subject." The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, origination, p, physfacet, ref, repository, unittitle
References:
MARC 600, 700
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<controlaccess>
<famname>
<part>Butts family</part>
<part>1810</part>
<part>Long Beach, CA</part>
</famname><famname relator="collector">
<part>Smith family</part>
</famname><famname encodinganalog="600" relator="subject" source="lcnaf" identifier="http://lccn.loc.gov/sh88007170">
<part>Kistler family</part>
</famname><famname encodinganalog="600" identifier="http://lccn.loc.gov/sh85128074">
</controlaccess><part>Stevens family</part>
</famname><indexentry>
<famname>
<part>Hely-Hutchinson family</part>
</famname><indexentry>
</indexentry><genreform>
<part>Pedigree, 20th cent.</part>
</genreform><ref target="EngC5769-f74" show="replace" actuate="onrequest">MS.
Eng. c. 5769, fol. 74</ref>
</indexentry><filedesc>
File Description [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <control> that binds together bibliographic
information about an EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <filedesc> to record a bibliographic description of the finding aid
itself, including its author, title, subtitle, sponsor, edition, publisher,
publishing series, and related notes. The prescribed order of all child
elements (both required and optional) is:
<titlestmt>
<editionstmt>
<publicationstmt>
<seriesstmt>
<notestmt>
<editionstmt>
<publicationstmt>
<seriesstmt>
<notestmt>
See also:
Do not confuse with <archdesc>, which refers to the materials
being described rather than the finding aid itself.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<control>
<recordid>AddMS88938</recordid>
<filedesc>
<titlestmt>
<titleproper>Catalogue of the Papers of James Graham
Ballard</titleproper>
</titlestmt><publicationstmt>
</filedesc><publisher>British Library</publisher>
</publicationstmt><maintenancestatus value="derived"></maintenancestatus>
. . . </control><filedesc>
<titlestmt>
<titleproper>Register of the Emily Higby Collection</titleproper>
</titlestmt><editionstmt>
</filedesc><edition>2nd ed.</edition>
<p>This edition reflects substantial additions to the collection in
1994.</p>
</editionstmt><fileplan>
File Plan [toc]
Summary:
An element for information about any classification scheme used by the original
creator to arrange, store, and retrieve the materials described.
Description and Usage:
A filing plan is usually identified by the type of system used, e.g.,
alphabetical, numerical, alpha-numerical, decimal, color-coded, etc. It is
often hierarchical and may include the filing guidelines of the originating
entity. Additional types include a drawing of a room layout or a scientific
scheme.
See also:
Do not confuse with <arrangement>, which describes the current
organization and/or filing sequence of the materials, as opposed to that
imposed by the original creator.
Do not confuse with <otherfindaid>, which contains references to additional descriptions of the material rather than descriptions of classification schemes by which the materials might still be arranged.
Do not confuse with <otherfindaid>, which contains references to additional descriptions of the material rather than descriptions of classification schemes by which the materials might still be arranged.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<fileplan>
<head>File List</head>
<p> The list below outlines the classification system used for the
central files of Vice President Mondale's office. This structure assigned
alpha-numeric codes to primary subjects and to secondary and tertiary
subdivisions thereunder.</p>
<fileplan>
<head>AGRICULTURE (AG)</head>
<list listtype="ordered" numeration="arabic">
</fileplan><item>Home Economics</item>
<item>Horticulture</item>
<item>Marketing</item>
<item>Price Support</item>
</list><fileplan>
</fileplan><head>ARTS (AR)</head>
<list listtype="ordered" numeration="arabic">
</fileplan><item>Languages</item>
<item>Museums</item>
<item>Music</item>
</list><footnote>
Footnote [toc]
Summary:
An element used to cite the source of a fact, quotation, etc.
Description and Usage:
Use <footnote>to annotate text to indicate the basis for an assertion or
citing the source of a quotation or other information.
Attribute usage:
Use @actuate to specify how the footnote is to be displayed to
a user, whether on loading of a window, on request by the user, other, or
none.
Use @show to specify how the source information is to appear after a user requests (clicks on) the footnote, whether embedded in the current window, replacing the current window, in a new window, other, or none.
Use @show to specify how the source information is to appear after a user requests (clicks on) the footnote, whether embedded in the current window, replacing the current window, in a new window, other, or none.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: none, onload, onrequest, other)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: embed, new, none, other replace)
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<scopecontent>
<head>Scope and Content</head>
<p>In letters from the spring of 1924, Lawrence outlines the adjustments
the family faced when moving from New York City to Badger, Iowa.
[. . .] </scopecontent><footnote>
In particular, the children had difficulty in their new
classroom settings. Lawrence notes "Sally cried again tonight because,
unlike the children who have attended this school their entire lives, she
cannot concentrate on sums while the instructor quizzes older children
about geography."
<p>Letters #42, #45, #47-54</p>
</footnote><footnote>
The family only remained six months in Badger before
moving again to Des Moines.</p><p>Letter #48</p>
</footnote><foreign>
Foreign [toc]
Summary:
An element that indicates that the language and/or script of the encoded
word(s) is different from that in the surrounding text.
Description and Usage:
Use <foreign> to indicate a language and/or script that differs from
that of the text surrounding it. Use <foreign> if you wish to render or
otherwise process such text. For example, encoding a phrase as <foreign>
and including the script attributes allows a machine to process the script
differently than that of the script around it.
Attribute usage:
Use @lang to indicate the language and @script to
identify the script of the encoded text.
Use @render to specify formatting of the encoded text for display and print purposes.
Use @render to specify formatting of the encoded text for display and print purposes.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
abstract, addressline, archref, author, bibref, citation, container, date, datesingle, didnote, dimensions, edition, emph, entry, event, fromdate, head, head01, head02, head03, item, label, materialspec, num, p, part, physdesc, physfacet, physloc, publisher, quote, sponsor, subtitle, titleproper, todate, unitdate, unitid, unittitle
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: altrender, bold, bolddoublequote,
bolditalic, boldsinglequote, boldsmcaps, boldunderline, doublequote,
italic, nonproport, singlequote, smcaps, sub, super, underline)
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<bibref>
<foreign lang="lat"> Arcana mundi </foreign>
: magic and the occult
in the Greek and Roman worlds : a collection of ancient texts / translated,
annotated, and introduced by Georg Luck. Baltimore : Johns Hopkins
University Press, c1985. </bibref><bioghist> [. . .]
<p>Thanatos (
[. . .] </bioghist><foreign lang="grc" script="Grek">
Θάνατος </foreign>
) was the personification of death. He was a
minor figure in Greek mythology, often referred to, but rarely appearing
in person. </p><fromdate>
From Date [toc]
Summary:
An optional child element of <daterange> that records the starting point
in a range of dates.
Description and Usage:
Use <fromdate> to record the beginning date in a range of dates.
<fromdate> may contain actual or approximate dates. The content of
the element is intended to be a human-readable, natural language expression of
the date. If, however, indexing or other machine processing of dates is
desired, the standarddate should be used to record the date in
machine-processable form as well.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype to supply a more specific characterization of
the start date.
Use @notafter and @notbefore to capture the earliest and latest possible dates in machine-processable form in cases when the date is uncertain.
Use @standarddate to provide a machine-processable form of the date.
Use @notafter and @notbefore to capture the earliest and latest possible dates in machine-processable form in cases when the date is uncertain.
Use @standarddate to provide a machine-processable form of the date.
See also:
Use <todate> to record the ending point of a date range.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<unitdatestructured calendar="gregorian" era="ce">
<dateset>
</unitdatestructured><datesingle standarddate="1963-01-22">22 January
1963</datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1971-06-01"> 1 June 1971 </fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1974-04-30">30 April 1974</todate>
</daterange><chronitem>
<daterange>
<fromdate> 1819 </fromdate>
<todate>1820</todate>
</daterange><event>Studies theology at Yale College</event>
</chronitem><unitdatestructured unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notafter="1962"> 1962 </fromdate>
<todate notafter="1968">1968</todate>
</daterange><unitdatestructured certainty="circa" unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notbefore="1971" notafter="1975"> around 1973 </fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1992">1992</todate>
</daterange><function>
Function [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding activities and processes related to the production of
materials.
Description and Usage:
<function> identifies activities and processes that generated the
described materials. Such terms often provide useful access points to the
materials, especially for corporate, government, or institutional records.
Examples include collecting taxes and entertaining.
<function> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part> elements may be used to capture each component
of the function term, e.g.,
Part 1: Coaching
Part 2: Oregon
Use <function> within <controlaccess> for encoding functions as
defined by controlled vocabularies or according to appropriate rules. You may
also use <function> for encoding functions as they appear within
text.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the function in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of function.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the function if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) between the function and the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce these values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the function in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of function.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the function if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) between the function and the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce these values elsewhere if desired.
See also:
Do not use <function> to describe occupations; use
<occupation> instead.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, p, physfacet, ref, unittitle
References:
MARC 657
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Example:
<controlaccess>
<function encodinganalog="657" source="aat">
<part>Legislating</part>
</function><function encodinganalog="657" source="aat">
<part>Law enforcing</part>
</function><function encodinganalog="657" source="aat">
</controlaccess><part>Convicting</part>
</function><genreform>
Genre/Physical Characteristic [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding a genre or form of material.
Description and Usage:
<genreform> identifies the types of material being described by naming
the style or technique of their intellectual content (genre), order of
information or object function (form), and physical characteristics. Examples
include: account books, architectural drawings, portraits, short stories, sound
recordings, and videotapes.
<genreform> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part>
elements may be used to capture each component of the genre/form term,
e.g.,
Part 1: Photographs
Part 2: 1910-1919
Use <genreform> within <controlaccess> for encoding genre terms
as defined by controlled vocabularies or according to appropriate rules. You
may also use <genreform> for encoding genre terms as they appear within
text.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the genre or physical characteristic in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of genre term.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the genre term if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the genre term has to the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the genre or physical characteristic in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of genre term.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the genre term if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the genre term has to the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, p, physfacet, ref, unittitle
References:
MARC 655
MODS <genre>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<controlaccess>
<genreform encodinganalog="655" source="gmgpc">
<part>Correspondence</part>
</genreform><genreform encodinganalog="655" source="gmgpc">
</controlaccess><part>Diaries</part>
</genreform><indexentry>
<famname>
<part>Hely-Hutchinson family</part>
</famname><indexentry>
</indexentry><genreform>
<part>Pedigree, 20th cent.</part>
</genreform><ref target="EngC5769-f74" show="replace" actuate="onrequest">MS.
Eng. c. 5769, fol. 74</ref>
</indexentry><geogname>
Geographical Name [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding place names.
Description and Usage:
An element for identifying the name of a place, natural feature, or political
jurisdiction. Examples include: Appalachian Mountains; Baltimore, MD;
Chinatown, San Francisco; and Kew Gardens, England.
<geogname> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part> elements may be used to capture each component
of the geographic name, e.g.,
Part 1: Mexico
Part 2: Baja California (Peninsula)
<geogname> also allows for an optional <geographiccoordinates>
element following the <part> element(s).
Use <geogname> within <controlaccess> for encoding geographical
names as defined by controlled vocabularies or according to appropriate rules.
You may also use <geogname> for encoding geographical names as they
appear within text.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the geographic name in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of geographical name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the geographical name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the geographical name has to the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the geographic name in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of geographical name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the geographical name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the geographical name has to the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, chronitem, chronitemset, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, p, physfacet, ref, relation, unittitle
References:
MARC 651, 752
MODS <geographic>, <hierarchicalGeographic>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <chronitem>, <indexentry> and <relation>: Optional,
not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<controlaccess>
<geogname>
</controlaccess><part>Clear Spring</part>
<part>Maryland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="UTM">18S 248556mE
4393694mN</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><controlaccess>
<geogname encodinganalog="651" identifier="http://viaf.org/viaf/155860715">
</controlaccess><part>Washington (State)</part>
</geogname><chronitem>
<datesingle standarddate="1927">1927</datesingle>
<geogname>
<part>Berlin, Germany </part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="mgrs">33UUU9029819737
</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Designs and builds Piscator Apartment</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
<datesingle standarddate="1932">1932</datesingle>
<geogname>
<part>Basel, Switzerland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="mgrs">
32TLT9469569092</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Designs and builds Wohnbedarf Furnniture Stores</event>
</chronitem><geographiccoordinates>
Geographic Coordinates [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <geogname> that encodes a set of geographic
coordinates.
Description and Usage:
Use <geographiccoordinates> to express a set of geographic coordinates
such as latitude, longitude, and altitude representing a point, line, or area
on the surface of the earth.
Attribute usage:
Use @coordinatesystem to provide a commonly used code for the
system used to express the coordinates. Examples include WGS84, OSGB36,
ED50.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
References:
MARC 255$c
MODS <coordinates>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Required
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<geogname>
<part localtype="place">Hardeeville</part>
<part localtype="state">South Carolina</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="WGS84"> -81.1, 32.2, -81.0,
32.3 </geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><geogname>
<part>Clear Spring</part>
<part>Maryland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="UTM"> 18S 248556mE 4393694mN
</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><geogname>
<part>Berlin, Germany </part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="mgrs"> 33UUU9029819737
</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><geogname>
<part>Basel, Switzerland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="mgrs"> 32TLT9469569092
</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><head>
Heading [toc]
Summary:
An element that encodes a title or caption for a section of text.
Description and Usage:
<head> is used for supplying title-like statements to a section of text,
such as a note, list, table, or series of paragraphs. When <head> is
used, it must be the first child element, followed by one or more other
elements.
See also:
Do not confuse with the children of <listhead> (<head01>,
<head02>, and <head03>), which designate headings for
facets in a multifacet list, or <thead>, which is used for column
headings in a table.
May contain:
May occur within:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, c, c01, c02, c03, c04, c05, c06, c07, c08, c09, c10, c11, c12, chronlist, controlaccess, custodhist, did, dsc, fileplan, index, legalstatus, list, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, table, userestrict
Attributes:
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<chronlist>
<head> Publications List </head>
<listhead>
<head01>Publication Year</head01>
<head02>Book Title</head02>
</listhead><chronitem>[...]</chronitem>
</chronlist><bioghist id="PRO123">
<head> Administrative History </head>
<p>In October 1964, the incoming Labour government created new office of
Secretary of State for Economic Affairs (combined with First Secretary of
State) and set up the Department of Economic Affairs under the Ministers
of the Crown Act 1964 to carry primary responsibility for long term
economic planning.</p>
</bioghist><head01>
First Heading [toc]
Summary:
A formatting element for the first facet heading in a multifacet list.
Description and Usage:
Use within <listhead> to designate the heading over the first facet in a
multifacet list.
See also:
Do not confuse with the generic <head>, which designates a heading
for an entire list or other section of text.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Example:
<chronlist>
<listhead>
<head01>Date(s)</head01>
<head02>Location(s)</head02>
<head03>Event(s)</head03>
</listhead><chronitem>
</chronlist><dateset>
<datesingle standarddate="1942-03">March 1942</datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1942-05">May 1946</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1946-09">September 1946</todate>
</daterange><chronitemset>
</chronitem><geogname>
<part>Clear Spring</part>
<part>Maryland</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="UTM">18S 248556mE
4393694mN</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><event>Enlisted in Civilian Public Service as a conscientious
objector.</event>
<event>Served at CPS Camp No. 24, subunit 4 in Clear Spring,
Maryland. Constructed fences to conserve soil, practiced
specialized tilling, and dug water diversion ditches. Fought
occasional forest fires.</event>
</chronitemset><head02>
Second Heading [toc]
Summary:
A formatting element for the second facet heading in a multifacet list.
Description and Usage:
Use <head02> within <listhead> if needed to designate the heading
over the second facet in a multifacet list.
See also:
Do not confuse with the generic <head>, which designates a heading
for an entire list or other section of text.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Example:
<chronlist>
<listhead>
[. . .] </chronlist><head01>Date(s)</head01>
<head02> Location(s) </head02>
<head03>Event(s)</head03>
</listhead><head03>
Third Heading [toc]
Summary:
A formatting element for the third facet heading in a multifacet list.
Description and Usage:
Use <head03> within <listhead> to provide a heading over the
third facet in a multifacet list.
See also:
Do not confuse with the generic <head>, which designates a heading
for an entire list or other section of text.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
<index>
Index [toc]
Summary:
A list of key terms and entities with reference pointers assembled to enhance
navigation of and access to the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
<index> can serve as a helpful alphabetical overview of subjects,
correspondents, photographers, or other entities represented in the collection.
It may provide hypertext links to the components referenced, or it may simply
note the container numbers useful for locating the position in the finding aid
where the indexed material appears.
The index may repeat terms and names found elsewhere in the finding aid or list
names not previously identified. For example, an index of correspondents may
list "Chilsolm, Shirley" with a reference pointing to a file with the general
name "Correspondence, 1969-1975." Use <indexentry> to capture each item
in the <index>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<indexentry>
Index Entry [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element that pairs an index term with zero or more linking
elements.
Description and Usage:
Each <indexentry> must contain an access element, such as
<corpname>, <persname>, <subject>, etc., or
<namegrp> to handle multiple access elements. It may also contain
<ref>, <ptr>, or <ptrgrp> to identify and/or provide a
link to the relevant position in the finding aid. If desired, use controlled
vocabulary terms to facilitate access to information within and across finding
aid systems.
Use the child <namegrp> to bundle access element entries, e.g., several
<famname> and <persname> elements that share the same
<ref>, <ptr>, or <ptrgrp>.
May contain:
corpname, famname, function, genreform, geogname, indexentry, name, namegrp, occupation, persname, ptr, ptrgrp, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<index>
<indexentry>
<name>
<part>12th Air Force Photo</part>
</name><ref target="LOT13105" actuate="onrequest" show="replace">>LOT
13105</ref>
</indexentry><indexentry>
</index><name>
<part>15th Air Force Command:</part>
</name><ref target="LOT13105" actuate="onrequest" show="replace">LOT
13105</ref>
</indexentry><item>
Item [toc]
Summary:
An element used in either <list> or as part of <defitem>.
Description and Usage:
An element used in two contexts: as an entry in a simple, random, or ordered
<list> or as part of <defitem> inside a definition list. In
the first instance, <item> can be a number, word, or phrase. In a
definition list, which is usually displayed as two columns, <defitem>
pairs <label> with a corresponding <item> containing text that
defines, describes, or explains the terms or other text tagged as
<label>.
See also:
Do not confuse with <chronitem>, which designates entries in
<chronlist>.
Related elements <list> and <defitem>.
Related elements <list> and <defitem>.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, list, name, num, occupation, persname, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <defitem>: Required, not repeatable
Within <list>: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<list listtype="unordered" mark="circle">
<head>List of ministers of May Memorial Unitarian Universalist
Church</head>
<item> John Storer, Minister 1839-1844 </item>
<item> Samuel Joseph May, Minister 1845-1868 </item>
<item> Samuel R. Calthrop, Minister 1868-1911 </item>
<item> John H. Applebee, Minister 1911-1929 </item>
<item> Waldemar W. Argow, Minister 1930-1941 </item>
<item> Robert E. Romig, Minister 1941-1946 </item>
<item> Glenn O. Canfield, Minister 1946-1952 </item>
<item> John Fuller, Minister, 1961-1973 </item>
</list><list listtype="deflist">
<defitem>
<label>ALS</label>
<item> Autograph Letter Signed </item>
</defitem><defitem>
</list><label>TLS</label>
<item> Typewritten Letter Signed </item>
</defitem><label>
Label [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <defitem> that identifies the term or
concept being defined or described.
Description and Usage:
In a definition list, <label> and <item> are paired within
<defitem>. <label> provides a term or concept that is then
defined, described, or explained in an <item>. A definition list is
often displayed in two columns.
See also:
Do not confuse with @label, available on children of
<did>, which allows the encoder to provide identifying information
for public display.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
<langmaterial>
Language of the Material [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that identifies languages represented in the
materials described.
Description and Usage:
<langmaterial> records information about languages and scripts
represented in the materials being described. <langmaterial> must
contain one or more <language> or <languageset> elements, but
cannot contain text.
Any comments or notes about languages or scripts represented in the materials
described must be encoded in an optional <descriptivenote> that follows
all <language> and <languageset> elements.
Attribute usage:
Use @lang and @scriptto indicate the language and written
scripts of the descriptive information, not the language of
materials.
Use @langcode in the <language> child element to record the language of the material using language codes.
Use @scriptcode in the <script> child element to record the script of the material using script codes.
Use @langcode in the <language> child element to record the language of the material using language codes.
Use @scriptcode in the <script> child element to record the script of the material using script codes.
See also:
Do not confuse with <languagedeclaration> in <control>,
which specifies the language(s) and script(s) in which the finding aid is
written. See also the descriptions for <language> and
<languageset>.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.4.3
MARC 546
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<langmaterial>
<languageset>
<language langcode="lat">Latin</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="ang">Old English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>The majority of the documents are written in Modern English.
Roberts copies multiple passages from original manuscripts in Latin
and Old English.</p>
</descriptivenote><langmaterial>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<language langcode="fre">French</language>
</langmaterial><langmaterial>
<languageset>
<language langcode="jpn">Japanese</language>
<script scriptcode="Hira">hiragana</script>
<script scriptcode="Kana">katakana</script>
</languageset><descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>This file contains documents in Japanese, in both the hiragana and
katakana scripts.</p>
</descriptivenote><language>
Language [toc]
Summary:
An element used to indicate the language or communication system of an EAD
instance or of the material being described.
Description and Usage:
Within <did>, <language> is a child element of
<langmaterial> and it identifies a language or communication system
of the materials being described. Within <control>, <language> is
a child element of <languagedeclaration> and it identifies the language
of the description itself. Multiple languages and scripts can be listed within
<languageset>.
Attribute usage:
Use @langcode to provide an identifying code for the language
according to the authoritative source identified in @langencoding.
In most cases this will be a three-letter ISO639-2b code.
Use @lang and @script to indicate the language and written scripts of the descriptive information, not the language of materials.
Use @lang and @script to indicate the language and written scripts of the descriptive information, not the language of materials.
See also:
Use <script> to specify, in a human-readable form, the script
corresponding to the language.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
References:
MARC 041 is equivalent to langcode
MODS <languageTerm>, <languageOfCataloging>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <langmaterial>:One of <language> or <languageset>
is required, repeatable
Within <languagedeclaration>:Required, not repeatable
Within <languageset>:Required, repeatable
Examples:
<langmaterial>
<languageset>
<language langcode="lat"> Latin </language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="ang"> Old English </language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="eng"> English </language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>The majority of the documents are written in Modern English.
Roberts copies multiple passages from original manuscripts in Latin
and Old English.</p>
</descriptivenote><langmaterial>
<language langcode="eng"> English </language>
<language langcode="fre"> French </language>
</langmaterial><langmaterial>
<languageset>
<language langcode="jpn"> Japanese </language>
<script scriptcode="Hira">hiragana</script>
<script scriptcode="Kana">katakana</script>
</languageset><descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>This file contains documents in Japanese, in both the hiragana and
katakana scripts.</p>
</descriptivenote><languagedeclaration>
Language Declaration [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <control> that indicates the language and script in
which an EAD instance is written.
Description and Usage:
Use <languagedeclaration> to identify the language and script of an EAD
instance with required <language> and <script> children. When the
archival description is in a single language or it is the maintenance agency’s
policy to declare a primary language, then a single instance of
<languagedeclaration> may be used. For declaring multiple languages,
<languagedeclaration> may be repeated. Any comments about the
languages and scripts in which the EAD instance is written may be included in
the optional <descriptivenote>.
The prescribed order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<language>
<script>
<descriptivenote>
<script>
<descriptivenote>
See also:
Do not confuse with <langmaterial>, which is used to identify
languages and scripts found in the materials being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<control>
<maintenanceagency>
<otheragencycode localtype="archon">GB-58</otheragencycode>
<agencyname>British Library</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><languagedeclaration>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn">Latin</script>
</languagedeclaration><maintenancehistory>
</control><maintenanceevent>
</maintenancehistory><eventtype value="derived"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2013-04-20T16:19:24Z"></eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine">machine</agenttype>
<agent>IAMS</agent>
</maintenanceevent><languageset>
Language Set [toc]
Summary:
Within <did>, <languageset> is a child element of
<langmaterial> that is used to pair languages with the scripts in
which they are written.
Description and Usage:
Use <languageset> within <langmaterial> when it is necessary to
associate <language> and <script>. Possible combinations include
one language and one script, multiple languages and one script, and one
language and multiple scripts. Although the EAD3 schema allows multiple
languages to be associated with multiple scripts this combination is unlikely
to convey useful information. <languageset> may be repeated as
necessary. Optionally, any comments about the language(s) and scripts(s) being
recorded may be captured in <descriptivenote> at the end, particularly
for display to finding aid users.
Attribute notes:
Use @lang and @script to indicate the language and
written scripts of the descriptive information, not the language of
materials.
See also:
Required child element <language>
Required child element <script>
Required child element <script>
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<langmaterial>
<languageset>
<language langcode="lat">Latin</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="ang">Old English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>The majority of the documents are written in Modern English.
Roberts copies multiple passages from original manuscripts in Latin
and Old English.</p>
</descriptivenote><langmaterial>
<languageset>
<language langcode="jpn">Japanese</language>
<script scriptcode="Hira">hiragana</script>
<script scriptcode="Kana">katakana</script>
</languageset><descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>This file contains documents in Japanese, in both the hiragana and
katakana scripts.</p>
</descriptivenote><lb>
Line Break [toc]
Summary:
A formatting element that forces the following text to start on a new line.
Description and Usage:
An empty formatting element that allows the author of an EAD instance to
explicitly indicate the point in the text where a new line should occur rather
than relying on a rendering application. Use only when a line break is needed
within an element. Use a style sheet to specify line breaks between
elements.
May contain:
[empty]
May occur within:
abstract, addressline, archref, author, bibref, citation, container, date, datesingle, didnote, dimensions, edition, emph, entry, event, fromdate, head, head01, head02, head03, item, label, materialspec, num, p, part, physdesc, physfacet, physloc, publisher, quote, ref, sponsor, subtitle, titleproper, todate, unitdate, unitid, unittitle
References:
Equivalent to <br/> in HTML.
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<publisher> San Joaquin County Historical Society and Museum
<lb></lb>
Lodi, California
<lb></lb>
<ptr actuate="onload" show="embed" entityref="sjmlogo"></ptr>
</publisher><legalstatus>
Legal Status [toc]
Summary:
An element for indicating the statutorily defined status of the materials being
described.
Description and Usage:
Use <legalstatus> to identify the status of the material being described
as defined by law, for example, the Public Records Act of 1958 in the United
Kingdom.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MARC 506
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<did>
<unitid label="Reference Code">PREM 8</unitid>
<unittitle label="Title">Prime Minister's Office: Correspondence and
Papers</unittitle>
<unitdate label="Creation Dates" unitdatetype="inclusive">1935-1951</unitdate>
</did><legalstatus>
<p>Public Record(s)</p>
</legalstatus><legalstatus>
<head>Legal status of records</head>
<p>Federal, state and local laws apply, as follows.</p>
<legalstatus>
<head>Student records</head>
<p>Student records are governed by the Family Educational Rights and
Privacy Act (FERPA),
</legalstatus><num localtype="us.usc">20 U.S.C. §
1232g</num>
.</p><legalstatus>
</legalstatus><head>Patient records</head>
<p>Patient records are governed by the Health Insurance Portability
and Accountability Act,
</legalstatus><num localtype="us.pub.l">Pub.L.
104–191</num>
and
<num localtype="us.stat">110 Stat.
1936</num>
.
<num localtype="eu.echr">Article 8
ECHR</num>
may also apply.</p><legalstatus>
<p>On deposit until 2025. See Deed of Gift for more information.</p>
</legalstatus><list>
List [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element for formatting a series of <item> or <defitem>
elements that are often presented in a vertical sequence.
Description and Usage:
A formatting element that contains a series of words or numerals (called
<item>s) separated from one another and arranged in a linear, often
vertical sequence.
Attribute usage:
Use @listtype to identify and format the list as a particular
type. The choices are: "deflist," "ordered," and "unordered."
See also:
Do not confuse with <chronlist>, which is used to designate the
temporal sequence of significant events associated with the entity or
material described.
May contain:
May occur within:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, blockquote, controlaccess, controlnote, custodhist, dsc, entry, event, fileplan, footnote, index, item, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, p, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, userestrict
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: deflist, ordered, unordered)
Optional (values limited to: circle, disc, inherit, none,
square)
Optional (values limited to: armenian, decimal, decimal-leading-zero,
georgian, inherit, lower-alpha, lower-greek, lower-latin, lower-roman,
upper-alpha, upper-latin, upper-roman)
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<list listtype="unordered" mark="circle">
<head>List of ministers of May Memorial Unitarian Universalist
Church</head>
<item>John Storer, Minister 1839-1844</item>
<item>Samuel Joseph May, Minister 1845-1868</item>
<item>Samuel R. Calthrop, Minister 1868-1911</item>
<item>John H. Applebee, Minister 1911-1929</item>
<item>Waldemar W. Argow, Minister 1930-1941</item>
<item>Robert E. Romig, Minister 1941-1946</item>
<item>Glenn O. Canfield, Minister 1946-1952</item>
<item>John Fuller, Minister, 1961-1973</item>
</list><list listtype="deflist">
<defitem>
<label>ALS</label>
<item>Autograph Letter Signed</item>
</defitem><defitem>
</list><label>TLS</label>
<item>Typewritten Letter Signed</item>
</defitem><processinfo>
<p>The following items were removed during processing due to
irrecoverable mold damage. Photographs were taken and placed in the
collection for reference purposes.
</processinfo><list listtype="ordered" numeration="lower-alpha">
</p><item>Correspondence from Feb 1987 (6 items)</item>
<item>Three photographs of unidentified cats</item>
<item>One silk scarf</item>
</list><listhead>
List Heading [toc]
Summary:
An element for grouping several headings for faceted lists.
Description and Usage:
A formatting element that groups headings for different facets in a definition
list (<list listtype="deflist">), <chronlist>, or <index>.
The headings are called <head01>, <head02>, and <head03>
and are available in that sequence, although each is optional.
See also:
Do not confuse with <head>, which designates a title or caption
for a section of text where columnar headings are not needed.
Do not confuse with <thead>, which is used in <table>.
Do not use <head03> within a definition list (<list listtype="deflist">). A definition list can only have two facets for the <label> and <item> elements within <defitem>.
Do not confuse with <thead>, which is used in <table>.
Do not use <head03> within a definition list (<list listtype="deflist">). A definition list can only have two facets for the <label> and <item> elements within <defitem>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Example:
<chronlist>
<head>Publications List</head>
<listhead>
<head01>Publication Year</head01>
<head02>Book Title</head02>
</listhead><chronitem>
<datesingle>1882</datesingle>
<event>
</chronitem><title>
London: Jos. Banks.</event><part>Across the Sea in a Sieve.</part>
</title><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle>1886</datesingle>
<event>
</chronitem><title>
London: Chatto and Windus.</event><part>My Life and Other Tragedies.</part>
</title><localcontrol>
Local Control [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <control>, used to specify any control information
necessary to accommodate local practice.
Description and Usage:
Administrative information about an EAD instance that is not accommodated by
other elements but is required to support local needs. The value of the element
should be given in a child <term>, and an associated date or range of
dates can be given as either <datesingle> or <daterange>.
Child elements of <localcontrol> must be provided in a specific
order:
<term>
<datesingle> or <daterange>
<datesingle> or <daterange>
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local practice requires recording the type of
entry.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<control> [. . .]
<languagedeclaration>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn">Latin</script>
</languagedeclaration><localcontrol localtype="levelofdetail">
<term>Minimum</term>
</localcontrol><maintenancehistory>
</control><maintenanceevent>
</maintenancehistory><eventtype value="derived"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2013-04-20T16:19:24Z"></eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine">machine</agenttype>
<agent>IAMS</agent>
</maintenanceevent><localcontrol localtype="fileSize">
<term>8 MB</term>
</localcontrol><localcontrol localtype="daoFlag">
<term>true</term>
</localcontrol><localcontrol localtype="maxComponentID">
<term>414</term>
</localcontrol><localcontrol localtype="processinglevel">
<term>item</term>
</localcontrol><localtypedeclaration>
Local Type Declaration [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <control> used to declare any local conventions or
controlled vocabularies used in localtype in the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
<localtypedeclaration> specifies the local conventions and controlled
vocabularies used in localtype attributes in the EAD instance. The child
<citation> must be used to cite the resource that lists the local
rules or controlled terms. Any notes relating to how these rules or conventions
have been used may be given in <descriptivenote>. The child
<abbr> may be used to identify any abbreviation or code representing
the local convention or controlled vocabulary.
It may not be necessary to include <localtypedeclaration> if
localtype values are documented externally.
The prescribed order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<abbr>
<citation>
<descriptivenote>
<citation>
<descriptivenote>
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<control> [. . .]
<conventiondeclaration>
<abbr>ISAD(G)</abbr>
<citation>ISAD(G): General International Standard Archival
Description, second edition, Ottawa 2000</citation>
</conventiondeclaration><localtypedeclaration>
<citation>IAMS Catloguing Guidelines Part 1: Describing Archives and
Manuscripts</citation>
</localtypedeclaration><localcontrol localtype="levelofdetail">
[. . .] </control><term>Minimum</term>
</localcontrol><localtypedeclaration>
<abbr>PM-AMC</abbr>
<citation>Processing manual for archival and manuscript
collections</citation>
<descriptivenote>
</localtypedeclaration><p>This finding aid conforms to the standards of description outlined
in the seventh section of the university's
</descriptivenote><title>
.</p><part>Processing manual for archival and manuscript
collections</part>
</title><maintenanceagency>
Maintenance Agency [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <control> that identifies the information or
service responsible for the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Information about the institution or service responsible for the creation,
maintenance, and/or dissemination of the EAD instance.
<maintenanceagency> must include a child <agencyname> to provide
the name of the institution or service. It is recommended to include the
optional <agencycode> and/or <otheragencycode> children to
unambiguously identify the institution or service. Any general information
about the institution in relation to the EAD instance may be given in
<descriptivenote>.
The prescribed order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<agencycode>
<otheragencycode>
<agencyname>
<descriptivenote>
<otheragencycode>
<agencyname>
<descriptivenote>
Attribute usage:
Use @countrycode to indicate a unique code for the country of
the maintenance agency.
See also:
Use <repository> to identify the institution or agency responsible
for providing intellectual access to the materials being described, which
may be the same as the maintenance agency.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<control> [. . .]
<maintenancestatus value="derived"></maintenancestatus>
<maintenanceagency>
<otheragencycode localtype="archon">GB-58</otheragencycode>
<agencyname>British Library</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><languagedeclaration>
[. . .] </control><language langcode="eng">English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn">Latin</script>
</languagedeclaration><control> [. . .]
<maintenancestatus value="revised"></maintenancestatus>
<publicationstatus value="published"></publicationstatus>
<maintenanceagency>
[. . .] </control><agencycode>DNASA-G</agencycode>
<otheragencycode localtype="agency">GSFC</otheragencycode>
<agencyname>NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><maintenanceevent>
Maintenance Event [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <maintenancehistory> used to record
information about maintenance activities in the history of the EAD
instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <maintenanceevent> to record an activity in the creation and ongoing
maintenance of an EAD instance, including revisions, updates, deletions, etc.
There will always be at least one maintenance event for each instance, which
will typically be its creation.
The type of each event must be defined in the child <eventtype>. The
child <agent> and <agenttype> elements are required to provide
information about who or what carried out, or was otherwise responsible for,
the work on the EAD instance. The child <eventdatetime> is also required
to record when the event took place. Optionally, the information about the
event may be described further in <eventdescription>.
The prescribed order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<eventtype>
<eventdatetime>
<agenttype>
<agent>
<eventdescription>
<eventdatetime>
<agenttype>
<agent>
<eventdescription>
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MODS <recordOrigin>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, repeatable
Examples:
<maintenancehistory>
<maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="created"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2006-10">October
2006</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="human"></agenttype>
<agent>Michael Rush</agent>
<eventdescription>Finding aid created.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="created"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2006-10">October
2006</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>Beinecke Library Edix/Wordix macros</agent>
<eventdescription>Encoded in EAD 1.0.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2007-08-13"></eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>brbl-migrate-01.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>converted for compliance with Yale EAD Best
Practice Guidelines </eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2007-07-26"></eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>v1to02.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>PUBLIC "-//Yale University::Beinecke Rare Book and
Manuscript Library//TEXT (US::CtYBR::::[ABRAHAM HAYWARD COLLECTION
])//EN" "hayward.xml" converted from EAD 1.0 to 2002 by v1to02.xsl
(sy2003-10-15).</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
</maintenancehistory><eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2010-02-10"></eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>yale.addEadidUrl.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>Transformed with yale.addEadidUrl.xsl. Adds @url
with handle for finding aid. Overwrites @url if already
present.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenancehistory>
<maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="derived"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-13T08:05:33-05:00">13
September 2015</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>EAD2002_to_EAD3.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>Conversion from EAD 2002 finding aid using XSL
transformation.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-14T10:05:23-05:00">14
September 2014</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="human"></agenttype>
<agent>Lisa Bolkonskaya</agent>
<eventdescription>Conversion from EAD 2002 revised. Conventions and
local control added..</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
</maintenancehistory><eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-16T14:23:42-05:00">16
September 2014</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="human"></agenttype>
<agent>Lisa Bolkonskaya</agent>
<eventdescription>Minor revisions. Added
sources.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenancehistory>
Maintenance History [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <control> that captures the history of the
EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
<maintenancehistory> is for recording the history of the creation,
revisions, updates, and other modifications to the EAD instance. There must be
at least one child <maintenanceevent> in <maintenancehistory>,
which usually will be a record of the creation of the instance, but there may
be many other <maintenanceevent> elements documenting the milestone
changes or activities in the maintenance of the instance.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<maintenancehistory>
<maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="created"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2006-10">October
2006</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="human"></agenttype>
<agent>Michael Rush</agent>
<eventdescription>Finding aid created.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="created"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2006-10">October
2006</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>Beinecke Library Edix/Wordix macros</agent>
<eventdescription>Encoded in EAD 1.0.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2007-08-13"></eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>brbl-migrate-01.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>converted for compliance with Yale EAD Best
Practice Guidelines</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2007-07-26"></eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>v1to02.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>PUBLIC "-//Yale University::Beinecke Rare Book and
Manuscript Library//TEXT (US::CtYBR::::[ABRAHAM HAYWARD COLLECTION
])//EN" "hayward.xml" converted from EAD 1.0 to 2002 by v1to02.xsl
(sy2003-10-15).</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
</maintenancehistory><eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2010-02-10"></eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>yale.addEadidUrl.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>Transformed with yale.addEadidUrl.xsl. Adds @url
with handle for finding aid. Overwrites @url if already
present.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenancehistory>
<maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="derived"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-13T08:05:33-05:00">13
September 2015</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="machine"></agenttype>
<agent>EAD2002_to_EAD3.xsl</agent>
<eventdescription>Conversion from EAD 2002 finding aid using XSL
transformation.</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
<eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-14T10:05:23-05:00">14
September 2014</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="human"></agenttype>
<agent>Lisa Bolkonskaya</agent>
<eventdescription>Conversion from EAD 2002 revised. Conventions and
local control added..</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenanceevent>
</maintenancehistory><eventtype value="revised"></eventtype>
<eventdatetime standarddatetime="2015-09-16T14:23:42-05:00">16
September 2014</eventdatetime>
<agenttype value="human"></agenttype>
<agent>Lisa Bolkonskaya</agent>
<eventdescription>Minor revisions. Added sources.
</eventdescription>
</maintenanceevent><maintenancestatus>
Maintenance Status [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <control> that records the current version
status of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <maintenancestatus> to indicate the current drafting status of an
EAD instance. The current version status should always be updated whenever an
EAD instance is modified (as recorded in <maintenancehistory>).
The current maintenance status must always be reflected in the required
value. The element should only have a text value if it is
necessary to provide a value for <maintenancestatus> in a language other
than English, otherwise it should remain empty.
Attribute usage:
Upon creation, record the status as "new."
On revision, change the status to "revised."
Because it is important to be clear about what has happened to instances, particularly when sharing and making links between them, a number of status values are available for records that are no longer current:
A "derived" status value is available to indicate that the record was derived from another descriptive system.
On revision, change the status to "revised."
Because it is important to be clear about what has happened to instances, particularly when sharing and making links between them, a number of status values are available for records that are no longer current:
A "derived" status value is available to indicate that the record was derived from another descriptive system.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Required (values limited to: revised, deleted, new, deletedsplit,
deletedmerged, deletedreplaced, cancelled, derived)
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<control>
<recordid>AddMS88938</recordid>
<filedesc>
<titlestmt>
<titleproper>Catalogue of the Papers of James Graham
Ballard</titleproper>
</titlestmt><publicationstmt>
</filedesc><publisher>British Library</publisher>
</publicationstmt><maintenancestatus value="derived"></maintenancestatus>
<publicationstatus value="approved"></publicationstatus>
<maintenanceagency>
[. . .] </control><otheragencycode localtype="archon">GB-58</otheragencycode>
<agencyname>British Library</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><control> [. . .]
<maintenancestatus value="revised"></maintenancestatus>
<publicationstatus value="published"></publicationstatus>
<maintenanceagency>
[. . .] </control><agencycode>DNASA-G</agencycode>
<otheragencycode localtype="agency">GSFC </otheragencycode>
<agencyname>NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><materialspec>
Material Specific Details [toc]
Summary:
A child elementof <did> for providing material specific details for a
small group of materials or an item.
Description and Usage:
<materialspec> is for recording material specific details that are
unique to a particular class or form of material and which are not recorded in
any other element of description. Examples of material specific details include
mathematical data, such as scale for cartographic and architectural records,
jurisdictional and denominational data for philatelic records, and presentation
data that describes the format of music manuscripts.
Most likely <materialspec> will be useful at the item or small group
level of description, such as a file of maps, a group of sound recordings,
etc.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype to specify the type of data being conveyed in
the element, e.g., <materialspec
localtype="scale">1:200</materialspec>.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MARC 254, 255
MODS <subject><cartographics><projection>, <subject><cartographics><scale>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c03 level="file">
<did> [ . . .]
</c03><materialspec label="Scale:" localtype="scale">
1:10000 </materialspec>
<materialspec label="Projection:" localtype="projection"> Universal
transverse Mercator projection </materialspec>
[ . . .] </did><c02>
<did>
</c02><unittitle>Rebecca (Selznick International Pictures)</unittitle>
<abstract>Autograph conductor's full score (pencil), with
mimeographed conductor's short score of certain sections interleaved.
Selections, including deletions.</abstract>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1940">1940</unitdate>
<materialspec> Full score. </materialspec>
</did><name>
Generic Name [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding generic names.
Description and Usage:
The proper noun or noun phrase designation for an entity that is difficult to
tag more specifically as <corpname>, <famname>,
<geogname>, or <persname>. <name> may be used in place of
the more specific access elements when it is not known what kind of name is
being described or when a higher degree of precision is unnecessary. For
example, <name> might be used in an <indexentry> when it is not
clear if the name "Bachrach" refers to a person or a photographic
corporation.
<name> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part> elements may be used to capture each component
of the name.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the name in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the name has to the described materials, for example "subject" or "photographer." The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the name in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the name has to the described materials, for example "subject" or "photographer." The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, origination, p, physfacet, ref, repository, unittitle
References:
MARC 720
MODS <name>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Example:
<controlaccess>
<name encodinganalog="610" rules="RDA">
</controlaccess><part>Winwood</part>
</name><namegrp>
Name Group [toc]
Summary:
An element for binding together multiple access element entries within an
<indexentry>.
Description and Usage:
Use <namegrp> to group multiple access elements that share the same
<ref>, <ptr>, or <ptrgrp>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
<notestmt>
Note Statement [toc]
Summary:
An optional child element of <filedesc> that binds together one or more
<controlnote> elements.
Description and Usage:
Use <notestmt> to record one or more general descriptive notes about the
EAD instance, each note being encoded in a single <controlnote>.
<controlnote> is similar to the "general note" in traditional
bibliographic descriptions.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<filedesc> [. . .]
<notestmt>
</filedesc><controlnote localtype="bpg">
</notestmt><p>This encoded finding aid is compliant with the Yale EAD Best
Practice Guidelines, Version 1.0.</p>
</controlnote><notestmt>
<controlnote>
<p>Contact information:
</controlnote><ref show="new" actuate="onrequest" href="http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.mss/mss.contact">
http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.mss/mss.contact</ref>
</p>http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.mss/mss.contact</ref>
<controlnote>
</notestmt><p>Catalog Record:
</controlnote><ref href="http://lccn.loc.gov/mm82036905" actuate="onrequest" linktitle="MARC record for collection">http://lccn.loc.gov/mm82036905</ref>
</p><num>
Number [toc]
Summary:
A generic element for expressing numeric information.
Description and Usage:
A generic element for encoding numeric information in any form. <num>
may be used when it is necessary to display a number in a special way, or to
identify it with localtype. For example, an accession number in
<acqinfo> might be designated as <num localtype="accession">. A
publication number might be designated as <publicationstmt> ...
<num>no. 42</num> ...
See also:
Do not confuse with <container>, <unitid>,
<recordid>, or <otherrecordid> which may also contain
numeric information.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, entry, event, item, p, physfacet, publicationstmt, ref, seriesstmt, unittitle
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<filedesc>
<titlestmt>[...]</titlestmt>
<seriesstmt>
</filedesc><titleproper encodinganalog="440$a">Archival Inventories and Guides
of the World; </titleproper>
<num encodinganalog="440$v"> no. 148 </num>
</seriesstmt><acqinfo>
<p>The collection (Donor No.
</acqinfo><num localtype="donor"> 8338 </num>
) was donated by
<persname relator="donor">
and
<part>Vonda Thomas</part>
</persname><persname relator="donor">
in March 1995.</p><part>Francine Farrow</part>
</persname><objectxmlwrap>
Object XML Wrap [toc]
Summary:
A sublement of <relation> and <source> that allows for the
inclusion of an XML element from any XML namespace other than EAD.
Description and Usage:
A wrapper element that provides a means for incorporating an XML element from
any XML encoding language other than EAD3. While not required, to facilitate
interoperability the XML included in <objectxmlwrap> should conform to
an open, standard XML schema. An xmlns attribute referencing the namespace URI
of the standard should be present, possibly on the <ead> root element or
at the root of the contained foreign element. <objectxmlwrap> may be
used to store related XML data locally rather than linking to external
resources in order to facilitate processing or in cases where the related data
may not be reliably accessible.
May contain:
[any element from any namespace other than EAD]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Available in Relax NG and W3C XML Schema versions only – not available in DTD
version of EAD3.
Example:
<sources>
<source lastdatetimeverified="2015-07-03T14:36:00-05:00" href="https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofamer00drakrich" actuate="onrequest" linktitle="Dictionary of American biography">
</sources><sourceentry>Dictionary of American biography: including men of the
time ... and a supplement</sourceentry>
<objectxmlwrap>Dictionary of American biography, including men of the
time; containing nearly ten thousand notices of persons of both
sexes, of native and foreign birth, who have been remarkable, or
prominently connected with the arts, sciences, literature,
politics, or history of the American continent. Giving also the
pronunciation of many of the foreign and peculiar American
names, a key to the assumed names of writers, and a
supplementDrake, Francis S. (Francis Samuel),
1828-18851872E176 .D725 1872
https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofamer00drakrich
</objectxmlwrap>
<descriptivenote>
</source><p>Basic biographical information about
</descriptivenote><persname source="lcnaf" normal="Freeman, Nathaniel, 1741-1827">
was taken from
<part>Nathaniel Freeman</part>
</persname><title>
, page 340.</p><part>Dictionary of American biography: including men of the
time ... and a supplement</part>
</title><occupation>
Occupation [toc]
Summary:
An element for specifying a profession.
Description and Usage:
A type of work, profession, trade, business, or avocation significantly
reflected in the materials being described.
<occupation> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part> elements may be used to capture each component
of the occupation term, e.g.,
Part 1:Public officers
Part 2:Maryland
Use <occupation> within <controlaccess> for encoding occupations
as defined by controlled vocabularies or according to appropriate rules. You
may also use <occupation> for encoding occupations as they appear within
text.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the occupation in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of occupation.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the occupation if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the occupation has to the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the occupation in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of occupation.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the occupation if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the occupation has to the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
See also:
Do not confuse <occupation> with @relator, which is used
to indicate a certain relationship between a name and the materials being
described.
Do not confuse <occupation> with <function>, which names activities and processes, but not professions.
Do not confuse <occupation> with <function>, which names activities and processes, but not professions.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, p, physfacet, ref, unittitle
References:
MARC 656
MODS <occupation>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Example:
<controlaccess>
<occupation encodinganalog="656" source="aat">
</controlaccess><part>Politicians</part>
</occupation><odd>
Other Descriptive Data [toc]
Summary:
For recording additional information about the described materials that is not
easily incorporated into one of the other named elements within
<archdesc> and <c>.
Description and Usage:
<odd> may be useful in converting legacy finding aids to the EAD format,
by designating as "other" information that does not easily map to a more
specific element. <odd> may be used when information about the described
materials does not correspond to another element’s definition, when the
information is heterogeneous enough to make a single classification difficult,
and when shifting the information to permit more specific content designation
would be too costly or burdensome.
Use <odd> only after considering how the existence of unspecified
content will affect search, retrieval, and display.
References:
ISAD(G) 3.6.1
MARC 500
MODS <note>
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype to more specifically designate the type of
information being provided.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.6.1
MARC 500
MODS <note>
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<odd>
<head>Selected list of correspondents</head>
<p>All correspondence in the collection is arranged chronologically.
Following is a list of notable correspondents, with dates.</p>
<list>
</odd><item>Adams, Samuel
<list>
</item><item>1870 Mar 3</item>
<item>1871 Jan 15</item>
</list><item>Barlow, Christine
[. . .] </list><list>
</item><item>1872 Feb 15</item>
<item>1872 Nov 24</item>
</list><originalsloc>
Location of Originals [toc]
Summary:
For conveying information about the existence of originals when the unit
described exists of copies.
Description and Usage:
<originalsloc> may be used to provide information about the location,
availability, and/or destruction of originals.
See also:
Do not confuse with <altformavail>, which is used to encode
information about copies of the material being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.5.1
MARC 535
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c01 level="file">
<did>
<unittitle>Dream diary, </unittitle>
<unitdate normal="1947/1948">1947-48</unitdate>
</did><originalsloc>
</c01><p>File contains photocopies of original still held by the
donor.</p>
</originalsloc><c01 level="series">
<did>[...]</did>
<originalsloc>
</c01><p>Originals destroyed after microfilming, 1981.</p>
</originalsloc><origination>
Origination [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that names the creator or collector of the
described materials.
Description and Usage:
<orgination> records the name of an individual, organization, or family
responsible for the creation, accumulation, or assembly of the described
materials prior to their accessioning by an archival repository.
<origination> may be used to indicate such agents as correspondents,
records creators, collectors, or dealers.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.2.1
MARC 100, 110, 111
MODS <name>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc level="collection">
<did>
[. . .] </archdesc><origination label="Creator">
[. . .] </did><corpname encodinganalog="110" source="lcnaf">
</origination><part>National Association for the Advancement of Colored
People</part>
</corpname><did>
<head>Descriptive Summary</head>
<unittitle label="Title">Donald C. Stone, Jr. Papers, </unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1971-1983</unitdate>
<unitid countrycode="US" repositorycode="cbgtu" label="Accession number">GTU 2001-8-03</unitid>
<origination label="Creator">
<persname source="lcnaf">
</origination><part>Stone, Donald C., Jr.</part>
</persname><physdesc label="Extent">4 boxes, (4 linear ft.)</physdesc>
<repository label="Repository">The Graduate Theological
Union</repository>
</did><origination label="Creator">
<persname>
</origination><part>Skinner</part>
<part>B. F.</part>
<part>Burrhus Frederic</part>
<part>1904-1990</part>
</persname><otheragencycode>
Other Agency Code [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <maintenanceagency> that provides an alternative code
for the institution or service responsible for the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <otheragencycode> to provide alternative and/or local institution
code that represents the institution or service responsible for the creation,
maintenance, and/or dissemination of the EAD instance. Any code other than that
given in <agencycode> may be provided in <otheragencycode>. The
addition of an ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code as the prefix to a local code is
recommended to ensure international uniqueness.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype to specify the type of code being
provided.
See also:
To provide an institution code in the format of the International
Standard identifier for Libraries and Related Organizations (ISIL: ISO
15511), use <agencycode>.
Provide the name of the agency in <agencyname>.
Provide the name of the agency in <agencyname>.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
References:
MODS <recordContentSource>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<maintenanceagency>
<otheragencycode localtype="archon"> GB-58 </otheragencycode>
<agencyname>British Library</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><maintenanceagency>
<agencycode>DNASA-G</agencycode>
<otheragencycode localtype="agency"> GSFC </otheragencycode>
<agencyname>NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><otherfindaid>
Other Finding Aid [toc]
Summary:
For identifying any other finding aids to the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
Information about additional or alternative guides to the described material,
such as card files, dealers' inventories, a catalog record, or lists generated
by the creator or compiler of the materials. <otherfindaid> is used to
indicate the existence of additional finding aids; it is not designed to encode
the content of those guides.
If desired, use <archref> to give a formal citation to the other finding
aid or to link to an online version of it.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.4.5
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<otherfindaid>
<bibref>The Society has published an expanded guide to this collection:
</otherfindaid><title>
. Compiled by
<part>Guide to the Records of the American Crystal Sugar Company.
</part>
</title><persname relator="author">
; assisted by
<part>David Carmichael</part>
</persname><persname relator="author">
and
<part>Lydia A. Lucas</part>
</persname><persname relator="author">
. St. Paul. Division of Archives and Manuscripts.
Minnesota Historical Society. 1985. </bibref><part>Marion E. Matters</part>
</persname><otherfindaid>
<head>Other Finding Aids</head>
<p>The inventory of individual titles is also available in
</otherfindaid><ref href="itemlist.xlsx" show="new" actuate="onrequest">an Excel
spreadsheet</ref>
, which can be sorted by author, title, subject,
and publication date.</p><otherrecordid>
Other Record Identifier [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <control> that encodes any local identifier for the
EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
<otherrecordid> can be used to record an identifier that is an
alternative to the mandatory identifier provided in <recordid>. These
might include identifiers from systems that were used to generate the EAD
instance or that are no longer current but had some part in the history and
maintenance of the EAD instance.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype to identify the institution or service
responsible for providing the associated record identifier, if not the same
as that given in <maintenanceagency>.
See also:
Use <representation> to capture URLs for transformed and
deliverable versions of the EAD instance (HTML, PDF, etc.).
Do not confuse with <unitid>, which records unique identifiers for the materials being described, rather than the finding aid itself.
Do not confuse with <unitid>, which records unique identifiers for the materials being described, rather than the finding aid itself.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<control>
<recordid>beinecke.hayward</recordid>
<otherrecordid localtype="url ">
http://hdl.handle.net/10079/fa/beinecke.hayward </otherrecordid>
<otherrecordid localtype="publicid"> -//Yale University::Beinecke Rare
Book and Manuscript Library//TEXT (US::CtY-BR::::[ABRAHAM HAYWARD
COLLECTION])//EN </otherrecordid>
<filedesc>
[. . .] </control><titlestmt>
</filedesc><titleproper localtype="formal">Guide to the Abraham Hayward
Collection </titleproper>
<titleproper localtype="filing" render="altrender" altrender="nodisplay" audience="internal"> Hayward (Abraham)
Collection </titleproper>
<author>by Michael Rush</author>
</titlestmt><control>
<recordid instanceurl="http://drs.library.yale.edu/findaids/wa-mss-s-2636.xml">WA
MSS S-2636</recordid>
<otherrecordid localtype="mss"> S-2636 </otherrecordid>
<filedesc>[. . .]</filedesc>
[. . .] </control><p>
Paragraph [toc]
Summary:
A general purpose element used to encode blocks of text.
Description and Usage:
Use <p> for bounding blocks of text. A paragraph may be a subdivision of
a larger composition or it may exist alone. It is usually typographically
distinguished: A line space is often left blank before it; the text begins on a
new line; and the first letter of the first word may be indented, enlarged, or
both.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, list, name, num, occupation, persname, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, blockquote, controlaccess, controlnote, custodhist, descriptivenote, dsc, editionstmt, fileplan, footnote, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, publicationstmt, relatedmaterial, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, seriesstmt, userestrict
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <descriptivenote>: Required, repeatable
Within all other parents: Optional, repeatable
Example:
<bioghist>
<head>Biographical Sketch</head>
<p>John Ferguson Godfrey was born in Toronto on December 19, 1942. He
received a B.A. (Hons.) from Trinity College, University of Toronto, in
1965, a M.Phil. degree from Balliol College, Oxford University, England,
in 1967, and a D.Phil. degree from St. Anthony's College, Oxford
University, in 1975. He holds the title of Doctor of Sacred letters
(honoris causa), Trinity College (1987).</p>
<p> Mr. Godfrey taught in the Department of History of Dalhousie
University, Halifax, first as Assistant Professor (1970-1975), and then
as Associate Professor (1980-1987). At King's College University, Halifax
he held the position of Assistant Professor (1975-1976), before becoming
President and Vice-Chancellor (1977-1987).</p>
</bioghist><part>
Part [toc]
Summary:
A required and repeatable child of controlled access elements used to encode
one or more parts of an access term.
Description and Usage:
Identifies a term contained in an access point element. Access point elements
may contain a single <part> for an entire string, or multiple
<part> elements when more granularity is desired in delineating and
identifying the components of a multi-term string. For post-coordinated access
points combining terms from multiple vocabularies, the identifier,
rules, and source attributes may be used to associate
individual parts to their respective vocabularies.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the part in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system, if different from the @identifier for the parent element. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of part.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the part in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system, if different from the @identifier for the parent element. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of part.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, repeatable.
Examples:
<persname encodinganalog="600" relator="creator" rules="RDA" identifier="http://viaf.org/viaf/23746712">
<part localtype="surname"> Casey </part>
<part localtype="givenname"> Silas </part>
<part localtype="dates"> 1807-1882 </part>
</persname><subject encodinganalog="650" rules="RDA" source="lcsh">
<part encodinganalog="a"> Railroads </part>
<part encodinganalog="z"> Washington (State) </part>
<part encodinganalog="x"> History </part>
</subject><subject encodinganalog="650" source="lcsh">
<part> Dance schools-- Massachusetts--Boston--Archival resources.
</part>
</subject><persname>
Personal Name [toc]
Summary:
An element for identifying a personal name.
Description and Usage:
Identifies a name, including any or all forenames, surnames, honorific titles,
and added names, of a person who is related to the materials being described as
either a source, creator, or subject.
<persname> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part> elements may be used to capture each component
of the personal name, e.g.,
Part 1: Skinner
Part 2: B. F.
Part 3: Burrhus Frederic
Part 4: 1904-1990
Use <persname> within <controlaccess> for encoding personal names
as defined by controlled vocabularies or according to appropriate rules. You
may also use <persname> for encoding personal names as they appear
within text.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the personal name in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of personal name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the personal name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the personal name has to the described materials, for example, "compiler," "creator," "collector," or "subject." The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the personal name in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of personal name.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the personal name if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the personal name has to the described materials, for example, "compiler," "creator," "collector," or "subject." The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, origination, p, physfacet, ref, repository, unittitle
References:
MARC 600, 700
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<controlaccess>
<persname encodinganalog="600" relator="creator" rules="RDA" identifier="http://viaf.org/viaf/23746712" source="viaf">
</controlaccess><part localtype="surname">Casey</part>
<part localtype="givenname">Silas</part>
<part localtype="dates">1807-1882</part>
</persname><origination label="Creator">
<persname>
</origination><part>Skinner</part>
<part>B. F.</part>
<part>Burrhus Frederic</part>
<part>1904-1990</part>
</persname><physdesc>
Physical Description [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that provides a simple, unstructured statement
about the physical characteristics of the material being described.
Description and Usage:
<physdesc> is for describing, in an unstructured statement, the physical
or logical extent, medium, appearance, or construction of the described
materials, such as their dimensions, a count of their quantity, a statement
about the space they occupy, and terms describing their genre, form, or
function, as well as any other aspects of their appearance, such as color,
substance, style, and technique or method of creation.
Those who wish to record formally structured elements of physical description
in order to enable consistent machine processing and data exchange will want to
use <physdescstructured> instead of <physdesc>.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.5
MARC 300
MODS <physicalDescription><extent>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c01 level="series">
<did>
</c01><unittitle>Seizure Records, </unittitle>
<unitdate>December 1908-January 1928.</unitdate>
<physdesc> 4 volumes and 1 folder. </physdesc>
</did><c level="subseries">
<did>
</c><unittitle>Documentary Movies, </unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1952-1964</unitdate>
<physdesc> 2.5 linear ft. </physdesc>
</did><did>
<unittitle>Class Notes, Undergraduate</unittitle>
<unitdatestructured unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notafter="1962">1962</fromdate>
<todate notafter="1968">1968</todate>
</daterange><physdesc> 12 notebooks </physdesc>
<container localtype="boxes">5-6</container>
<didnote>The notebooks contain months and days, not years. Estimated
dates are based on the years Scully attended the University of
Maryland.</didnote>
</did><physdescset>
Physical Description Set [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> used to bind two or more structured expressions
of the physical description of the materials.
Description and Usage:
<physdescset> binds together two or more <physdescstructured>
elements. A set of <physdescstructured> elements may relate in one of
two ways: they may be parallel to each other or they may describe disparate
parts that together represent the whole or part of the material described.
For example, a <physdescset> with @parallel="true" might bind a
<physdescstructured> element with @physdescstructuredtype="carrier"
and a <physdescstructured> element with
@physdescstructuredtype="spaceoccupied," indicating that the two
<physdescstrutured> elements describe the same materials in different
ways and are therefore parallel statements of extent. @parallel="true" denotes
that <physdescset> and its child <physdescstructured> elements
share the same coverage value, i.e., a statement of extent for part
of the materials described cannot be parallel to a statement of extent for the
whole of the materials described.
Alternately, a <physdescset> with @parallel="false" may combine two or
more <physdescstructured> elements that do not describe the same
materials. @parallel="false" denotes that <physdescstructured> elements
that comprise the set all share @coverage="part" (two or more extent statements
with @coverage="whole" are by definition parallel).
A <physdescset> with @parallel="false" and @coverage="whole" indicates
multiple statements of extent that in sum represent the whole of the materials
being described.
A <physdescset> with @parallel="false" and @coverage="part" indicates
multiple statements of extent that in sum represent a part of the materials
being described.
It is not necessary to bind multiple <physdescstructured> elements
within <physdescset>. Only do so when you need to convey the
relationships indicated by parallel and coverage.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional (values limited to: part, whole)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<physdescset parallel="true">
<physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="spaceoccupied">
<quantity>650</quantity>
<unittype>gigabytes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity>1</quantity>
<unittype>hard disk</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
</physdescset><quantity>7500</quantity>
<unittype>electronic files</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescset parallel="false" coverage="whole">
<physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity>50</quantity>
<unittype>boxes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
</physdescset><quantity>5</quantity>
<unittype>broadside folders</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescset parallel="false" coverage="part">
<physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity>10</quantity>
<unittype>videocassettes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
</physdescset><quantity>25</quantity>
<unittype>audiocassettes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescset>
<physdescstructured label="Quantity: " physdescstructuredtype="carrier" coverage="whole" encodinganalog="300">
<quantity>3 </quantity>
<unittype>boxes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured label="Quantity: " physdescstructuredtype="spaceoccupied" coverage="whole" encodinganalog="300">
<quantity>1.2</quantity>
<unittype>cubic feet</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured label="Quantity: " physdescstructuredtype="materialtype" coverage="whole" encodinganalog="300">
</physdescset><quantity>50</quantity>
<unittype>diaries</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured>
Structured Physical Description [toc]
Summary:
An element that provides a method for expressing structured statements about
the extent and physical characteristics of the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
<physdescstructured> creates structured statements describing the
physical or logical extent or the medium of the materials being described. The
use of <physdescstructured> allows for quantifying the extent of the
whole or a part of the materials described in a form that will be machine
processable and that will facilitate reporting, statistics, sorting, and
importing and exporting data in a collection management system.
The prescribed order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<quantity>
<unittype>
<physfacet> or <dimensions>
<descriptivenote>
<unittype>
<physfacet> or <dimensions>
<descriptivenote>
Attribute usage:
Use the required @physdescstructuredtype to specify the nature
of the statement about the materials being described.
See also:
Use <physdesc> to express physical description in a
non-machine-processable form and in instances where data exchange is not a
concern.
Use <physdescset> to bind two or more <physdescstructured> elements in order to convey parallel or coverage relationships between them.
Use <physdescset> to bind two or more <physdescstructured> elements in order to convey parallel or coverage relationships between them.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.5
MARC 300
MODS <physicalDescription><extent>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Required (values limited to: part, whole)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Required (values limited to: carrier, materialtype,
otherphysdescstructuredtype, spaceoccupied)
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<physdescstructured coverage="whole" physdescstructuredtype="spaceoccupied">
<quantity>12</quantity>
<unittype>linear feet</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="whole" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity>24</quantity>
<unittype>boxes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity>5</quantity>
<unittype>dageurreotypes</unittype>
<physfacet>hand-tinted</physfacet>
<dimensions>6.5 x 8.5 inches</dimensions>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity></quantity>
<unittype identifier="http://vocab.getty.edu/aat/300247651">
Volvelles</unittype>
<dimensions>10 cm in diameter</dimensions>
</physdescstructured><physdescset parallel="true" coverage="part">
<physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="spaceoccupied">
<quantity>6</quantity>
<unittype>terabytes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity>12</quantity>
<unittype>hard drives</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
</physdescset><quantity>1800</quantity>
<unittype>electronic files</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="whole" physdescstructuredtype="otherphysdescstructuredtype" otherphysdescstructuredtype="duration">
<quantity>30</quantity>
<unittype>minutes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physfacet>
Physical Facet [toc]
Summary:
Achild element of <physdescstructured> that provides more detailed
information about the physical nature of or techniques and methods of creation
of the material described in terms that are often taken from a controlled
vocabulary list.
Description and Usage:
<physfacet> records information about an aspect of the physical nature –
such as color, style, marks, substances, materials, playback speed, duration,
track configuration, and motion picture presentation format – or techniques and
methods of creation of the units identified by <unittype> within
<physdescstructured>. It generally should not be used for aspects of
physical description that are covered more directly by <unittype>,
<dimensions> and <genreform>.
Physical facet terminology can be found in the Art and Architecture Thesaurus
and other sources for authorized data values.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, expan, emph, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, name, num, occupation, persname, quote, ptr, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity>5</quantity>
<unittype>dageurreotypes</unittype>
<physfacet> hand-tinted </physfacet>
<dimensions>6.5 x 8.5 inches</dimensions>
</physdescstructured><physdescset parallel="false" coverage="part">
<physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity>10</quantity>
<unittype>videocassettes</unittype>
<physfacet> tabs removed </physfacet>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
</physdescset><quantity>25</quantity>
<unittype>audiocassettes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physloc>
Physical Location [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that specifies the physical location of the
materials.
Description and Usage:
<physloc> is used to identify where the described materials are stored,
and it may contain such information as the name or number of the building,
room, stack, shelf, etc., where the materials may be stored and retrieved.
<physloc> can be used to designate onsite and offsite storage
locations.
Attribute usage:
Like all child elements of <did>, <physloc> has
@label that may be used to provide a readily understandable
heading for the element's content.
See also:
Do not confuse with <container>, which is used to identify the
cartons, boxes, reels, folders, and other storage devices used to hold the
described materials.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MARC 852
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (IDREFS)
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc localtype="inventory" level="subgrp">
<did>
</archdesc><head>Overview of the Records</head>
<repository label="Repository:">
<corpname>
</repository><part>Minnesota Historical Society</part>
</corpname><origination label="Creator:">
<corpname>
</origination><part>Minnesota. Game and Fish Department</part>
</corpname><unittitle label="Title:">Game laws violation
records,</unittitle>
<unitdate label="Dates:">1908-1928</unitdate>
<abstract label="Abstract:">Records of prosecutions for and seizures
of property resulting from violation of the state's hunting and
fishing laws.</abstract>
<physdesc label="Quantity:">2.25 cu. ft. (7 v. and 1 folder in 3
boxes)</physdesc>
<physloc label="Location:"> Offsite </physloc>
</did><c02 level="file">
<did>
</c02><physloc localtype="shelf"> 27:A:4 </physloc>
<container localtype="box">2</container>
<unittitle>Printed material</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">December 1908-July
1917</unitdate>
</did><phystech>
Physical Characteristics and Technical Requirements [toc]
Summary:
For describing the physical condition of the materials and/or technical
requirements that affect their use.
Description and Usage:
<phystech> is used to capture any physical or technical characteristics
that affect the storage or use of the materials described. This may include
details of their physical composition, preservation requirements, or particular
hardware or software needed to access the materials.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.4.4
MARC 340, 538
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c04 level="item">
<did>[...]</did>
<phystech>
</c04><p>Some oxydization of the aluminum layer.</p>
</phystech><c02 level="subseries">
<did>[...]</did>
<phystech>
</c02><head>System Requirements</head>
<p>48K RAM; Apple Disk II with controller; colour monitor</p>
</phystech><prefercite>
Preferred Citation [toc]
Summary:
An element for specifying how users should cite the described materials in
publication credits.
Description and Usage:
Use <prefercite> to supply users with a prescribed wording or format for
references to the described materials to be included in bibliographies,
footnotes, screen credits, etc.
See also:
Do not confuse with <archref> or <bibref>, which are used
to cite materials other than those described in the finding aid.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MARC 524
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<prefercite>
<head>Preferred Citation</head>
<p>[Identification of item], Arequipa Sanatorium Records, BANC MSS
92/894c, The Bancroft Library, University of California,
Berkeley.</p>
</prefercite><prefercite>
<p>item, folder title, box number, Charles Thomas, Jr. Papers, Bentley
Historical Library, University of Michigan.</p>
</prefercite><processinfo>
Processing Information [toc]
Summary:
For encoding information about archival activities related to the described
materials.
Description and Usage:
<processinfo> is used for basic information about accessioning,
arranging, describing, preserving, storing, conserving, or otherwise preparing
the described materials for research use. Where appropriate, encode more
specific information about each of these activities separately within other
elements, such as <acqinfo>, <appraisal>, <arrangement>,
<physloc>, etc.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.7.1
MARC 583
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<processinfo>
<head>Processing Information:</head>
<p>These records were organized and cataloged in
</processinfo><date>1977</date>
by Lydia Lucas.</p><processinfo>
<head>Processing Information:</head>
<p>Material was processed over several years.</p>
<chronlist>
</processinfo><chronitem>
<datesingle>1982</datesingle>
<event>Correspondence processed</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
<datesingle>1984</datesingle>
<event>Published material transferred to Rare Books for
cataloging.</event>
</chronitem><chronitem>
</chronlist><datesingle>1989</datesingle>
<event>Processing completed, including integration of 1986 and
1987 accessions</event>
</chronitem><processinfo>
<p>Re-bound in 1987 as two volumes for conservation purposes.</p>
</processinfo><ptr>
Pointer [toc]
Summary:
An empty element that provides links to content that may be internal or
external to the finding aid.
Description and Usage:
An empty linking element that provides links both to content within a finding
aid, or from a finding aid to external content. <ptr> may be used in a
variety of ways in an encoded finding aid. For example, <ptr> may
provide an internal link from one location in a finding aid to another. Or,
<ptr> might be used to embed an image into the text of a finding aid.
Unlike <ref>, <ptr> cannot contain text or child elements to
describe the referenced object. When <ptr> is used to embed internal
links, the text of the link must be generated by the transforming style
sheet.
Attribute usage:
Use @target to link to another element within the finding
aid.
Use @href to link to or embed an external file.
Use @linkrole to provide a URI that characterizes the nature of the remote resource to which <ptr> links.
Use @arcrole to provide a URI that characterizes the nature of the link itself.
Use @href to link to or embed an external file.
Use @linkrole to provide a URI that characterizes the nature of the remote resource to which <ptr> links.
Use @arcrole to provide a URI that characterizes the nature of the link itself.
See also:
<ref>, if you wish to encode text and child elements to display a
link to the external file.
<dao>, if you wish to link to or embed an external file in <did>.
<dao>, if you wish to link to or embed an external file in <did>.
May contain:
[empty]
May occur within:
abstract, addressline, archref, author, bibref, citation, container, date, datesingle, didnote, dimensions, edition, emph, entry, event, fromdate, head, head01, head02, head03, indexentry, item, label, materialspec, num, p, part, physdesc, physfacet, physloc, ptrgrp, publisher, quote, ref, sponsor, subtitle, titleproper, todate, unitdate, unitid, unittitle
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: none, onload, onrequest, other)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: embed, new, none, other, replace)
Optional (IDREF)
Optional
Availability:
Within <ptrgrp>: One of <ptr> or <ref> is required,
repeatable
Within all other parents: Optional, repeatable
Example:
<appraisal>
<p>This collection was re-appraised by repository staff in 1992 in order
to facilitate use by weeding the collection of materials no longed deemed
as having evidential or informational value. A list of materials removed
from the collection after the re-appraisal is provided at the end of this
guide.
</appraisal><ptr actuate="onrequest" show="replace" target="mss1982-062_add2"></ptr>
</p><ptrgrp>
Pointer Group [toc]
Summary:
An element for binding together two or more <ptr> or <ref>
elements.
Description and Usage:
<ptrgrp> is used to group multiple <ptr> or <ref> elements
within an <indexentry>. Use <ptrgrp> within <indexentry>
when there are multiple pointers and/or references related to a single access
heading in <index>. For example, if the name "Emily Dickinson" is found
in multiple places in a finding aid, the name could be entered as a single
<persname> in <indexentry>, with a <ptrgrp> containing
multiple <ref> or <ptr> elements to link to the occurences of
that name elsewhere within the EAD instance. <ptrgrp> prevents the entry
from having to appear multiple times in the index.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
<publicationstatus>
Publication Status [toc]
Summary:
An optional child element of <control> that records the current
publishing status of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <publicationstatus> to indicate the current publication status of
the EAD instance, whether in process or final. An optional element,
<publicationstatus>, is only necessary if it supports local
maintenance practice.
If present, the current publication status must always be reflected in the
required value attribute. The element should only have a text value
if it is necessary to provide a value for <publicationstatus> in a
language other than English, otherwise it should remain empty.
Attribute usage:
Use @value, which offers a controlled list of terms, to provide
information about the current publication status of the EAD instance.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Required (values limited to: inprocess, approved, published)
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<control> [. . .]
<maintenancestatus value="derived"></maintenancestatus>
<publicationstatus value=" approved "></publicationstatus>
<maintenanceagency>
[. . .] </control><otheragencycode localtype="archon">GB-58</otheragencycode>
<agencyname>British Library</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><control> [. . .]
<maintenancestatus value="revised"></maintenancestatus>
<publicationstatus value="published"></publicationstatus>
<maintenanceagency>
[. . .] </control><agencycode>DNASA-G</agencycode>
<otheragencycode localtype="agency">GSFC</otheragencycode>
<agencyname>NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</agencyname>
</maintenanceagency><publicationstmt>
Publication Statement [toc]
Summary:
An optional child element of <filedesc> that provides information
concerning the publication or distribution of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <publicationstmt> to record and bind together information about the
publication or distribution of a finding aid. Such information includes the
publisher’s name and contact information, publication date, and other details
of publication or distribution. <publicationstmt> may contain free text
within one or more <p> elements, or it may include <publisher>,
<address>, <date>, and <num> child elements, which
allow for more specific tagging of a publisher's name and address, the date of
publication, and the number, if any, assigned to the published finding aid.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
<publisher>
Publisher [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <publicationstmt> that identifies the institution or
agency responsible for distribution of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <publisher> to record the name of the agent responsible for issuing
or distributing the EAD instance. Often this is the same corporate body
identified in <repository> in <did>.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local practice requires recording the type of
name.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <publicationstmt> one of <address>, <date>,
<num>, <p>, or <publisher> is required, repeatable
Examples:
<publicationstmt>
<publisher> Yale University Library </publisher>
<publisher> Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library </publisher>
<publisher> General Collection of Modern Books and Manuscripts </publisher>
<address>
<addressline>New Haven, Connecticut</addressline>
</address><date localtype="original" normal="2006-10">October 2006</date>
<p>
</publicationstmt><ref actuate="onrequest" show="new" href="http://hdl.handle.net/10079/9p8czk9 "> Copyright ©
</p><date localtype="copyright" normal="1996/2007">1996-2007</date>
by
the Yale University Library.</ref><publicationstmt>
<publisher> British Library </publisher>
</publicationstmt><quantity>
Quantity [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <physdescstructured> that indicates the
number of units present as described by <unittype>.
Description and Usage:
<quantity> is for indicating the number of <unittype>s being
described. The content of <quantity> should be a number. Use of
<quantity> enables extent statements to be machine processable. If
the quantity is unknown, the element should remain empty.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<physdescstructured physdescstructuredtype="materialtype" coverage="whole">
<quantity> 15 </quantity>
<unittype>daguerreotypes</unittype>
<dimensions>3.25" x 4.25"</dimensions>
<physfacet>hand colored</physfacet>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity> 1 </quantity>
<unittype>hard disk</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity> 7500 </quantity>
<unittype>electronic files</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity> 50 </quantity>
<unittype>boxes</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity> 5 </quantity>
<unittype>broadside folders</unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
<quantity> 10 </quantity>
<unittype>videocassettes</unittype>
<physfacet>tabs removed</physfacet>
</physdescstructured><quote>
Quote [toc]
Summary:
A phrase-level element for identifying or formatting an inline quotation.
Description and Usage:
Use <quote> to identify inline quotations within a block of text.
See also:
Use <blockquote> to designate an extended quotation.
May contain:
References:
Equivalent to the element <q> in HTML.
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<p>In 1963, at the age of 27, Turnbull co-founded the firm of MLTW with
fellow principals Charles Moore, Donlyn Lyndon, and Richard Whitaker. In a
1968 letter to architectural historian David Gebhardt, Turnbull writes of
the MLTW collaboration,
<quote>Essentially Chuck, Don, Dick and I are or
were all designers. We worked together with the man having the strongest
opinion about a subject usually prevailing. This built-in system of
checks and balances was one of the reasons why the quality of design was
so high . . .</quote>
</p><recordid>
Record Identifier [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <control> that designates a unique
identifier for the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
<recordid> is used for recording a unique identifier for the EAD
instance. The institution assigning the identifier ensures uniqueness of the
<recordid> value within the archival descriptions under its control.
A globally unique identifier may be constructed within <recordid>
according various external protocols (i.e. HTTP URI, DOI, PURL, or UUID), or in
combination with <agencycode>, which is a required child element of
<maintenanceagency>.
Attribute usage:
Use @instanceurl to record the URL of the EAD XML
instance.
See also:
If recording alternative identifiers is desired, use
<otherrecordid>.
Use <representation> to capture URLs for transformed and deliverable versions of the EAD instance (HTML, PDF, etc.).
Do not confuse with <unitid>, which records unique identifiers for the materials being described, rather than the finding aid itself.
Use <representation> to capture URLs for transformed and deliverable versions of the EAD instance (HTML, PDF, etc.).
Do not confuse with <unitid>, which records unique identifiers for the materials being described, rather than the finding aid itself.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.1
MODS <recordIdentifier>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<control>
<recordid> AddMS88938 </recordid>
<filedesc>
[. . .] </control><titlestmt>
<titleproper>Catalogue of the Papers of James Graham
Ballard</titleproper>
</titlestmt><publicationstmt>
</filedesc><publisher>British Library</publisher>
</publicationstmt><control>
<recordid instanceurl="http://drs.library.yale.edu/findaids/wa-mss-s-2636.xml"> WA
MSS S-2636 </recordid>
<otherrecordid localtype="mss">S-2636</otherrecordid>
<filedesc>[. . .]</filedesc>
[. . .] </control><ref>
Reference [toc]
Summary:
An element that provides a link to content that may be internal or external to
the finding aid.
Description and Usage:
<ref> may be used in a variety of ways in an encoded finding aid. For
example, <ref> may provide an internal link from one <c> to
another related <c> in the same way that See and See also references
direct readers of paper-based finding aids. Or, <ref> might be used to
direct the reader from text in a scope and content note to a description of a
<c> in a contents list. <ref> might also point to an external
file, for example, a finding aid for a related collection at another
repository.
Attribute usage:
Use @target to link to another element within the finding
aid.
Use @href to link to or embed an external file.
Use @linkrole to provide a URI that characterizes the nature of the remote resource to which <ref> links.
Use @arcrole to provide a URI that characterizes the nature of the link itself.
Use @href to link to or embed an external file.
Use @linkrole to provide a URI that characterizes the nature of the remote resource to which <ref> links.
Use @arcrole to provide a URI that characterizes the nature of the link itself.
See also:
Use <ptr> to provide a reference to a file when text or child
elements that describe the referenced object are not needed, for example,
when providing an image to be embedded in the finding aid.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, function, genreform, geogname, lb, name, num, occupation, persname, ptr, quote, subject, title
May occur within:
abstract, addressline, archref, author, bibref, citation, container, date, datesingle, didnote, dimensions, edition, emph, entry, event, fromdate, head, head01, head02, head03, indexentry, item, label, materialspec, num, p, part, physdesc, physfacet, physloc, ptrgrp, publisher, quote, sponsor, subtitle, titleproper, todate, unitdate, unitid, unittitle
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: none, onload, onrequest, other)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: embed, new, none, other, replace)
Optional (IDREF)
Optional
Availability:
Within <ptrgrp>: One of <ptr> or <ref> is required,
repeatable
Within all other parents: Optional, repeatable
Example:
<indexentry>
<genreform>
<part>Pedigree, 20th cent.</part>
</genreform><ref linkrole="internal" target="EngC5769-f74" show="replace" actuate="onrequest">MS. Eng. c. 5769, fol. 74</ref>
</indexentry>
Related Material [toc]
Summary:
For identifying archival materials that have an association to the materials
being described.
Description and Usage:
<relatedmaterial> is used to identify associated materials in the same
repository or elsewhere. These materials may be related by sphere of activity,
or subject matter.
See also:
Do not confuse with <separatedmaterial>, which provides
information about materials that have been separated or physically removed
from the described materials but that are related to them by
provenance.
Do not confuse with <altformavail>, which encodes information about copies of the described materials, such as microforms, photocopies, and reproductions in digital formats.
Do not confuse with <originalsloc>, which encodes information regarding the existence and location of the originals when the unit being described consists of copies.
Do not confuse with <altformavail>, which encodes information about copies of the described materials, such as microforms, photocopies, and reproductions in digital formats.
Do not confuse with <originalsloc>, which encodes information regarding the existence and location of the originals when the unit being described consists of copies.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.5.3
MARC 544
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<relatedmaterial>
<p>See also the following collections:</p>
<archref>Mary Smith Papers</archref>
<archref>Jeremiah Smith Correspondence</archref>
</relatedmaterial><separatedmaterial>
<p>Photographs and sound recordings have been transferred to the
appropriate custodial divisions of the Library where they are identified
as part of these papers. Among the sound recordings are the following
broadcasts:</p>
<list>[...]</list>
</separatedmaterial><relatedmaterial>
<p>Records relating to the Warren Commission are held in the National
Archives and Records Administration.</p>
</relatedmaterial><relatedmaterial>
<p>Several genealogies and biographies of the Smith family have been
published and are held in the Rare Books Department.</p>
<bibref>Kavanaugh, Carol.
<title>
. (New York: Penguin)
<part>The Smith Family in Johnson County</part>
</title><num localtype="bibid">4569982</num>
</bibref><bibref>Llewellyn, Gareth.
</relatedmaterial><title>
. (London: Jonathan Cape)
<part>Smythe, Smith: What's the Difference?</part>
</title><num localtype="bibid">336712</num>
</bibref><relation>
Relation [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <relations> for describing a relationship between the
materials described in the EAD instance and a related entity.
Description and Usage:
<relation> records descriptive information about a relationship between
the materials being described and a related entity, such as: an archival,
bibliographic, or other resource; a corporate body, person, or family; a
function; or any other entity.
Use <relationentry> to provide a textual description of the related
entity. Use <objectxmlwrap> to embed XML documenting the related entity
from any namespace other than EAD3. Use <date>, <daterange>, or
<dateset> for specifying the time period of the relationship and
<geogname> for relevant location information.
<descriptivenote> may be included for more detailed specifications or
explanations of the relationship.
The prescribed order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<relationentry>
<objectxmlwrap>
<datesingle>, <daterange>, and/or <dateset>
<geogname>
<descriptivenote>
<objectxmlwrap>
<datesingle>, <daterange>, and/or <dateset>
<geogname>
<descriptivenote>
Element status:
Attribute usage:
Use @relationtype to specify the kind of relationship being
encoded.
Use @otherrelationtype to specify the alternate type of relationship, when @relationtype is set to "otherrelationtype"
Use @arcrole to supply a URI that describes the nature of the relationship between the materials being described and the related entity.
Use @linkrole to supply a URI that describes the nature of the remote resource.
Use @otherrelationtype to specify the alternate type of relationship, when @relationtype is set to "otherrelationtype"
Use @arcrole to supply a URI that describes the nature of the relationship between the materials being described and the related entity.
Use @linkrole to supply a URI that describes the nature of the remote resource.
See also:
The children of <controlaccess>, which can be used to specify the
individuals, organizations, families, topics, and functions related to the
materials being described using controlled vocabularies.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: none, onload, onrequest, other)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (must follow pattern based on ISO 8601)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Required (values limited to: cpfrelation, functionrelation,
resourcerelation, otherrelationtype)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: embed, new, none, other, replace)
Availability:
Required, repeatable
Experimental in EAD3
Example:
<relationentry>
Relation Entry [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <relation> that identifies an entity related to the
materials being described.
Description and Usage:
<relationentry> identifies an entity that has a relationship to the
materials being described. The entry may name a corporate body, person, family,
resource, function, or other entity as defined by the relationtype
of the parent <relation>.
<relationentry> should only repeat when necessary to express the same
<relationentry> in multiple languages or scripts.
Element status:
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local practice requires recording the type of
relation entry.
Use @transliteration to indicate the conventions or rules that prescribe a method for converting one script to another.
Use @transliteration to indicate the conventions or rules that prescribe a method for converting one script to another.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<relations>
Relations [toc]
Summary:
An element that groups one or more <relation> elements, which identify
external entities and characterize the nature of their relationships to the
materials being described.
Description and Usage:
A wrapper element that groups together one or more <relation> elements,
each of which encodes a specific relationship.
The material described in an EAD instance may have relationships with other
resources:
For archival collections, bibliographic resources, or artifacts, use
<relation> with the @relationtype set to
"resourcerelation."
For corporate bodies, persons or families, use <relation> with the @relationtype set to "cpfrelation."
For functions use, <relation> with the @relationtype set to "functionrelation."
For relationships to other entities such as places, events and topics, use <relation> with the @relationtype set to "otherrelationtype" and the type of related entity specified in the @otherrelationtype.
For corporate bodies, persons or families, use <relation> with the @relationtype set to "cpfrelation."
For functions use, <relation> with the @relationtype set to "functionrelation."
For relationships to other entities such as places, events and topics, use <relation> with the @relationtype set to "otherrelationtype" and the type of related entity specified in the @otherrelationtype.
Element status:
See also:
<controlaccess>, which binds together elements containing access
headings from controlled vocabularies related to the described
materials.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc>
<did>
<unittitle>Michael Butterworth Papers</unittitle>
[...] </did><relations>
[...] </archdesc><relation relationtype="resourcerelation" href="http://resolver.bl.uk/ark:/81055/vdc_100000000035.0x000122" actuate="onrequest" show="new" arcrole="http://www.w3c.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#seeAlso" linkrole="http://purl.org/archival/vocab/arch#Collection">
</relations><relationentry>Add MS 88967: Michael Butterworth and J G
Ballard: Correspondence, 1965-2011</relationentry>
</relation><c01 level="series">
<did>
<unittitle>Archives du Bretagne</unittitle>
[...] </did><relations>
</c01><relation relationtype="resourcerelation">
</relations><relationentry>Archives du cabinet du préfet du
Morbihan</relationentry>
<geogname>
</relation><part>Morbihan, département du (France) </part>
</geogname><archdesc level="collection">
<did>
<unittitle>Johann Sebastian Bach Papers</unittitle>
</did><relations>
</archdesc><relation relationtype="cpfrelation" arcrole="http://purl.org/dc/terms/subject" linkrole="http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person" href="http://socialarchive.iath.virginia.edu/ark:/99166/w6v988fv">
<relationentry>Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach</relationentry>
<descriptivenote>
</relation><p>Bach's son</p>
</descriptivenote><relation relationtype="cpfrelation" arcrole="http://purl.org/dc/terms/subject" linkrole="http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person" href="http://viaf.org/viaf/71579513">
</relations><relationentry>Georg Philipp Telemann</relationentry>
<descriptivenote>
</relation><p>Bach's godfather</p>
</descriptivenote><archdesc level="collection">
<did>
<unittitle>Henry VIII Papers</unittitle>
[...] </did><relations>
</archdesc><relation relationtype="cpfrelation" arcrole="http://purl.org/dc/terms/subject" linkrole="http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person" href="http://n2t.net/ark:/99166/w62r4rsz">
</relations><relationentry>Katherine of Aragon</relationentry>
<daterange>
<fromdate standarddate="1509-06-11">11 June 1509</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1533-05-23">23 May 1533</todate>
</daterange><descriptivenote>
</relation><p>Wife</p>
</descriptivenote><c01 level="series">
<did>
<unittitle>Commissioned projects</unittitle>
[...] </did><relations>
</c01><relation relationtype="cpfrelation">
<relationentry>Wohnbedarf Furniture Company</relationentry>
<geogname>
</relation><part>Basel, Switzerland</part>
</geogname><relation relationtype="cpfrelation">
</relations><relationentry>New York World’s Fair</relationentry>
<datesingle standarddate="1939">1939</datesingle>
<geogname>
</relation><part>New York, NY</part>
</geogname><archdesc level="collection">
<did>
<unittitle>ExxonMobil Corporate Records</unittitle>
[...] </did><relations>
[...] </archdesc><relation relationtype="resourcerelation" href="http://www.amazon.com/Private-Empire-ExxonMobil-American-Power/dp/0143123548">
<relationentry>Private Empire: ExxonMobil and American Power, by
Steve Coll (Penguin Books : 2013)</relationentry>
</relation><relation relationtype="resourcerelation" href="http://www.lib.utexas.edu/taro/utcah/00462/cah-00462.html">
<relationentry>ExxonMobil Historical
Collection</relationentry>
<descriptivenote>
</relation><p>Dolph Briscoe Center for American History,The University of
Texas at Austin; includes predecessor organizations</p>
</descriptivenote><relation relationtype="cpfrelation" href="http://lccn.loc.gov/n79053084">
<relationentry>Exxon</relationentry>
<daterange>
<fromdate standarddate="1972">1972</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1999">1999</todate>
</daterange><geogname>
</relation><part>United States</part>
</geogname><relation relationtype="cpfrelation" href="http://lccn.loc.gov/n82045453">
<relationentry>Mobil</relationentry>
<daterange>
<fromdate standarddate="1911">1911</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1999">1999</todate>
</daterange><geogname>
</relation><part>United States</part>
</geogname><relation relationtype="cpfrelation" href="http://lccn.loc.gov/n85037919">
<relationentry>Imperial Oil Limited</relationentry>
<daterange>
<fromdate standarddate="2012">2012</fromdate>
</daterange><geogname>
</relation><part>Canada</part>
</geogname><relation relationtype="cpfrelation">
<relationentry>Rockefeller, John D.</relationentry>
<descriptivenote>
</relation><p>Founder</p>
</descriptivenote><relation relationtype="functionrelation" href="http://lccn.loc.gov/sh85063317">
<relationentry>Hydraulic fracturing</relationentry>
</relation><relation relationtype="functionrelation">
<relationentry>Gasoline retail</relationentry>
<daterange>
<fromdate standarddate="1999">1999</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="2008">2008</todate>
</daterange><descriptivenote>
</relation><p>Transitioning out of retail business as of 2008; retail will
be taken over by subsidiaries</p>
</descriptivenote><relation relationtype="functionrelation" href="http://lccn.loc.gov/sh85100427">
<relationentry>Petroleum engineering</relationentry>
<descriptivenote>
</relation><p>including production of plastics, lubricants, etc.</p>
</descriptivenote><relation relationtype="otherrelationtype" otherrelationtype="Creator">
</relations><relationentry>Exxon Valdez oil spill</relationentry>
<geogname>
</relation><part>Bligh Reef, Prince William Sound, Alaska</part>
<geographiccoordinates coordinatesystem="utm">6V 490800mE
6719917mN</geographiccoordinates>
</geogname><repository>
Repository [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that names the institution, person, or family
responsible for providing intellectual access to the materials being
described.
Description and Usage:
<repository> records the name of the institution or agency, family, or
individual responsible for providing intellectual access to the materials being
described. <corpname>, <famname>, <name>, or
<persname> must be used within <repository> to encode the
proper name. This may be followed by an optional <address> to provide
contact information for the repository.
Although the repository providing intellectual access usually also has physical
custody over the materials, this is not always the case. For example, an
archives may assume responsibility for long-term intellectual access to
electronic records, but the actual electronic data files or systems may
continue to reside in the office where they were created and maintained, or
they may be held for long-term storage by a unit such as a data library that is
able to provide the appropriate technical facilities for storage and
remounting.
When it is clear that the physical custodian does not provide intellectual
access, use <physloc> to identify the custodian and <repository>
to designate the intellectual caretaker. When a distinction cannot be made,
assume that the custodian of the physical objects also provides intellectual
access to them and should be recognized as the <repository>.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MARC 852
MODS <location><physicalLocation>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc localtype="inventory" level="subgrp">
<did>
</archdesc><head>Overview of the Records</head>
<repository label="Repository:">
<corpname>
</repository><part>Minnesota Historical Society</part>
</corpname><origination label="Creator:">
<corpname>
</origination><part>Minnesota. Game and Fish Department</part>
</corpname><unittitle label="Title:">Game laws violation
records,</unittitle>
<unitdate label="Dates:">1908-1928</unitdate>
<abstract label="Abstract:">Records of prosecutions for and seizures
of property resulting from violation of the state's hunting and
fishing laws.</abstract>
<physdesc label="Quantity:">2.25 cu. ft. (7 v. and 1 folder in 3
boxes)</physdesc>
<physloc label="Location:">See Detailed Description section for box
location</physloc>
</did><archdesc level="fonds">
<did>
</archdesc><unitid>EW</unitid>
<unittitle>Records of the Department of Economic
Affairs</unittitle>
<origination>
<corpname>
</origination><part>Department of Economic Affairs</part>
</corpname><unitdate>1945-1979</unitdate>
<physdesc>28 series</physdesc>
<repository>
</did><corpname>
</repository><part>The National Archives</part>
</corpname><representation>
Representation [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <control> for recording a link to a transformed and
deliverable version of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <representation> to record a link to a transformed and deliverable
version of an EAD instance, for example an HTML or PDF version. If desired, the
localtype attribute can be used to differentiate multiple
<representation> elements.
See also:
Do not confuse with the @instanceurl on <recordid>, used
to record the URL of the XML version of the EAD.
Use <otherrecordid> to provide any local identifier for the EAD instance that does not link to a deliverable version.
Use <otherrecordid> to provide any local identifier for the EAD instance that does not link to a deliverable version.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: none, onload, onrequest, other)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: embed, new, none, other, replace)
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<control>
<recordid instanceurl=
"http://drs.library.yale.edu:8083/fedora/get/beinecke:jonesss/EAD"
>beinecke.jonesss</recordid>
"http://drs.library.yale.edu:8083/fedora/get/beinecke:jonesss/EAD"
>beinecke.jonesss</recordid>
<representation href="http://hdl.handle.net/10079/fa/beinecke.jonesss" linkrole="text/html">HTML version of finding aid</representation>
<representation href="http://drs.library.yale.edu:8083/fedora/get/beinecke:jonesss/PDF" linkrole="application/pdf">PDF version of finding
aid</representation>
[. . .] </control><row>
Table Row [toc]
Summary:
A formatting element that contains one or more horizontal cells in a table.
Description and Usage:
A formatting element that contains one or more <entry> elements in a
table. By convention, a rule specified by rowsep prints or displays
below the row. Vertical rules are specified by colsep in
<table> or one of its column-related descendant elements; external
rules are specified by frame available on <table>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: bottom, middle, top)
Availability:
Within <tbody> and <thead>, required, repeatable
<scopecontent>
Scope and Content [toc]
Summary:
An element that provides information about the nature of and activities
reflected in the described materials.
Description and Usage:
<scopecontent> contains a narrative statement that summarizes the range
and topical coverage of the materials. It provides the researcher with the
information necessary to evaluate the potential relevance of the materials
being described. <scopecontent> may include information about the form
and arrangement of the materials; dates covered by the materials; significant
organizations, individuals, events, places, and subjects represented in the
materials; and functions and activities that generated the materials being
described. It may also identify strengths of or gaps in the materials.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.3.1
MARC 520
MODS <abstract>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc level="fonds">
<did>[...]</did>
<scopecontent encodinganalog="520">
</archdesc><head>Scope and Content</head>
<p>Fonds includes records relating to the Department of Plant
Ecology's administration, teaching and research; extension work
relating to the Saskatchewan Weed Survey; and correspondence with a
variety of institutions and individuals. A series of minutes and
correspondence relating to the Saskatchewan Committee on the Ecology
and Preservation of Grasslands (established in 1935) documents the
efforts to establish permanent reserves of significant grasslands in
Saskatchewan.</p>
</scopecontent><dsc dsctype="combined">
<head>Detailed Description of the Collection</head>
<c01 level="series">
</dsc><did>
<unittitle>Record of Prosecutions, </unittitle>
<unitdate>1916-1927. </unitdate>
<physdesc>3 volumes.</physdesc>
</did><scopecontent>
</c01><p>Information provided in each entry: date of report, name and
address of person arrested, location where offense was committed,
date of arrest, nature of offense, name of judge or justice, result
of trial, amounts of fine and court costs, number of days served if
jailed, name of warden, and occasional added remarks. Types of
offenses included hunting or fishing out of season or in
unauthorized places, exceeding catch or bag limits, taking
undersized fish, illegal fishing practices such as gill-netting or
dynamiting, illegal hunting practices such as night-lighting,
killing non-game birds, fishing or hunting without a license, and
hunting-related offenses against persons such as fraud and
assault.</p>
</scopecontent><c02>
<did>
<unittitle>Suspicion (RKO Radio Pictures) </unittitle>
<unitdate normal="1941" unitdatetype="inclusive">1941</unitdate>
<container localtype="Oversize">102A</container>
</did><relatedmaterial>
<p>See also
</relatedmaterial><ref target="cftm1">Classic Film Themes Medley
[I]</ref>
and
<ref target="nft">Nostalgic Film
Themes</ref>
.</p><scopecontent>
</c02><p>Production score - excerpted reductions, photostats:</p>
<list>
</scopecontent><item>PROD. #306 M:10 Main title / before the fact</item>
<item>PROD. #306 M:60 Melbeck's office / before the
fact</item>
<item>PROD. #306 M:74 Looking for Johnny / before the
fact</item>
<item>PROD. #306 M:85 Lina alone / before the fact</item>
<item>PROD. #306 M:94 The morning mail / before the
fact</item>
<item>PROD. #306 M:106 Too fast / before the fact</item>
<item>PROD. #306 M:74 Looking for Johnny / before the
fact</item>
</list><script>
Script [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <languagedeclaration> and <languageset> that
identifies the writing script for a language of the EAD instance or the
materials being described, respectively.
Description and Usage:
<script> is for identifying the script used to write a particular
language or languages, whether that of the materials being described or the
language of the description itself.
Attribute usage:
Use @scriptcode to provide an identifying code for the script
according to the authoritative source identified in
@scriptencoding. In most cases this will be a four-letter
ISO15924 code.
See also:
Use <language> to specify, in human-readable form, the
corresponding language.
Do not confuse <script> with @script and @lang, which can be used on all elements to indicate the script and language of the descriptive information, not the language of the materials.
Do not confuse <script> with @script and @lang, which can be used on all elements to indicate the script and language of the descriptive information, not the language of the materials.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <languagedeclaration>: Required, not repeatable
Within <languageset>: Required, repeatable
Examples:
<languagedeclaration>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"> Latin </script>
</languagedeclaration><languagedeclaration>
<language langcode="fre">French</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn">Latin </script>
</languagedeclaration><langmaterial>
<languageset>
<language langcode="lat">Latin</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="ang">Old English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><languageset>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"></script>
</languageset><descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>The majority of the documents are written in Modern English.
Roberts copies multiple passages from original manuscripts in Latin
and Old English.</p>
</descriptivenote><langmaterial>
<languageset>
</langmaterial><language langcode="eng">English</language>
<language langcode="fre">French</language>
<script scriptcode="Latn"> Latin </script>
</languageset><langmaterial>
<language langcode="eng">English</language>
<language langcode="fre">French</language>
<languageset>
</langmaterial><language langcode="jpn">Japanese</language>
<script scriptcode="Hira"> hiragana </script>
<script scriptcode="Kana"> katakana </script>
</languageset><separatedmaterial>
Separated Material [toc]
Summary:
For identifying materials associated by provenance that have been physically
separated or removed.
Description and Usage:
<separatedmaterial> identifies materials that are associated by
provenance to the described materials that have been physically separated or
removed. Examples include the separation of special formats; the destruction of
duplicate or nonessential material; and the deliberate or unintentional
dispersal of a creator’s records among different repositories.
See also:
Do not confuse with <relatedmaterial>, which is used for
references to materials that are not physically or logically included in the
material described in the finding aid.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.5.3
MARC 544
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<separatedmaterial>
<head>Materials Cataloged Separately</head>
<p>Photographs have been transferred to Pictorial Collections of The
Bancroft Library.</p>
</separatedmaterial><separatedmaterial>
<p>Photographs and sound recordings have been transferred to the
appropriate custodial divisions of the Library where they are identified
as part of these papers. Among the sound recordings are the following
broadcasts:</p>
<list>[...]</list>
</separatedmaterial><separatedmaterial>
<p>Other papers of Earl Warren, which relate chiefly to his early years
and public service in California, are held by the California State
Archives in Sacramento.</p>
</separatedmaterial><relatedmaterial>
<p>Records relating to the Warren Commission are held in the National
Archives and Records Administration.</p>
</relatedmaterial><seriesstmt>
Series Statement [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <filedesc> that groups information about the
published monographic series to which an EAD instance belongs.
Description and Usage:
Use <seriesstmt> to record and bind together information about the
published monographic series of which the encoded finding aid is a part.
<seriesstmt> may contain text, formed in paragraphs, or it may
include <titleproper> and <num>, which allow for more specific
tagging of names or numbers associated with the series.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
<source>
Source [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <sources> used to identify a particular source of
evidence used in describing the archival material.
Description and Usage:
Use <source> to cite a published resource used in describing the
archival material. Though not required, a reference for the source should be
included as a textual description in the child <sourceentry>. Use the
optional <descriptivenote> for any additional notes about the source.
Use the optional <objectxmlwrap> to embed XML documenting the source
from any namespace other than EAD3.
The child elements of <source> are optional, but when present they must
be provided in a specific order:
<sourceentry>
<objectxmlwrap>
<descriptivenote>
<objectxmlwrap>
<descriptivenote>
See also:
Do not confuse with <citation>, used in
<conventiondeclaration> and <localtypedeclaration> to
identify any rules and conventions applied in the description.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: none, onload, onrequest, other)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (value limited to: embed, new, none, other, replace)
Availability:
Required, repeatable
Examples:
<control> [. . .]
<sources>
</control><source>
<sourceentry>HMC, Principal Family and Estate Collections: Family
Names L-W, 1999</sourceentry>
</source><source>
</sources><sourceentry>HMC, Complete Peerage, 1936</sourceentry>
</source><sources>
<source lastdatetimeverified="2015-07-03T14:36:00-05:00" href="https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofamer00drakrich" actuate="onrequest" linktitle="Dictionary of American biography">
</sources><sourceentry>Dictionary of American biography: including men of the
time ... and a supplement</sourceentry>
[. . .] </source><sourceentry>
Source Entry [toc]
Summary:
A child element within <source> that identifies a specific source used
in creating the archival description.
Description and Usage:
Used to cite a source used in the construction of the archival description.
<sourceentry> should be used for brief citation information, with any
additional information provided in <descriptivenote>.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<control> [. . .]
<sources>
</control><source>
<sourceentry> HMC, Principal Family and Estate Collections: Family
Names L-W, 1999 </sourceentry>
</source><source>
</sources><sourceentry> HMC, Complete Peerage, 1936 </sourceentry>
</source><sources>
<source lastdatetimeverified="2015-07-03T14:36:00-05:00" href="https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofamer00drakrich" actuate="onrequest" linktitle="Dictionary of American biography">
</sources><sourceentry> Dictionary of American biography: including men of the
time ... and a supplement </sourceentry>
<objectxmlwrap>Dictionary of American biography, including men of the
time; containing nearly ten thousand notices of persons of both
sexes, of native and foreign birth, who have been remarkable, or
prominently connected with the arts, sciences, literature,
politics, or history of the American continent. Giving also the
pronunciation of many of the foreign and peculiar American
names, a key to the assumed names of writers, and a
supplementDrake, Francis S. (Francis Samuel),
1828-18851872E176 .D725 1872
https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofamer00drakrich
</objectxmlwrap>
<descriptivenote>
</source><p>Basic biographical information about
</descriptivenote><persname source="lcnaf" normal="Freeman, Nathaniel, 1741-1827">
was taken from
<part>Nathaniel Freeman</part>
</persname><title>
, page 340.</p><part>Dictionary of American biography: including men of the
time ... and a supplement</part>
</title><sources>
Sources [toc]
Summary:
An optional child element of <control> that groups one or more
<source>s of evidence used in describing the archival material.
Description and Usage:
Use <sources> to bind together one or more <source> elements.
Attribute usage:
Use @base to specify a URI (other than the base URI of the EAD
instance) to be used for resolving relative URIs within <sources> or
descendant elements.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<control> [. . .]
<sources>
</control><source>
<sourceentry>HMC, Principal Family and Estate Collections: Family
Names L-W, 1999</sourceentry>
</source><source>
</sources><sourceentry>HMC, Complete Peerage, 1936</sourceentry>
</source><sources>
<source lastdatetimeverified="2015-07-03T14:36:00-05:00" href="https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofamer00drakrich" actuate="onrequest" linktitle="Dictionary of American biography">
</sources><sourceentry>Dictionary of American biography: including men of the
time ... and a supplement</sourceentry>
<objectxmlwrap>Dictionary of American biography, including men of the
time; containing nearly ten thousand notices of persons of both
sexes, of native and foreign birth, who have been remarkable, or
prominently connected with the arts, sciences, literature,
politics, or history of the American continent. Giving also the
pronunciation of many of the foreign and peculiar American
names, a key to the assumed names of writers, and a
supplementDrake, Francis S. (Francis Samuel),
1828-18851872E176 .D725 1872
https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofamer00drakrich
</objectxmlwrap>
<descriptivenote>
</source><p>Basic biographical information about
</descriptivenote><persname source="lcnaf" normal="Freeman, Nathaniel, 1741-1827">
was taken from
<part>Nathaniel Freeman</part>
</persname><title>
, page 340.</p><part>Dictionary of American biography: including men of the
time ... and a supplement</part>
</title><sponsor>
Sponsor [toc]
Summary:
An optional child element of <titlestmt> for providing the name of an
institution or individual who contributed significant support, monetary or
otherwise, to the processing of the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
<sponsor> may be used to identify institution(s) and individual(s) who
endorsed, financed, or arranged the acquisition, appraisal, and processing of
the described materials or the preparation and distribution of the finding
aid.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local practice requires recording the type of
sponsor.
See also:
Do not confuse with <author>, which is for identifying the persons
or institutions responsible for the intellectual content of the finding aid,
or with <repository>, which is used to identify the institution or
corporate body providing intellectual access to the described
materials.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
MARC 536
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<titlestmt>
<titleproper encodinganalog="245$a">The Edgar Holden Papers,
1978-1993</titleproper>
<subtitle encodinganalog="245$b">A Guide to the Holden Papers at the
University of Ishtaba</subtitle>
<author>Finding aid prepared by Avery Thimble</author>
<sponsor>Processing sponsored by grant funding from the National
Historical Publications and Records Commission, grant number
94-0123</sponsor>
</titlestmt><subject>
Subject [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding topics represented in the materials being
described.
Description and Usage:
Indicates a topic reflected in the described materials.
<subject> must contain one or more <part> elements. A single
<part> may be used for the entire string, or if more granularity is
desired, multiple <part> elements may be used to capture each component
of the subject term, e.g.,
Part 1: Boats
Part 2: California
Part 3: 20th Century
Use <subject> within <controlaccess> for encoding subjects as
defined by controlled vocabularies or according to appropriate rules. You may
also use <subject> for encoding subjects as they appear within text.
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the subject in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of subject.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the subject if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the subject has to the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the subject in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of subject.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the subject if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, other relationship(s) the subject has to the described materials. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
See also:
Personal, corporate, family and geographic names used as subjects are
tagged as <persname>, <corpname>, <famname>, and
<geogname> respectively. The term "subject" can be used as the
value of @relator when indicating a personal name, corporate name,
family, or geographic name is a subject of the materials being
described.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, p, physfacet, ref, unittitle
References:
MARC 650, 69X
MODS <topic>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<controlaccess>
<subject encodinganalog="650" rules="RDA" source="lcsh">
<part>Indians of North America</part>
<part>Idaho</part>
</subject><subject encodinganalog="650" rules="RDA" source="lcsh">
</controlaccess><part>Railroads</part>
<part>Washington (State)</part>
<part>History</part>
</subject><controlaccess>
<subject>
<part>Alien and Sedition laws, 1798</part>
</subject><subject>
<part>American Confederate voluntary exiles</part>
</subject><subject>
</controlaccess><part>Kentucky and Virginia resolutions of 1798</part>
</subject><subtitle>
Subtitle [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <titlestmt> that captures a secondary or subsidiary
portion of the title of the EAD instance.
Description and Usage:
Use <subtitle> to record a portion of the title of an encoded finding
aid that is subordinate to the main title recorded in <titleproper>.
<subtitle> is available only within <titlessmt> and is
intended to support additional title information.
See also:
Do not confuse with <title>. Subtitles of monographs, serials,
paintings, and other such works mentioned in the finding aid are not
separately encoded, but they may be listed as <part> within
<title>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<table>
Table [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element for formatting information in a row and column display.
Description and Usage:
The application of <table> is based on the XML Exchange Table Model, an
XML expression of the Exchange subset of the full CALS table model DTD.
Attribute usage:
Use @colsep to indicate if the columns in the table are to be
separated by vertical rules.
Use @frame to indicate if there are rules surrounding the table.
Use @pgwide to indicate if the table is the width of the page or of the text column.
Use @rowsep to indicate if the rows in the table are to be separated by horizontal rules.
Use @frame to indicate if there are rules surrounding the table.
Use @pgwide to indicate if the table is the width of the page or of the text column.
Use @rowsep to indicate if the rows in the table are to be separated by horizontal rules.
May contain:
May occur within:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement, bibliography, bioghist, blockquote, controlaccess, controlnote, custodhist, dsc, fileplan, footnote, index, legalstatus, odd, originalsloc, otherfindaid, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, userestrict
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional (values limited to: all, bottom, none, sides, top,
topbot)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Example:
<table frame="none">
<tgroup cols="3">
</table><colspec colnum="1" colname="1" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<colspec colnum="2" colname="2" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<colspec colnum="3" colname="3" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<thead>
<row>
</thead><entry colname="1">Major Family Members</entry>
<entry colname="2">Spouses</entry>
<entry colname="3">Children</entry>
</row><tbody>
</tgroup><row>
[. . .] </tbody><entry colname="1">John Albemarle (1760-1806)</entry>
<entry colname="2">Mary Frances Delaney (1769-1835)</entry>
<entry colname="3">John Delaney Albemarle
(1787-1848)</entry>
</row><tbody>
Table Body [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <tgroup> that binds together one or more rows forming
the main body of a table.
Description and Usage:
A formatting element that contains one or more <row> elements, which in
turn contain <entry> elements in <table>. <tbody>
identifies the body of the information in <table>, as distinct from the
column headings (<thead>).
See also:
Related elements <entry>, <row>, <table>,
<tgroup>, and <thead>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: bottom, middle, top)
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Example:
<table frame="none">
<tgroup cols="3">
</table><colspec colnum="1" colname="1" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<colspec colnum="2" colname="2" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<colspec colnum="3" colname="3" align="left" colwidth="50pt"></colspec>
<thead>
<row>
</thead><entry colname="1">Major Family Members</entry>
<entry colname="2">Spouses</entry>
<entry colname="3">Children</entry>
</row><tbody>
</tgroup><row>
[. . .] </tbody><entry colname="1">John Albemarle (1760-1806)</entry>
<entry colname="2">Mary Frances Delaney (1769-1835)</entry>
<entry colname="3">John Delaney Albemarle
(1787-1848)</entry>
</row><term>
Term [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <localcontrol> used to specify a descriptive term in
accordance with local rules.
Description and Usage:
Use <term> to record the value of the entry enabled by the
localtype in <localcontrol>. For example, if the content
of localtype is "levelofdetail," <term> might be
"minimum."
Attribute usage:
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g.,
URI) that uniquely identifies the term in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy,
ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with
@id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML
instance.
Use @lastdatetimeverified to specify when the term captured was last verified for accuracy.
Use @rules to indicate any rules used in formulating the term.
Use @source to indicate the vocabulary from which the term has been taken.
Use @transliteration for indicating the conventions or rules that prescribe a method for converting one script to another.
Use @lastdatetimeverified to specify when the term captured was last verified for accuracy.
Use @rules to indicate any rules used in formulating the term.
Use @source to indicate the vocabulary from which the term has been taken.
Use @transliteration for indicating the conventions or rules that prescribe a method for converting one script to another.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (must follow pattern based on ISO 8601)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<localcontrol localtype="levelofdetail">
<term> Minimum </term>
</localcontrol><localcontrol localtype="fileSize">
<term> 8 MB </term>
</localcontrol><localcontrol localtype="daoFlag">
<term> true </term>
</localcontrol><localcontrol localtype="maxComponentID">
<term> 414 </term>
</localcontrol><localcontrol localtype="processinglevel">
<term> item </term>
</localcontrol><tgroup>
Table Group [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element that binds together <colspec>, <thead>, and
<tbody> elements in a table.
Description and Usage:
Tables comprise one or more <tgroup> elements depending on the number of
times the column specifications change. <tgroup> provides a subgrouping
of rows within a table that all use the same column specifications.
Attribute usage:
The required @cols specifies the number of columns in the table
group.
By convention, any rule specified in @colsep is printed or displayed to the right of the column.
External rules are specified with the @frame of <table>; horizontal rules are specified with <table> or <tgroup>@rowsep.
By convention, any rule specified in @rowsep prints or displays below the row.
Vertical rules are specified by @colsep; external rules are specified by @frame in <table>.
By convention, any rule specified in @colsep is printed or displayed to the right of the column.
External rules are specified with the @frame of <table>; horizontal rules are specified with <table> or <tgroup>@rowsep.
By convention, any rule specified in @rowsep prints or displays below the row.
Vertical rules are specified by @colsep; external rules are specified by @frame in <table>.
See also:
Related elements <colspec>, <table>, <tbody>,
<thead>.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional (values limited to: center, char, justify, left,
right)
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Required
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: false, true)
Optional
Availability:
Required, repeatable
<thead>
Table Head [toc]
Summary:
A formatting element that contains the heading information in
<table>.
Description and Usage:
Use <thead> to record column headings that appear at the top of a table
and may appear again at the top of any physical break in rows in the body.
<thead> may be used in an ordinary structural <table>, or to
provide column headings for components (<c> or <c0x>) or
<dsc> in a container list.
See also:
Related elements <table> and <tgroup> for general table
information.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: bottom, middle, top)
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
<title>
Title [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding the formal name of a work.
Description and Usage:
The name of an intellectual work, such as a monograph, serial, or painting,
listed in a finding aid. Within <controlaccess>, the formal, authorized
name should be used, but <title> may also be used to encode titles as
they appear within other elements to enable formatting such as italics or
quotations.
Subtitles of such works are not separately encoded but may instead be listed as
part of <title>, either along with the title in a single <part>,
or in multiple parts as follows:
Part 1: Private eyeballs
Part 2: A golden history of bad taste
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the title in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of title.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the title if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, the relationship between the title and the materials being described. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @render to indicate how the title should be displayed. Options are limited to altrender, bold, bolddoublequote, bolditalic, boldsinglequote, boldsmcaps, boldunderline, doublequote, italic, nonproport, singlequote, smcaps, sub, super, and underline.
Use @rules to specify the descriptive rules followed for forming the title statement.
Use @source to indicate the vocabulary from which the title statement has been taken.
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g., URI) that uniquely identifies the title in a controlled vocabulary, taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the XML instance.
Use @localtype, if local practice requires specification of the type of title.
Use @normal to identify a standardized form of the title if not provided in the element itself.
Use @relator to specify, either as a URI or a string, the relationship between the title and the materials being described. The schema does not limit possible values of @relator, but an institution could define and enforce values elsewhere if desired.
Use @render to indicate how the title should be displayed. Options are limited to altrender, bold, bolddoublequote, bolditalic, boldsinglequote, boldsmcaps, boldunderline, doublequote, italic, nonproport, singlequote, smcaps, sub, super, and underline.
Use @rules to specify the descriptive rules followed for forming the title statement.
Use @source to indicate the vocabulary from which the title statement has been taken.
See also:
Do not confuse with <titleproper>, which is used for the title of
the encoded finding aid.
Do not confuse with <unittitle>, which is used to encode the name of the described materials, such as the title of a collection, record group, fonds, series, file, or item. <title> may be a child of <unittitle>, and it is possible that <unittitle> may contain no text other than that which is further specified by <title>.
Do not confuse with @linktitle, which is found in linking elements.
Do not confuse with <unittitle>, which is used to encode the name of the described materials, such as the title of a collection, record group, fonds, series, file, or item. <title> may be a child of <unittitle>, and it is possible that <unittitle> may contain no text other than that which is further specified by <title>.
Do not confuse with @linktitle, which is found in linking elements.
May contain:
May occur within:
abstract, archref, bibref, controlaccess, entry, event, indexentry, item, namegrp, p, physfacet, ref, unittitle
References:
MARC 630, 730, 740
MODS <subject><titleInfo>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: altrender, bold, bolddoublequote,
bolditalic, boldsinglequote,
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Within <indexentry>: Optional, not repeatable
Within all other elements: Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c01>
<did>
<unittitle>Short stories, </unittitle>
<unitdate>1946-1954</unitdate>
</did><c02>
</c01><did>
</c02><unittitle>
</did><title render="italic">
</unittitle><part>The Lottery</part>
</title><bibref>
<title render="italic">
, p. 29. </bibref><part>Library of Congress Acquisitions: Manuscript Division,
1982</part>
</title><titleproper>
Title Proper of the Finding Aid [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <titlestmt> and <seriesstmt> that indicates
the title of a findingc aid or finding aid series.
Description and Usage:
Use <titleproper> to record the title of a finding aid or finding aid
series.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype if local practice requires recording the type of
title.
Use @render to specify formatting of <titleproper> for display and print purposes.
Use @render to specify formatting of <titleproper> for display and print purposes.
See also:
Do not confuse with <title>, which is used to encode the formal
names of works such as monographs, serials, paintings, etc., mentioned in
the finding aid.
Do not confuse with <unittitle>, which identifies the name of the described materials.
Do not confuse with <unittitle>, which identifies the name of the described materials.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: altrender, bold, bolddoublequote,
bolditalic, boldsinglequote, boldsmcaps, boldunderline, doublequote,
italic, nonproport, singlequote, smcaps, sub, super, underline)
Optional
Availability:
Within <seriesstmt>: Required, not repeatable
Within <titlestmt>: Required, repeatable
Examples:
<titlestmt>
<titleproper> The Edgar Holden Papers, 1978-1993 </titleproper>
<subtitle>A Guide to the Holden Papers at the University of
Ishtaba</subtitle>
<author>Finding aid prepared by Avery Thimble</author>
<sponsor>Processing sponsored by grant funding from the National
Historical Publications and Records Commission, grant number
94-0123</sponsor>
</titlestmt><titlestmt>
<titleproper> Catalogue of the Papers of James Graham Ballard
</titleproper>
</titlestmt><titlestmt>
<titleproper localtype="formal"> Guide to the Abraham Hayward Collection </titleproper>
<titleproper localtype="filing" render="altrender" altrender="nodisplay" audience="internal"> Hayward (Abraham) Collection </titleproper>
<author>by Michael Rush</author>
</titlestmt><titlestmt>
Title Statement [toc]
Summary:
A required child element of <filedesc> that binds together information
about the name of an encoded finding aid and those responsible for its
content.
Description and Usage:
Use <titlestmt> to bind together elements containing bibliographic
information about a finding aid, including its title and the names and roles of
those responsible for the finding aid’s intellectual content. The prescribed
order of all child elements (both required and optional) is:
<titleproper>
<subtitle>
<author>
<sponsor>
<subtitle>
<author>
<sponsor>
See also:
Do not confuse with <title>, which is used to encode the formal
names of works such as monographs, serials, paintings, etc., mentioned in
the finding aid.
Do not confuse with <unittitle>, which identifies the name of the described materials.
Do not confuse with <unittitle>, which identifies the name of the described materials.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<titlestmt>
<titleproper>The Edgar Holden Papers, 1978-1993</titleproper>
<subtitle>A Guide to the Holden Papers at the University of
Ishtaba</subtitle>
<author>Finding aid prepared by Avery Thimble</author>
<sponsor>Processing sponsored by grant funding from the National
Historical Publications and Records Commission, grant number
94-0123</sponsor>
</titlestmt><titlestmt>
<titleproper>Catalogue of the Papers of James Graham
Ballard</titleproper>
</titlestmt><titlestmt>
<titleproper localtype="formal">Guide to the Abraham Hayward Collection </titleproper>
<titleproper localtype="filing" render="altrender" altrender="nodisplay" audience="internal"> Hayward (Abraham) Collection </titleproper>
<author>by Michael Rush</author>
</titlestmt><todate>
To Date [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <daterange> that records the end point in a range of
dates.
Description and Usage:
Use <todate> to record the end date in a range of dates, whether they be
known or approximate. The content of the element is intended to be a
human-readable, natural language expression of the date. If, however, indexing
or other machine process of dates is desired, the standarddate
should be used to record the date in machine-processable form as well.
<todate> may be omitted from <daterange> if the date span is
ongoing.
Attribute usage:
Use @localtype to supply a more specific characterization of
the date range.
Use @notafter and @notbefore to capture the earliest and latest possible dates in machine-processable form in cases when the date is uncertain.
Use @standarddate to provide a machine-processable form of the date.
Use @notafter and @notbefore to capture the earliest and latest possible dates in machine-processable form in cases when the date is uncertain.
Use @standarddate to provide a machine-processable form of the date.
See also:
Use <fromdate> to record the starting point of a date
range.
May contain:
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, not repeatable
Examples:
<unitdatestructured calendar="gregorian" era="ce">
<dateset>
</unitdatestructured><datesingle standarddate="1963-01-22">22 January
1963</datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1971-06-01">1 June 1971</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1974-04-30"> 30 April 1974 </todate>
</daterange><chronitem>
<daterange>
<fromdate>1819</fromdate>
<todate> 1820 </todate>
</daterange><event>Studies theology at Yale College</event>
</chronitem><unitdatestructured unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notafter="1962">1962</fromdate>
<todate notafter="1968"> 1968 </todate>
</daterange><unitdatestructured certainty="circa" unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notbefore="1971" notafter="1975">around 1973</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1992"> 1992 </todate>
</daterange><unitdate>
Date of the Unit [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that provides a simple statement of the date(s)
covered by the described materials.
Description and Usage:
<unitdate> is for indicating the date or dates the described materials
were created, issued, copyrighted, broadcast, etc. <unitdate> may be in
the form of text or numbers, and may consist of a single date, a date range, or
a combination of single dates and date ranges.
Attribute usage:
Use @unitdatetype to indicate if <unitdate> represents
inclusive dates or bulk (predominant) dates.
See also:
Use <unitdatestructured> to provide a more granular,
machine-processable statement for the dates of the materials being
described.
Do not confuse <unitdate> with <date>, which is used to encode dates not related to the creation or accumulation of the records being described.
Do not confuse <unitdate> with <date>, which is used to encode dates not related to the creation or accumulation of the records being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.3
MARC 245 subfield f for inclusive dates, 245 subfield g for bulk dates, or 260
subfield c
MODS <originInfo><dateCreated>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: bulk, inclusive)
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<archdesc level="collection">
<did>
</archdesc><head>Collection Summary</head>
<origination label="Creator">
<corpname encodinganalog="110">
</origination><part>National Association for the Advancement of Colored
People</part>
</corpname><unittitle label="Title" encodinganalog="245">Visual Materials from
the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People Records
(Library of Congress)</unittitle>
<unitdate label="Dates" unitdatetype="inclusive" encodinganalog="260"> ca. 1838-1969 </unitdate>
<unitdate unitdatetype="bulk"> bulk 1944-1955 </unitdate>
</did><did>
<unittitle encodinganalog="245$a">Philip M. Wagner
papers</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" encodinganalog="245$f"> 1839-1995 </unitdate>
<unitdate unitdatetype="bulk" encodinganalog="245$g"> bulk 1942-1989 </unitdate>
<physdesc encodinganalog="300$a$f">8 boxes (9.35 linear
feet)</physdesc>
[...] </did><dsc type="analyticover">
<c level="subseries">
[. . .] </dsc><did>
</c><unittitle>Documentary Movies</unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive" normal="1952/1964"> 1952-1964 </unitdate>
<abstract>Includes scores, arranged alphabetically by movie title,
and some correspondence, arranged chronologically.</abstract>
</did><unitdatestructured>
Structured Date of the Unit [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that enables structured, machine-processable
expressions of the dates of the materials being described.
Description and Usage:
<unitdatestructured> provides a machine-processable statement of the
date or dates the materials described were created, issued, copyrighted,
broadcast, etc. <unitdatestructured> must contain one of the following
child elements: <datesingle>, <daterange>, or
<dateset>.
<unitdatestructured> may contain only one child, therefore
<dateset> must be used in situations where complex date information
needs to be conveyed and requires at least two child elements. A date set may
combine two or more <datesingle> and <daterange> elements.
Attribute usage:
Use @unitdatetype to indicate if <unitdatestructured>
represents inclusive dates or bulk (predominant) dates.
See also:
Do not confuse <unitdatestructured> with <date>, which is
used to encode dates not related to the creation or accumulation of the
records being described.
Use <unitdate> to provide an unstructured statement of the dates of the material being described.
Use <unitdate> to provide an unstructured statement of the dates of the material being described.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.3
MARC 245 subfield f for inclusive dates, 245 subfield g for bulk dates, or 260
subfield c
MODS <originInfo><dateCreated>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional (values limited to: bulk, inclusive)
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<did>
<unittitle>Class Notes, Undergraduate</unittitle>
<unitdatestructured unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notafter="1962">1962</fromdate>
<todate notafter="1968">1968</todate>
</daterange><physdesc>12 notebooks</physdesc>
<container localtype="boxes">5-6</container>
<didnote>The notebooks contain months and days, not years. Estimated
dates are based on the years Scully attended the University of
Maryland.</didnote>
</did><unitdatestructured unitdatetype=" inclusive " encodinganalog="245">
<dateset>
</unitdatestructured><datesingle standarddate="1963-01-22">1963 January
22</datesingle>
<daterange>
</dateset><fromdate standarddate="1971-06-01">1971 June 1</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1974-04-30">1974 April 30</todate>
</daterange><unitdatestructured certainty="circa" unitdatetype="inclusive">
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate notbefore="1971" notafter="1975">around 1973</fromdate>
<todate standarddate="1992">1992</todate>
</daterange><unitdatestructured>
<daterange>
</unitdatestructured><fromdate>1900</fromdate>
<todate>1910</todate>
</daterange><unitdatestructured unitdatetype=" inclusive ">
<datesingle standarddate=" 2015-06 ">2015 June</datesingle>
</unitdatestructured><unitid>
ID of the Unit [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that provides an identifier for the materials
being described, such as an accession number.
Description and Usage:
<unitid> may contain any alpha-numeric text string that serves as a
unique reference point or control number for the described material, such as a
lot number, an accession number, a classification number, or an entry number in
a bibliography or catalog. <unitid> is primarily a logical designation,
which sometimes indirectly provides location information, as in the case of a
classification number.
Attribute usage:
Although not required, the @countrycode and
@repositorycode should be used in <unitid> at the
<archdesc>/<did> level to comply with ISAD(G) element
3.1.1.
See also:
Use <container> and <physloc> to designate the physical
housing or location of the described materials.
Do not confuse with <recordid> or <otherrecordid>, which are identifiers for the finding aid itself, not the materials described therein.
Do not confuse with <recordid> or <otherrecordid>, which are identifiers for the finding aid itself, not the materials described therein.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.1
MODS <identifier>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c01>
<did>
<unittitle>Manouche</unittitle>
</did><c02>
[. . .] </c01><did>
</c02><unittitle>Recording</unittitle>
<unitid> grove_005 </unitid>
<abstract>45-rpm phonodisc of Manouche singing two unidentified
French songs</abstract>
<container localtype="Box">559</container>
</did><archdesc level="collection">
<did>
[. . .] </archdesc><head>Descriptive Summary</head>
<unittitle label="Title">Donald C. Stone, Jr. Papers, </unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1971-1983</unitdate>
<unitid countrycode="US" repositorycode="cbgtu" identifier="http://library.syr.edu/guides/s/stone_dc.htm" label="Accession number"> GTU 2001-8-03 </unitid>
<origination label="Creator">
<persname source="lcnaf">
</origination><part>Stone, Donald C., Jr.</part>
</persname><physdesc label="Extent">4 boxes, 4 linear ft. </physdesc>
<repository label="Repository">
<corpname>
<part>The Graduate Theological Union</part>
</corpname><address>
</repository><addressline>Berkeley, California</addressline>
</address><abstract label="Abstract">The papers document Donald C. Stone's work
with Ornstein and Swencionis on the
<emph render="italic">est</emph>
Outcome Project, and the development of his
doctoral research, including his various publications on the human
potential movement, up to the completion of his doctoral
dissertation.</abstract><physloc label="Shelf location">5/D/4-5</physloc>
</did><unittitle>
Title of the Unit [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that specifies a title for the described
materials.
Description and Usage:
<unittitle> is for recording the title statement, either formal or
supplied, of the described materials. The title statement may consist of a word
or phrase. <unittitle> is used at both the highest unit or
<archdesc> level (e.g., collection, record group, or fonds) and at
all the subordinate <c> levels (e.g., subseries, files, items, or other
intervening stages within a hierarchical description).
Attribute usage:
Use @encodinganalog to indicate corresponding data elements in
another data format, such as MARC.
Use @localtype if local use requires recording the type of <unittitle>.
Use @normal to allow for normalization of unit titles with initial articles.
Use @localtype if local use requires recording the type of <unittitle>.
Use @normal to allow for normalization of unit titles with initial articles.
See also:
Do not confuse <unittitle> with <title>, an element used to
encode the formal names of works such as monographs, serials, paintings,
etc.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, emph, expan, famname, footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, name, num, occupation, persname, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.2
MARC 130, 240, 245
MODS <titleInfo><title>
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<c level="subseries">
<did>
</c><unittitle> Documentary Movies </unittitle>
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">1952-1964</unitdate>
<physdesc>2.5 linear ft.</physdesc>
<abstract label="Summary:">Includes scores, arranged alphabetically
by movie title, and some correspondence, arranged
chronologically.</abstract>
</did><archdesc level="collection" relatedencoding="MARC21" localtype="inventory">
<did>
<head>Overview of the Collection</head>
<repository encodinganalog="852$a" label="Repository:">
<corpname>
</repository><part>Syracuse University Special Collections Research
Center</part>
</corpname><origination label="Creator:">
<persname encodinganalog="100">
</origination><part>Langner, William R.</part>
</persname><unittitle encodinganalog="245$a" label="Title:"> William Langner
Papers </unittitle>
<abstract encodinganalog="520$a" label="Abstract:">William Langner
worked for the Department of Education's Division of Adult Education
and Literacy for many years. He was active in raising awareness of
education for the disabled (Langner himself was a paraplegic from the
age of 18 due to a car accident). Collection includes correspondence
(both personal and professional), writings, memorabilia, and large
amounts of printed material (papers, reports, handbooks, manuals,
etc).concerning adult education.</abstract>
<langmaterial encodinganalog="546" label="Language:">
</did><language langcode="eng"></language>
<language langcode="spa"></language>
<descriptivenote>
</langmaterial><p>English, some printed material in Spanish</p>
</descriptivenote><accessrestrict>
</archdesc><head>Access Restrictions</head>
<p>Unprocessed. Accessible by special permission only.</p>
</accessrestrict><unittype>
Unit Type [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <physdescstructured> that indicates the type of unit
being quantified, e.g., boxes, linear feet, etc.
Description and Usage:
Required in <physdescstructured>, <unittype> identifies the type
of unit being quantified.
Attribute usage:
Use @identifier to provide a number, code, or string (e.g.,
URI) that uniquely identifies the unit type in a controlled vocabulary,
taxonomy, ontology, or other knowledge organization system. Do not confuse
with @id, which provides a unique id for the element within the
XML instance.
Use @rules to specify the descriptive rules followed for forming the unit type.
Use @rules to specify the descriptive rules followed for forming the unit type.
May contain:
[text]
May occur within:
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Required, not repeatable
Examples:
<physdescset>
<physdescstructured coverage="whole" physdescstructuredtype="spaceoccupied">
<quantity>12</quantity>
<unittype> linear feet </unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="whole" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
</physdescset><quantity>24</quantity>
<unittype> boxes </unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescset>
<physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="spaceoccupied">
<quantity>6</quantity>
<unittype> terabytes </unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="carrier">
<quantity>24</quantity>
<unittype> 3 ½" floppy disks </unittype>
</physdescstructured><physdescstructured coverage="part" physdescstructuredtype="materialtype">
</physdescset><quantity>1800</quantity>
<unittype> electronic files </unittype>
</physdescstructured><userestrict>
Conditions Governing Use [toc]
Summary:
An element for indicating any conditions that affect the use of the described
materials, such as in publications.
Description and Usage:
Use <userestrict> for information about any limitations, regulations, or
special procedures imposed by a repository, donor, legal statute, or other
agency. These conditions may be related to reproduction, publication, or
quotation of the described materials after access to the materials has been
granted. <userestrict> may also be used to indicate the absence of
restrictions, such as when intellectual property rights have been dedicated to
the public.
See also:
Do not confuse with <accessrestrict>, which contains information
about conditions affecting the availability of the described
materials.
<prefercite> may be used to specify how the described materials should be referenced.
<prefercite> may be used to specify how the described materials should be referenced.
May contain:
May occur within:
References:
ISAD(G) 3.4.2
MARC 540
Attributes:
Optional
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
Examples:
<userestrict>
<p>Until 2015 permission to photocopy some materials from this
collection has been limited at the request of the donor. Please ask
repository staff for details if you are interested in obtaining
photocopies from Series 1: Correspondence.</p>
</userestrict><userestrict>
<p>Copyright to the collection has been transferred to the Regents of
the University of Michigan.</p>
</userestrict><userestrict>
<head>Restrictions on usage</head>
<p>Per the deed of gift:</p>
<blockquote>Any use of quotations, excerpts, reproductions, or any other
portion of the collection, either in print or electronically, requires
permission of the heirs of the Smith Estate.</blockquote>
</userestrict>Appendix A : EAD Crosswalks [toc]
ISAD(G) to EAD3 [toc]
ISAD(G)
EAD
3.1.1 Reference code(s)
<agencycode> and <recordid> within <control>;
<unitid> with @countrycode and @repositorycode
3.1.2 Title
<unittitle>
3.1.3 Dates
<unitdate>, <unitdatestructured>
3.1.4 Level of description
<archdesc> and <c>@level
3.1.5 Extent and medium of the unit
<physdesc>, <physdescstructured>
3.2.1 Name of creator
<origination>
3.2.2 Administrative/Biographical history
<bioghist>
3.2.3 Archival history
<custodhist>
3.2.4 Immediate source of acquisition
<acqinfo>
3.3.1 Scope and content
<scopecontent>
3.3.2 Appraisal, destruction and scheduling
<appraisal>
3.3.3 Accruals
<accruals>
3.3.4 System of arrangement
<arrangement>
3.4.1 Conditions governing access
<accessrestrict>
3.4.2 Conditions governing reproduction
<userestrict>
3.4.3 Language/scripts of material
<langmaterial>
3.4.4 Physical characteristics and technical requirements
<phystech>
3.4.5 Finding aids
<otherfindaid>
3.5.1 Existence and location of originals
<originalsloc>
3.5.2 Existence and location of copies
<altformavail>
3.5.3 Related units of description
<relatedmaterial>, <separatedmaterial>
3.5.4 Publication note
<bibliography>
3.6.1 Note
<didnote>, <odd>
3.7.1 Archivist's note
<processinfo>
3.7.2 Rules or conventions
<conventiondeclaration>
3.7.3 Date(s) of descriptions
<maintenanceevent>/<eventdatetime>
MARC21 to EAD3 [toc]
MARC
EAD
041 Language
<langmaterial>/<language>@langcode
100 Main entry--personal name
<origination><persname>, <origination><famname>
110 Main entry--corporate name
<origination><corpname>
111 Main entry--meeting name
<origination><corpname>
130 Main entry--uniform title OR 240 Uniform title
<unittitle>
245 Title statement
<unittitle>
245$f Title statement/inclusive dates
<unitdate unitdatetype="inclusive">, <unitdatestructured
unitdatetype="inclusive">
245$g Title statement/bulk dates
<unitdate unitdatetype="bulk">, <unitdatestructured
unitdatetype="bulk">
254 Musical presentation statement
<materialspec>
255 Cartographic mathematical data
<materialspec>
255$c Cartographic mathematical data/statement of coordinates
<geographiccoordinates>
256 Computer file characteristics
<physdescstructured><quantity> and <physdescstructured><unittype>
260$c Date
<unitdate>, <unitdatestructured>
300 Physical description
<physdesc>, <physdescstructured> subelements <quantity>,
<unittype>, <dimensions>, <physfacet>
340 Physical medium
<phystech>
351 Organization and arrangement
<arrangement>
351$c Hierarchical level
<archdesc>@level
355 Security classification control
<accessrestrict>
500 General note
<didnote>, <odd>
506 Restrictions on access note
<accessrestrict>, <legalstatus>
510 Citation/references
<bibliography>
520 Summary, etc.
<abstract>, <scopecontent>
524 Preferred citation of described materials
<prefercite>
530 Additional physical form available
<altformavail>
535 Location of Originals/Duplicates
<originalsloc>
536 Funding information
<sponsor>
538 System Details
<phystech>
540 Terms governing use and reproduction
<userestrict>
541 Immediate source of acquisition
<acqinfo>
544 Location of other archival materials
<relatedmaterial>, <separatedmaterial>
545 Biographical or historical data
<bioghist>
546 Language
<langmaterial>
555 Cumulative index/finding aids2 In a MARC21 record a note in the 55
field would mention the existence of the EAD-encoded finding aid, but no
specific EAD element maps to this field. The existence of other finding aids
can be noted in <otherfindaid>.
561 Ownership and custodial history
<custodhist>
581 Publications about described materials
<bibliography>
583 Action
<appraisal>, <processinfo>
584 Accumulation and frequency of use
<accruals>
600 Subject--personal name
<controlaccess><persname relator="subject">,
<controlaccess><famname relator="subject">
610 Subject--corporate name
<controlaccess><corpname relator="subject">
611 Subject--meeting
<controlaccess><corpname relator="subject">
630 Subject--uniform title
<controlaccess>>ltitle relator="subject">
650 Subject--topical
<controlaccess><subject>
651 Subject--geographic name
<controlaccess><geogname relator="subject">
655 Genre/form
<controlaccess><genreform>
656 Occupation
<controlaccess><occupation>
657 Function
<controlaccess><function>
69x Local subject access
<controlaccess><subject source="local">
700 Added entry--personal name
<controlaccess><persname>,<controlaccess><famname>
710 Added entry--corporate name
<controlaccess><corpname>
711 Added entry--meeting name
<controlaccess><corpname>
720 Added entry--uncontrolled
<name>
730 Added entry--uniform title
<controlaccess><title>
740 Added entry--uncont./related anal. title
<title>
752 Added entry--hierarchical place name
<geogname>
852 Location
<repository>, <physloc>
MODS to EAD3 [toc]
MODS
EAD
<abstract>
<abstract>, <scopecontent>
<accessCondition>
<accessrestrict>
<genre>
<controlaccess><genreform>
<identifier>
<unitid>
<language><languageTerm>
<langmaterial><language>,
<langmaterial><languageset><language>
<location><physicalLocation>
<repository>
<location><url>
<dao>, <daoset>
<name>
<origination>
<note>
<didnote>, <odd>
<originInfo><dateCreated>
<unitdate>, <unitdatestructured>
<physicalDescription><extent>
<physdesc>, <physdescstructured><quantity> and
<physdescstructured><unittype>,
<physdescstructured><dimensions>
<recordInfo><recordContentSource>
<maintenanceagency><agencyname>,
<maintenanceagency><agencycode>,
<maintenanceagency><otheragencycode>
<recordInfo><recordCreationDate>
<maintenancehistory><maintenanceevent><eventdatetime>
(where <eventtype> @value='created')
<recordInfo><recordChangeDate>
<maintenancehistory><maintenanceevent><eventdatetime>
<recordInfo><recordIdentifier>
<recordid>
<recordInfo><recordOrigin>
<maintenancehistory><maintenanceevent> (where
eventtype/@value='created' or 'derived')
<recordInfo><languageOfCataloging>
<control><languagedeclaration><language>
<recordInfo><descriptionStandard>
<conventiondeclaration>
<subject><cartographics><coordinates>
<geographiccoordinates>
<subject><cartographics><projection>
<materialspec>
<subject><cartographics><scale>
<materialspec>
<subject><genre>
<controlaccess><genreform>
<subject><geographic>
<controlaccess><geogname>
<subject><hierarchicalGeographic>
<controlaccess><geogname>
<subject><name>
<controlaccess><name>
<subject><occupation>
<controlaccess><occupation>
<subject><titleInfo>
<controlaccess><title>
<subject><topic>
<controlaccess><subject>
<titleInfo><title>
<unittitle>
Appendix B : Deprecated and Obsolete Elements and Attributes [toc]
The revision of EAD 1.0 to EAD 2002 established a precedent that elements to be
removed from EAD would first be deprecated – suppressed but available if necessary –
before being removed from subsequent versions. All elements deprecated in EAD 2002
were removed from EAD3. Elements present in the DTD version of EAD 2002 but removed
from the schema versions of EAD 2002 (<archdescgrp>, <dscgrp>, and
<eadgrp>) were also removed from EAD3.
The Society of American Archivists' Technical Subcommittee on EAD (TS-EAD) endeavored
to honor the commitment to deprecate removed elements.However, the extent of the
changes in EAD3 made comprehensive deprecation impossible. Elements to be removed
entirely from the standard remain available in undeprecated versions of EAD3.
Elements that were replaced by other elements offering commensurate functionality, or
whose availability within the standard changed are in most cases not supported in
undeprecated EAD3.
The following attributes and elements are not available in the default versions of
EAD3 (ead3.rng, ead3.xsd, and ead3.dtd), but are available in the undeprecated
versions (ead3_undeprecated.rng, ead3_undeprecated.xsd, and ead3_undeprecated.dtd).
Definitions for these attributes and elements follow below.
Deprecated Attributes
placement
tpattern
tpattern
Deprecated Elements
<bibseries>
<descgrp>
<div>
<extent>
<frontmatter>
<imprint>
<runner>
<titlepage>
<descgrp>
<div>
<extent>
<frontmatter>
<imprint>
<runner>
<titlepage>
In addition to including the attributes and elements listed above, the undeprecated
versions of EAD3 also include the full EAD 2002 content models for the
<physdesc> and <unittitle> elements. The undeprecated
<physdesc> includes <extent>, <dimensions>,
<physfacet>, and the access point elements (e.g. <genreform>)
whereas the default <physdesc> in EAD3 does not. The undeprecated
<unittitle> includes <bibseries>,<imprint>, <edition>,
and <unitdate>, whereas the default <unittitle> in EAD3 does not.
Style sheets for migrating EAD 2002 to EAD3 will include an option to preserve
deprecated elements. However, when future versions of EAD are released, support for
elements and attributes deprecated in EAD3 will be removed and their forward
migration will not be supported.
The following obsolete attributes and elements were removed entirely in EAD3. Their
semantics or functionality were replaced by new attributes or elements.
Obsolete Attributes
authfilenumber
continuation
findaidstatus
from / xlink:from
linktype / xlink:type
mainagencycode
othertype
publicid
role / xlink:role
to / xlink:to
type
urn
url
continuation
findaidstatus
from / xlink:from
linktype / xlink:type
mainagencycode
othertype
publicid
role / xlink:role
to / xlink:to
type
urn
url
Obsolete Elements
<arc>
<change>
<creation>
<daodesc>
<daogrp>
<daoloc>
<descrules>
<eadheader>
<eadid>
<eventgrp>
<extptr>
<extptrloc>
<extref>
<extrefloc>
<langusage>
<linkgrp>
<note>
<ptrloc>
<refloc>
<resource>
<revisiondesc>
<subarea>
<change>
<creation>
<daodesc>
<daogrp>
<daoloc>
<descrules>
<eadheader>
<eadid>
<eventgrp>
<extptr>
<extptrloc>
<extref>
<extrefloc>
<langusage>
<linkgrp>
<note>
<ptrloc>
<refloc>
<resource>
<revisiondesc>
<subarea>
Deprecated Attributes [toc]
@placement
Summary:
The location where the information in the <runner> element is
displayed in print (foot or head) or as a digital watermark
(background).
Values:
background, footer, header
@tpattern
Summary:
A reference to a pattern that defines the specifications of particular HTML
output tables. Available in <c>, <c01>-<c12>, and
<dsc>.
Data Type:
NMTOKEN
Deprecated Elements [toc]
<bibseries>
Bibliographic Series [toc]
Summary:
An element for identifying information about the published series in which a
book finding aid, or other published work appeared. Refers to monographic
series only.
Description and Usage:
An element for encoding information about the published series in which a
book, encoded finding aid, or other published work has appeared. Refers to
monographic series only. Not to be used for archival series.
May contain:
[text], emph, lb, num, ptr, ref, title
May occur within:
bibref, titlepage, unittitle
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
encodinganalog
Optional
id
Optional
lang
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<descgrp>
Description Group [toc]
Summary:
An element for grouping together any number of elements that are following
siblings of the <did> element.
Description and Usage:
An element for grouping together any number of elements that are following
siblings of the <did> element except for the <dsc> element.
<descgrp> might be used, for example, to cluster elements into
groups that correspond to the areas specified by the General International
Standard Archival Description (ISAD(G)).
May contain:
accessrestrict, accruals, acqinfo, altformavail, appraisal, arrangement,
bibliography, bioghist, blockquote, chronlist, controlaccess, custodhist,
descgrp, fileplan, head, index, legalstatus, list, odd, originalsloc,
otherfindaid, p, phystech, prefercite, processinfo, relatedmaterial,
relations, scopecontent, separatedmaterial, table, userestrict
May occur within:
archdesc, c, c01, c02, c03, c04, c05, c06, c07, c08, c09, c10, c11, c12,
descgrp
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
encodinganalog
Optional
id
Optional
lang
Optional
localtype
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<div>
Text Division [toc]
Summary:
A generic element that designates a major section of text within
<frontmatter>.
Description and Usage:
A generic element that designates a major section of text within
<frontmatter>. Examples of these text divisions include a title
page, preface, acknowledgments, or instructions for using a finding aid. Use
the <head> element to identify the div's purpose.
May contain:
blockquote, chronlist, div, head, list, p, table
May occur within:
div, frontmatter
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
id
Optional
lang
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<extent>
Extent [toc]
Summary:
A child of <physdesc> used for information about the quantity of the
materials being described or an expression of the physical space they
occupy.
Description and Usage:
A <physdesc> subelement for information about the quantity of the
materials being described or an expression of the physical space they
occupy. Includes such traditional archival measurements as cubic and linear
feet and meters; also includes counts of microfilm reels, photographs, or
other special formats, the number of logical records in a database, or the
volume of a data file in bytes. Repeat the element when more than one type
or unit of extent is provided, such as, when both linear feet and quantity
of containers are given.
May contain:
[text], abbr, emph, expan, foreign, lb, ptr, ref
May occur within:
physdesc
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
encodinganalog
Optional
id
Optional
label
Optional
lang
Optional
localtype
Optional
script
Optional
unit
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<frontmatter>
Front Matter [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element that bundles prefatory text found before the start of
<archdesc>.
Description and Usage:
A wrapper element that bundles prefatory text found before the start of
<archdesc>. It focuses on the creation, publication, or use of the
finding aid rather than information about the materials being described.
Examples include a title page, preface, dedication, and instructions for
using a finding aid. The optional <titlepage> element within
<frontmatter> can be used to repeat selected information from
<control> to generate a title page that follows local preferences
for sequencing information. The other <frontmatter> structures, such
as a dedication, are encoded as Text Divisions <div>s, with a
<head> element containing word(s) that identify the nature of the
text.
May contain:
div, titlepage
May occur within:
ead
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
id
Optional
lang
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, non repeatable
<imprint>
Imprint [toc]
Summary:
An element for encoding information relating to the publication or
distribution of a work cited in a <bibref> or <unittitle>.
Description and Usage:
An element for encoding information relating to the publication or
distribution of a work cited in a <bibref> or <unittitle>. In
both elements the place of publication, name of the publisher, and date of
publication can be encoded as either plain text or wrapped in the
<imprint> subelements <geogname>, <publisher>, and
<date>. It is seldom, if ever, appropriate to use <imprint>
in a citation for an unpublished work cited in a <bibref>.
May contain:
[text], date, emph, geogname, lb, ptr, publisher
May occur within:
bibref, unittitle
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
encodinganalog
Optional
id
Optional
lang
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<physdesc>
Physical Description [Deprecated Data Model] [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that provides a statement about the physical
characteristics of the material being described.
Description and Usage:
<physdesc> is a wrapper element for bundling information about the
appearance or construction of the described materials, such as their
dimensions, a count of their quantity or statement about the space they
occupy, and terms describing their genre, form, or function, as well as any
other aspects of their appearance, such as color, substance, style, and
technique or method of creation. The information may be presented as plain
text, or it may be divided into the <dimensions>, <extent>,
<genreform>, and <physfacet> subelements.
May contain:
[text], abbr, corpname, date, dimensions, emph, expan, extent, famname,
footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, lb, name, num, occupation,
persname, physfacet, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title
May occur within:
did
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.5
MARC 300
MODS <physicalDescription><extent>
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
encodinganalog
Optional
id
Optional
label
Optional
lang
Optional
localtype
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<runner>
Runner [toc]
Summary:
An optional formatting element that provides for a header, footer, or
watermark to appear on every page of a printed finding aid or throughout an
electronic version.
Description and Usage:
An optional formatting element that provides for a header, footer, or
watermark to appear on every page of a printed finding aid or throughout an
electronic version. If a transparent image is desired as background, use
<ptr> instead. The <runner> is available within
<archdesc> and must appear before the <did>.
May contain:
[text], emph, lb, ptr
May occur within:
archdesc
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
id
Optional
lang
Optional
placement
Optional (values limited to: header, footer, watermark)
role
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
<titlepage>
Title Page [toc]
Summary:
A wrapper element within <frontmatter> that groups bibliographic
information about a finding aid, including its name, author, and other
aspects of its creation and publication.
Description and Usage:
A wrapper element within <frontmatter> that groups bibliographic
information about a finding aid, including its name, author, and other
aspects of its creation and publication. It contains much of the same
information found in the <filedesc> portion of <control>, such
as the <titleproper>, <subtitle>, <author>,
<sponsor>, <publisher>, and <date> of the finding
aid. Although it is possible to generate an electronic or printed title page
directly from <control>, use of the <titlepage> may be more
accommodating of local preferences, including displays of photographic
illustrations, institutional logos, or other graphic images.
May contain:
author, bibseries, blockquote, chronlist, date, edition, list, num, p,
publisher, sponsor, subtitle, table, titleproper
May occur within:
frontmatter
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
id
Optional
lang
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, non repeatable
<unittitle>
Title of the Unit [Deprecated Data Model] [toc]
Summary:
A child element of <did> that specifies a title for the described
materials.
Description and Usage:
A <unittitle> is for recording the title statement, either formal or
supplied, of the described materials. The title statement may consist of a
word or phrase. The <unittitle> is used at both the highest unit or
<archdesc> level (e.g., collection, record group, or fonds) and at
all the subordinate <c> levels (e.g., subseries, files, items, or
other intervening stages within a hierarchical description).
May contain:
[text], abbr, bibseries, corpname, date, edition, emph, expan, famname,
footnote, foreign, function, genreform, geogname, imprint, lb, name, num,
occupation, persname, ptr, quote, ref, subject, title, unitdate
May occur within:
did
References:
ISAD(G) 3.1.2
MARC 130, 240, 245
MODS <titleIfo><title>
Attributes:
altrender
Optional
audience
Optional (values limited to: external, internal)
encodinganalog
Optional
id
Optional
label
Optional
lang
Optional
localtype
Optional
normal
Optional
script
Optional
Availability:
Optional, repeatable
